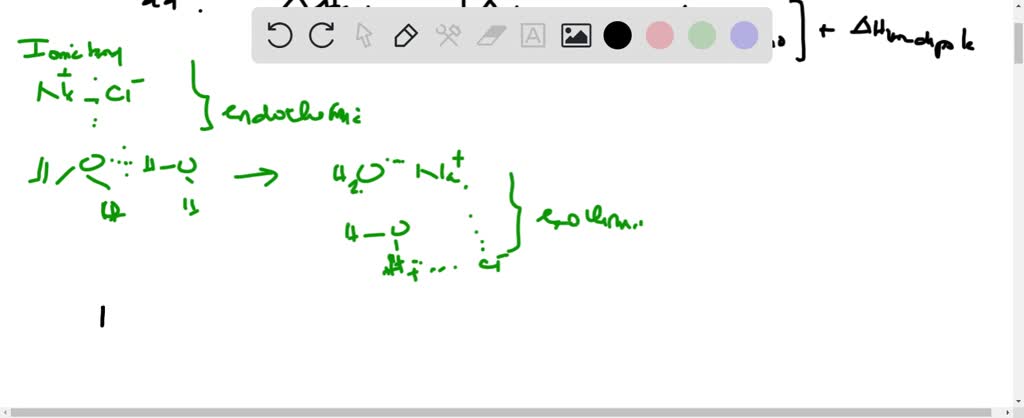
As the name suggests, ion-dipole force exists between an ion and a polar molecule. Ion-dipole interactions occur when an ionic compound is dissolved in a polar solvent. Since these are electrostatic forces, a greater charge on the ion and a higher magnitude of dipole on the polar molecule increases the strength.
What is the difference between an ion and a dipole?
CONTENTS
- Overview and Key Difference
- What is Ion Dipole Forces
- What is Dipole Dipole Forces
- Similarities Between Ion Dipole and Dipole Dipole Forces
- Side by Side Comparison – Ion Dipole vs Dipole Dipole Forces in Tabular Form
- Summary
What does dipole mean in chemistry?
What does dipole mean in chemistry? Dipole: A bond or molecule whose ends have opposite charges. What is the dipole moment of CH2CL2? In CH2Cl2 , the dipole moments of two C-Cl bonds add on but the resultant dipole moment of CH2CL2 is 1.6D whereas that of CH3Cl is 1.95D. Does CH4 have a dipole moment? The dipole moment of methane CH4 is zero.
What is the strongest dipole dipole force?
Intermolecular forces In the order of weakest to strongest:
- dispersion force.
- Dipole-dipole force.
- Hydrogen bond.
- Ion-dipole force.
What is a real life example of dipole dipole interaction?
Dipole–dipole interactions are a type of intermolecular attraction—attractions between two molecules. Dipole-dipole interactions are electrostatic interactions between the permanent dipoles of different molecules. For example, a water molecule (H2O) has a large permanent electric dipole moment.
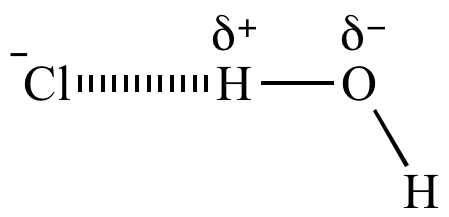
What is ion-dipole example?
Example: An example of the ion-dipole interaction is the interaction between a Na+ ion and water (H2O) where the sodium ion and oxygen atom are attracted to each other, while the sodium and hydrogen are repelled by each other.
How do you identify an ion-dipole?
0:011:36Identifying Ion-Dipole force - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd we want to know what the interactions between na. And this dipole are na is an ion. So we canMoreAnd we want to know what the interactions between na. And this dipole are na is an ion. So we can tell that it's between an ion and a polar molecule or a dipole.
Is ion-dipole intermolecular force?
An ion-dipole force is an electrostatic interaction between a fully charged ion and a neutral molecule that has a dipole. Moreover, it is an intermolecular force that is most commonly found in solutions, especially ionic compounds dissolved in polar liquids.
How does ion-dipole occur?
An ion-dipole interaction is the result of an electrostatic interaction between a charged ion and a molecule that has a dipole. It is an attractive force that is commonly found in solutions, especially ionic compounds dissolved in polar liquids.
What is the difference between dipole-dipole and ion dipole?
The key difference between ion-dipole and dipole-dipole forces is that ion-dipole forces exist between ionic species and polar molecules whereas dipole-dipole forces exist between polar molecules.
Is ion dipole van der Waals?
Answer and Explanation: Ion-dipole forces are not considered as van der Waals forces due to the following reasons. The van der Waals forces of attraction occurs between...
What are the 4 types of intermolecular forces?
12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces- Dispersion, Dipole–Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole.
Why is ion-dipole stronger than hydrogen bonding?
The hydrogens have a more polar bond, so their electrons are distributed in a way that causes their bond to be stronger, whereas the ion-dipole bond has a greater distance between their electrons so their bond is weaker.
What compounds have ion-dipole forces?
Ion-Dipole Forces are involved in solutions where an ionic compound is dissolved into a polar solvent, like that of a solution of table salt (NaCl) in water. Note, these must be for solutions (and not pure substances) as they involve two different species (an ion and a polar molecule).
What is ion ion intermolecular force?
Interactions between two or more molecules are called intermolecular interactions, while the interactions between the atoms within a molecule are called intramolecular interactions. Intermolecular interactions occur between all types of molecules or ions in all states of matter.
Why are ion dipole forces strong?
Ion-dipole forces are stronger than dipole interactions because the charge of any ion is much greater than the charge of a dipole; the strength of the ion-dipole force is proportionate to ion charge. Ion-dipole bonding is also stronger than hydrogen bonding.
What is the ion dipole force?
Ion-dipole forces, therefore, are the electrostatic interactions between the fixed dipole in one molecule and an ion. An ion-dipole force is a type of intermolecular force in which forces of attraction or repulsion occur between neighboring ions, molecules or atoms. The ion-dipole force results from the attraction of an ion ...
Why are ion-dipole forces stronger than dipole forces?
However, ion-dipole forces possess ions instead of non-polar or polar molecules. An ion has a far greater charge than a dipole, which explains why ion-dipole forces are much stronger than dipole interactions. Ion-dipole forces involve the interaction between an ion and a polar molecule. The molecules align so that the positive ...
What is the interaction between an ion and a polar molecule?
Ion-dipole forces involve the interaction between an ion and a polar molecule. The molecules align so that the positive and negative forces are side by side allowing for maximum bonding.
What are the three types of intermolecular forces?
In addition to ion-dipole forces, there are three other types of attractive intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole forces; dipole-induced dipole forces; and instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces . Ion-dipole forces operate much like induced-dipole and dipole-dipole interactions.
What is the result of an electrostatic interaction between a charged ion and a molecule that has?
An ion-dipole interaction is the result of an electrostatic interaction between a charged ion and a molecule that has a dipole. It is an attractive force that is commonly found in solutions, especially ionic compounds dissolved in polar liquids.
What attracts the positive end of a polar molecule?
A cation can attract the partially negative end of a neutral polar molecule, while an anion attracts the positive end of a polar molecule. Ion-dipole attractions become stronger as the charge on the ion increases or as the magnitude of the dipole of the polar molecule increases. These interactions can be very significant factors in many chemical ...
Does sodium attract negatively charged water molecules?
These interactions can be very significant factors in many chemical situations, so it is important to learn how to work with them. Sodium only attracts the negatively charged end of water molecules, leading to the orientation shown. Public Domain Image.
What is the relationship between ion and dipole?
The relative strength of these forces can be understood in terms of Coulomb's law, which tells us that the electrostatic attraction between ion and dipole is directly related to the magnitudes of the ion charge and the dipole and inversely related to the distance between them. Created by Sal Khan.
Which type of bonding involves positive ions?
Ions engage in ionic bonding where positive ions (cations) are attracted to negative ions (anions). A dipole exists in a molecule which engages in covalent bonding, but one side of the molecule has more electronegativity than the other side.
What happens when an ion loses or gains electrons?
Ions were once neutral atoms which either gained or lost a number of electrons which now results in imbalance between the number of negative electrons and positive protons. Technically ions and atoms are categorized differently.