Which Bond is the strongest ionic or covalent?
Ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds, because there is a stronger attraction between ions that have opposite charges, which is why it takes a lot of energy to separate them. Covalent bonds are bonds that involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Key Points
- The two main types of chemical bonds are ionic and covalent bonds.
- An ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond, while electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms.
- The only pure covalent bonds occur between identical atoms. ...
- Ionic bonds form between a metal and a nonmetal. ...
What are some examples of ionic bonds?
Some ionic bond examples include:
- NaCl: sodium chloride
- NaBr: sodium bromide
- NaF: sodium fluoride
- NaI: sodium iodide
- KF: potassium fluoride
- KCl: potassium chloride
- KI: potassium iodide
- KBr: potassium bromide
- LiI: lithium iodide
- Li2O: lithium oxide
What are 5 examples of ionic compounds?
Ionic bond examples include:
- LiF - Lithium Fluoride
- LiCl - Lithium Chloride
- LiBr - Lithium Bromide
- LiI - Lithium Iodide
- NaF - Sodium Fluoride
- NaCl - Sodium Chloride
- NaBr - Sodium Bromide
- NaI - Sodium Iodide
- KF - Potassium Fluoride
- KCl - Potassium Chloride

What are 5 examples of covalent bonds?
Five examples of covalent bonds are hydrogen (H₂), oxygen (O₂), nitrogen (N₂), water (H₂O), and methane(CH₄). 2. What is a covalent bond? A chemical bond involving the sharing of electron pairs between atoms is known as a covalent bond.
What are 3 examples of an ionic bond?
Examples of Ionic Bonds Some ionic bond examples include: NaCl: sodium chloride. NaBr: sodium bromide. NaF: sodium fluoride.
What is ionic and covalent bond give examples?
A molecule or compound is made when two or more atoms form a chemical bond, linking them together. The two types of bonds are ionic bonds and covalent bonds....Ionic vs Covalent Bonds Summary.Ionic BondsCovalent BondsExamplesSodium chloride (NaCl), Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4 )Methane (CH4), Hydrochloric acid (HCl)7 more rows•Jan 23, 2020
What is covalent bond for example?
These electron pairs are known as shared pairs orbonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. example could be "Water, H2O" as it is formed by the share of electrons of hydrogen and oxygen (which are both non-metals).
What are 10 examples of covalent?
Examples of Covalent BondsHydrogen (H2) Hydrogen (H) is the simplest of all elements. ... Oxygen (O2) The valency of oxygen (O) is two, which means that it requires two electrons to complete its outermost (valence) shell. ... Nitrogen (N2) ... Water (H2O) ... Carbon Dioxide (CO2) ... Methane (CH4) ... Ammonia (NH3) ... Carbon Monoxide (CO)
What is the best example of ionic bond?
A salt such as sodium chloride (NaCl) is a good example of a molecule with ionic bonding (see Figure 3-3). The atomic number of the element sodium (Na) is 11, meaning that a sodium atom possesses eleven protons and eleven electrons.
What are two examples of ionic?
Examples: Table salt, NaCl, is an ionic compound. Another example is silver iodide, AgI.
What are ionic give examples?
Ionic Compounds Are Balanced Table salt is an example of an ionic compound. Sodium and chlorine ions come together to form sodium chloride, or NaCl. The sodium atom in this compound loses an electron to become Na+, while the chlorine atom gains an electron to become Cl-.
What are ionic examples?
Examples of ionic compounds in everyday life include table salt, baking soda, lye, Epsom salt, and bleach. There are many examples of ionic compounds in everyday life. Ionic compounds consist of atoms joined together by ionic bonds. Many ionic compounds are binary compounds formed by a metal and a nonmetal.
What are the 3 types of covalent bonds?
Types of Covalent BondsSingle Covalent Bond.Double Covalent Bond.Triple Covalent Bond.
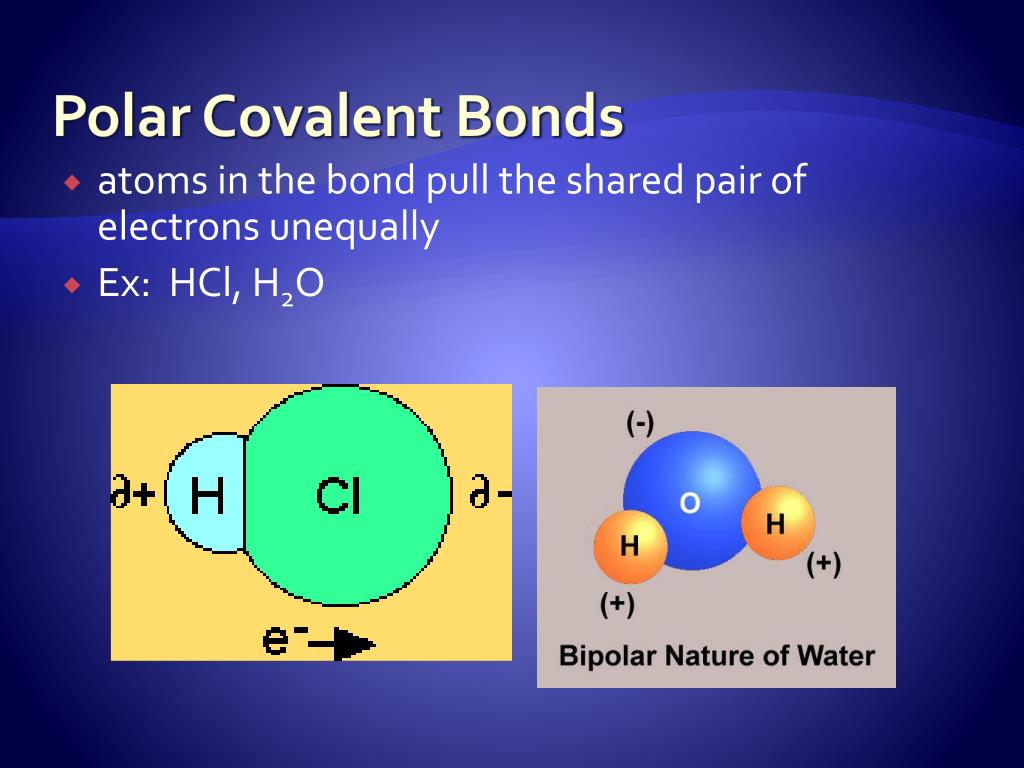
Is water a covalent bond?
Water is a Polar Covalent Molecule The unequal sharing of electrons between the atoms and the unsymmetrical shape of the molecule means that a water molecule has two poles - a positive charge on the hydrogen pole (side) and a negative charge on the oxygen pole (side).
What is a real life example of a covalent bond?
Many molecules around us are held together by covalent bonding. Sugar molecules, the gases present in the air such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and hydrogen, LPG, vinegar, plastic and diamond are all examples of molecules with covalent bonds in them.
What are 3 ionic compounds?
What are Ionic Compounds?sodium chloride: NaCl, with Na+ and Cl- ions.lithium nitride: Li3N, with Li+ and N3- ions.magnesium oxide: MgO, with Mg2+ and O2- ions.calcium phosphide: Ca3P2, with Ca2+ and P3- ions.
What are Type 3 ionic compounds?
Compounds containing only non-metal elements are named using Type III binary compound rules. These compounds are always neutral (not ions which have charges), and consist of only two elements (see acid naming below for compounds containing only non-metal elements, but with more than two elements.
What is an example of a ionic?
Table salt is an example of an ionic compound. Sodium and chlorine ions come together to form sodium chloride, or NaCl. The sodium atom in this compound loses an electron to become Na+, while the chlorine atom gains an electron to become Cl-.
What are 4 common ionic compounds?
The anions in these compounds have a fixed negative charge (S2−, Se2− , N3−, Cl−, and SO2−4), and the compounds must be neutral....Solutioniron(III) sulfide.copper(II) selenide.gallium(III) nitride.chromium(III) chloride.titanium(III) sulfate.
How many electrons does magnesium need to accept?
In this example, the magnesium atom is donating both of its valence electrons to chlorine atoms. Each chlorine atom can only accept 1 electron before it can achieve its noble gas configuration; therefore, 2 atoms of chlorine are required to accept the 2 electrons donated by the magnesium.
Why is covalent bonding important?
Covalent bonds are especially important since most carbon molecules interact primarily through covalent bonding. Covalent bonding allows molecules to share electrons with other molecules, creating long chains of compounds and allowing more complexity in life.
Why do atoms share electrons?
Because both atoms have the same affinity for electrons and neither has a tendency to donate them , they share electrons in order to achieve octet configuration and become more stable. In addition, the ionization energy of the atom is too large and the electron affinity of the atom is too small for ionic bonding to occur.
What type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element?
Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms. This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements close to each other in the periodic table. This bonding occurs primarily between nonmetals; however, it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals.
How many electrons are needed to bond a nonmetal?
Similarly, nonmetals that have close to 8 electrons in their valence shells tend to readily accept electrons to achieve noble gas configuration. In ionic bonding, more than 1 electron can be donated or received to satisfy the octet rule.
Why do metals have ionic bonds?
In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to become a positively charged cation , whereas the nonmetal accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged anion. Ionic bonds require an electron donor, often a metal, and an electron acceptor, a nonmetal. Ionic bonding is observed because metals have few electrons in their outer-most orbitals.
What type of bond is a chemical bond?
There are many types of chemical bonds and forces that bind molecules together. The two most basic types of bonds are characterized as either ionic or covalent. In ionic bonding, atoms transfer electrons to each other. Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron acceptor.
How does a chemical bond work?
How It Works. The type of chemical bond formed between two atoms or between a metal and set of nonmetals depends on the electronegativity difference between them. It's important to remember the way bonds are classified is somewhat arbitrary.
What is the difference between a polar covalent bond and an ionic bond?
The only real difference between a polar covalent bond and an ionic bond is the degree of charge separation.
What are the different types of bonds?
Remember the electronegativity ranges, so you'll be able to predict the types of bonds in a compound: 1 nonpolar covalent bond - The electronegativity difference is less than 0.4. 2 polar covalent bond - The electronegativity difference is between 0.4 and 1.7. 3 i onic bond - The electronegativity difference between species forming a bond is greater than 1.7.
What is an ionic bond?
Updated May 24, 2019. An ionic bond is a chemical bond between two atoms in which one atom seems to donate its electron to another atom. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, appear to involve two atoms sharing electrons reach a more stable electron configuration. Some compounds contain both ionic and ...
What are some examples of compounds that exhibit both types of chemical bonding?
However, other examples contain a metal joined via an ionic bond to covalently bonded nonmetals. Here are examples of compounds that exhibit both types of chemical bonding: NaNO 3 - sodium nitrate.
When both ionic and covalent bonding occur in a compound, the ionic portion is almost always?
When both ionic and covalent bonding occurs in a compound, the ionic portion is almost always between the cation and anion of the compound. The covalent bonds could occur in a polyatomic ion in either the cation or the anion. Cite this Article. Format.
Which compounds are ionically bonded?
Here are examples of compounds that exhibit both types of chemical bonding: In ammonium sulfide, the ammonium cation and the sulfide anion are ionically bonded together, even though all of the atoms are nonmetals. The electronegativity difference between ammonium and the sulfur ion allows for an ionic bond.