.PNG)
The elements of the periodic table sorted by ionization energy
| The chemical elements of the periodic ch ... | Ionization Energy | Name chemical element | Symbol | Atomic number |
| - Name alphabetically | 3,8939 | Cesium | Cs | 55 |
| - Atomic number | 4,0727 | Francium | Fr | 87 |
| - Symbol | 4,1771 | Rubidium | Rb | 37 |
| - Atomic Mass | 4,3407 | Potassium | K | 19 |
How to calculate the first ionization energy?
How to Calculate Ionization Energy. Ionization potential for hydrogen can be calculated using the following equation: E = hcRH (1/n 2 ), where. E is energy of the electron (or the amount of energy it takes to remove the electron, ionization energy) h is Planck’s constant = 6.626 * 10 -34 Js (joules*seconds)
What trend in ionization energy occurs across a period on the periodic table?
Ionization energy exhibits periodicity on the periodic table. The general trend is for ionization energy to increase moving from left to right across an element period. Moving left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases, so electrons are more attracted to the (closer) nucleus.
What is the equation for ionization energy?
eV /atom = −2.18× 10−18 × n2Z2. . J /atom. Ionization energy for the removal of an electron from a neutral atom can be calculated, by substituting, the orbit number of the electron before transition as ‘n 1 ‘ and orbit number of the electron after transition as ‘∞' ( infinity) as ‘n 2 ‘ in Bohr’s energy equation.
How do you define ionization energy?
Summary
- The ionization energy ( IE) is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state.
- In general successive ionization energies increase in magnitude IE1 < IE2 < IE3 < IE4 and so on.
- First ionization energy increases across the period
- First ionization energy decreases down the group
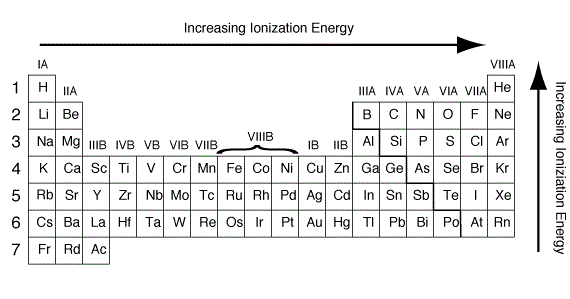
What is the best explanation of ionization energy?
Ionization energies measure the tendency of a neutral atom to resist the loss of electrons. It takes a considerable amount of energy, for example, to remove an electron from a neutral fluorine atom to form a positively charged ion.
How do you define ionization?
ionization, in chemistry and physics, any process by which electrically neutral atoms or molecules are converted to electrically charged atoms or molecules (ions) through gaining or losing electrons.
How do you determine ionization energy?
Ionization energy for the removal of an electron from a neutral atom can be calculated, by substituting the orbit number of the electron before transition as 'n1' and orbit number of the electron after transition as '∞'( infinity) as 'n2' in Bohr's energy equation.
What is ionization energy formula?
Numerically, we describe ionization energy as the orbital energy of the electron with the reverse sign. The ionization energy = + 2.18 × 10–18 J/atom (or + 1312.3 KJ/mole).
Q1. Can You distinguish the element Which has the Highest Ionization Energy?
Ans: The first ionization energy differs expectedly across the periodic table. The ionization energy reduces from top to bottom in groups and rises...
Q2. Calculate the net Energy that All Aluminum Atoms desire to turn into Al3+ that are Existing in 0...
Ans: We know that the net energy to make the change in Al to Al3+ will be= IE1 + IE2 +IE3= 568 + 1807 + 2735 kJmol−1kJmol−1= 5110 kJmol−1Now, the n...
Q3. Explain the Working Procedure of the Ionization Energy.
Ans: The working process of ionization energy can be explained as the amount of energy that must be absorbed by an isolated, gaseous atom in the gr...
Q4. What is the Possibility of the Ionization Energy; Positive or Negative?
Ans: The answer is the ionization energy is always positive because every solitary electron is bound and therefore, the electron has negative energ...
What is ionization energy?
What is Ionization Energy. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom. Periodic Table
How much ionization energy is needed to remove an electron?
Some of these electrons are more tightly bound in the atom than others. For example, only 7.38 eV is required to remove the outermost electron from a lead atom, while 88,000 eV is required to remove the innermost electron.
What is the unit of energy of an electron?
Electronvolt (unit: eV). Electronvolts are a traditional unit of energy particularly in atomic and nuclear physics. Electronvolt is equal to energy gained by a single electron when it is accelerated through 1 volt of electric potential difference. The work done on the charge is given by the charge times the voltage difference, therefore the work W on electron is: W = qV = (1.6 x 10 -19 C) x (1 J/C) = 1.6 x 10-19 J. Since this is very small unit, it is more convenient to use multiples of electronvolts : kilo-electronvolts (keV), mega-electronvolts (MeV), giga-electronvolts (GeV) and so on. Since Albert Einstein showed that mass and energy are equivalent and convertible one into the other, the electronvolt is also a unit of mass. It is common in particle physics, where units of mass and energy are often interchanged, to express mass in units of eV/c 2, where c is the speed of light in vacuum (from E = mc 2 ). For example, it can be said the proton has mass of 938.3 MeV, although strictly speaking it should be 938.3 MeV/c2. For another example, an electron–positron annihilation occurs when a negatively charged electron and a positively charged positron (each with a mass of 0.511 MeV/c 2) collide. When an electron and a positron collide, they annihilate resulting in the complete conversion of their rest mass to pure energy (according to the E=mc 2 formula) in the form of two oppositely directed 0.511 MeV gamma rays (photons).
How much energy is released in a reactor?
The total energy released in a reactor is about 210 MeV per 235 U fission, distributed as shown in the table. In a reactor, the average recoverable energy per fission is about 200 MeV, being the total energy minus the energy of the energy of antineutrinos that are radiated away.
How to find the work of an electron?
The work done on the charge is given by the charge times the voltage difference , therefore the work W on electron is: W = qV = (1.6 x 10-19 C) x (1 J/C) = 1.6 x 10-19 J.
How many EV is needed to remove the outermost electron from a lead atom?
For example, only 7.38 eV is required to remove the outermost electron from a lead atom, while 88,000 eV is required to remove the innermost electron.
What is the energy of a thermal neutron?
Most probable energy at 17°C (62°F) for Maxwellian distribution is 0.025 eV (~2 km/s).
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom. X + energy → X+ + e− where X is any atom or molecule capable of being ionized, X+ is that atom or molecule with an electron removed (positive ion), and e− is the removed electron. Periodic Table
How much ionization energy is needed to remove an electron?
Some of these electrons are more tightly bound in the atom than others. For example, only 7.38 eV is required to remove the outermost electron from a lead atom, while 88,000 eV is required to remove the innermost electron. Helps to understand reactivity of elements (especially metals, which lose electrons).
Which metal has the lowest ionization energy?
Ionization energy is lowest for the alkali metals which have a single electron outside a closed shell.
How many eV does sodium need to ionize?
For example, sodium requires only 496 kJ/mol or 5.14 eV/atom to ionize it. On the other hand neon, the noble gas, immediately preceding it in the periodic table, requires 2081 kJ/mol or 21.56 eV/atom.
How to Calculate Ionization Energy?
For ionization energy, the concept is to study a quantity of the tendency of an atom or ion to give up an electron or the effectiveness of the electron binding.
Why does ionization energy rise?
If we spectate on the periodic table and travel from left to right across the elements, the ionization energy will rise due to a declining atomic radius.
What is the least amount of energy required for an electron in a vaporous atom or ion to?
There are also some technical ways to describe the ionization energy as the least amount of energy required for an electron in a vaporous atom or ion to consume to come out of the effect of the nucleus.
Why does ionization energy decrease when we go from head to toe?
This is mostly because of the existence of other electron shells in the elements as we move down the group. Also, the electrons are kept at a longer distance from the forces of attraction of the nucleus.
What happens to the electrons when the charge of the nucleus is positive?
If the charge of the nucleus is positive, the attraction of the electrons is so strong towards it. If an electron exists adjacent to or near to the nucleus, the attraction will be superior to the one when the electron is a little far.
Why is ionization energy always positive?
Ans: The answer is the ionization energy is always positive because every solitary electron is bound and therefore, the electron has negative energy.
What is the working process of ionization energy?
Ans: The working process of ionization energy can be explained as the amount of energy that must be absorbed by an isolated, gaseous atom in the ground electronic state to release an electron. This process results in cation production.
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy: Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the gaseous atom or ion. In simple words, the electron itself cannot escape out of the orbit.
Can an electron escape an orbit?
In simple words, the electron itself cannot escape out of the orbit. It requires some external energy to be supplied on it in order to escape out of the orbit. And this required energy is known as ionization energy.
Can you find every detail of an interactive periodic table?
You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
What is Ionization Energy?
So what is the definition of ionization energy? It is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom, which forms an ion. It is usually measured in kJ/mol, and the measurement is based on an isolated atom in its gaseous phase. Let’s learn how to calculate it, what is meant by first and second ionization energy, and how it trends on the periodic table.
Which element has the highest ionization energy?
In general, (first) ionization energies increase toward the top right corner of the periodic table, with helium having the highest ionization energy. Before we break down the trend into its period and group trends, let’s talk about a major contributing factor to this trend: the octet rule.
Why does ionization decrease when you go down a group?
This is because as you go down a group, electrons are located in successively higher energy levels, farther away from the attraction of the nucleus. Furthermore, down a group, there are more electrons between the outside valence electrons and the nucleus. These middle electrons help “shield” the outer electrons from the attractive forces of the nucleus. Therefore, it is easier to remove an electron from lower in a group.
Why does a group 1 element have very low ionization energies?
Thus, group 1 elements have very low ionization energies. It takes very little energy to remove an electron because the atom can be more stable without it.
How do ions get their charge?
An ion is a positively or negatively charged atom—it gets the charge by having a number of electrons unequal to that of its protons. For example, the sodium ion, also written as Na +, has 11 protons and 10 electrons. There is one more proton than there are electrons, making the ion positively charged. The number of protons for any atom or ion is always constant (the number of protons determines the atomic number).
What is the energy of an electron?
E is energy of the electron (or the amount of energy it takes to remove the electron, ionization energy)
Which group of gases has the highest ionization potential?
As you can see on the graph, the noble gases have the highest ionization energies, and the alkali metals have the lowest ionization energies. Between groups 1 and 18, ionization potentials generally increase across a period.
What is ionization energy?
Explanation: Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove one electron from an atom in the gaseous state. This electron would be a valence electron, or an electron in the outermost energy level/shell, because they're the easiest to remove. Ionization energy depends mainly on the strength of the attraction between the negative electron and ...
Which element has a higher first ionization energy?
Magnesium is found to have a higher first ionization energy value than aluminum, how would you explain this exception to the general trend in terms of electron arrangements and attraction/repulsion?
What happens when you move down a group in the periodic table?
When we move down a group in the periodic table, more energy levels are added, and so valence electrons would become further and further away from the positive nucleus. This causes the attraction between valence electrons and the nucleus to decrease, something known as the shielding effect. The less attraction between the electrons and ...
What is the unity of ionization energy?
The unity for ionization energy is eV.
How many elements are in chemistry?
This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
