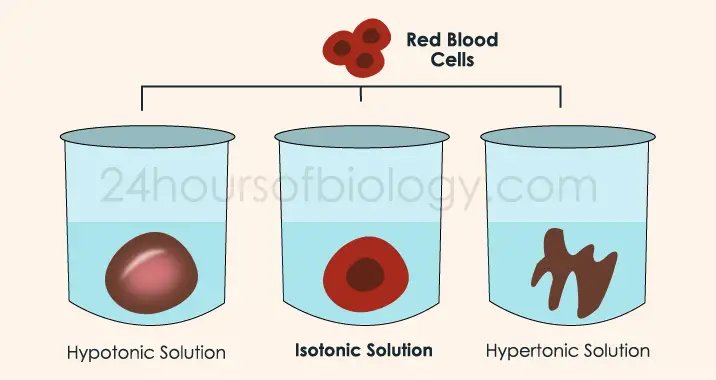
Isotonic Crystalloids. Because water moves between ICF and ECF toward the compartment with a higher concentration of dissolved molecules, an infusion of isotonic crystalloids does not cause a shift of water between ECF and ICF compartments.
What are some examples of isotonic exercises?
Sample Beginner’s Isotonic Workout
- Bench Press. Set up with the bar just over your eyes. ...
- Dip. Suspend your body over the bars of a dip station and brace your core. ...
- Pullup. Place your hands on the bar with palms facing forward, just outside your shoulders. ...
- Overhead Banded Triceps Extension. Attach a circle band to a sturdy object overhead and grasp an end in each hand. ...
- Dumbbell Reverse Fly. ...
What is IV fluids?
What are IV Fluids? Intravenous fluids, also known as intravenous solutions, are supplemental fluids used in intravenous therapy to restore or maintain normal fluid volume and electrolyte balance when the oral route is not possible.
What is a colloid IV fluid?
What is a colloid IV fluid? Crystalloids fluids such as normal saline typically have a balanced electrolyte composition and expand total extracellular volume. Colloid solutions (broadly partitioned into synthetic fluids such as hetastarch and natural such as albumin) exert a high oncotic pressure and thus expand volume via oncotic drag.
What is an isotonic solution biology?
What is isotonic in biology
- Examples of isotonic solutions: Following are the concepts that describe what does isotonic solution mean.
- Relieving Dehydration. A mixture of water and sodium chloride (NaCl) makes a saline solution. ...
- Alcohol Proof. Beer has less alcohol content by volume, or lower proof, than whiskey. ...

What does isotonic crystalloid mean?
Crystalloid solutions, which contain water-soluble electrolytes including sodium and chloride, lack proteins and insoluble molecules. They are classified by tonicity, so that isotonic crystalloids contain the same amount of electrolytes as the plasma.
What are examples of isotonic Crystalloids?
Isotonic sodium chloride (normal saline [NS]) and lactated Ringer (LR) are isotonic crystalloids, the standard intravenous (IV) fluids used for initial volume resuscitation. They expand the intravascular and interstitial fluid spaces.
What are the 3 types of crystalloid solutions?
These solutions were designed to sustain a normal physiologic plasma pH. The three commonly used molecules are lactate, acetate, and gluconate.
Is isotonic crystalloid the same as normal saline?
There is no significant difference between balanced crystalloids and isotonic saline in the incidence of in-hospital mortality, AKI, ICU mortality, or need for new RRT in critically ill patients. Further powerful studies are required to determine the relationship between two fluid groups and various clinical outcomes.
What are the 3 main types of IV fluids?
There are three types of IV fluids:Isotonic.Hypotonic.Hypertonic.
Is lactated Ringer's isotonic?
Ringer's lactate solution, or lactated Ringer's solution, is a type of isotonic, crystalloid fluid further classified as a balanced or buffered solution used for fluid replacement.
Is lactated Ringer's a crystalloid or colloid?
Crystalloids, such as saline and Ringer's lactate, are solutions of salt, water and minerals, and are commonly used in the clinical setting. They have small molecules, and, when used intravenously, they are effective as volume expanders.
What is the difference between crystalloid and colloid?
Colloids are those substances which are not easily crystallized from their aqueous solutions. Crystalloids are those substances which are easily crystallized from their aqueous solution. Colloids contain much larger particles than crystalloids (1 – 200 nm).
Is normal saline a crystalloid fluid?
Currently, providers choose between two classes of available crystalloid solutions: 0.9% sodium chloride (saline) and “balanced” crystalloids (such as lactated Ringer's, Hartmann's solution, or Plasma-lyte®).
Which IV fluids are isotonic?
Isotonic solutions are IV fluids that have a similar concentration of dissolved particles as blood. An example of an isotonic IV solution is 0.9% Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl).
What are the 5 most common IV solutions?
Here is a brief description of each:0.9% Normal Saline (NS, 0.9NaCl, or NSS) ... Lactated Ringers (LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL) ... Dextrose 5% in Water (D5 or D5W, an intravenous sugar solution) ... 0.45% Normal Saline (Half Normal Saline, 0.45NaCl, .
Which IV fluid is best for dehydration?
For severe dehydration, start IV fluids immediately. If the patient can drink, give ORS by mouth while the IV drip is set up. Ringer's lactate IV fluid is preferred. If not available, use normal saline or dextrose solution.
Is lactated Ringer's a crystalloid or colloid?
Crystalloids, such as saline and Ringer's lactate, are solutions of salt, water and minerals, and are commonly used in the clinical setting. They have small molecules, and, when used intravenously, they are effective as volume expanders.
What is an example of hypertonic solution?
Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of dissolved particles than blood. An example of hypertonic IV solution is 3% Normal Saline (3% NaCl). When infused, hypertonic fluids cause an increased concentration of dissolved solutes in the intravascular space compared to the cells.
What are isotonic IV fluids?
Isotonic. Isotonic IV solutions that have the same concentration of solutes as blood plasma. Hypotonic. Hypotonic solutions have lesser concentration of solutes than plasma.
Is Hartmann's solution a crystalloid or colloid?
Other crystalloid solutions are compound sodium lactate solutions (Ringer's lactate solution, Hartmann's solution) and glucose solutions (see 'Preparations containing glucose' below).
What are Crystalloids made of?
Crystalloids are made up of very small molecules like sodium, chlorine, and glucose. They flow through semipermeable membranes with ease.
What is an example of an isotonic crystalloid solution?
An example of an isotonic solution is 0.9% saline, which is also known as normal saline. It is a sterile, nonpyrogenic crystalloid fluid administer...
Are Crystalloids hypertonic or hypotonic?
Crystalloid solutions can be both hypertonic and hypotonic, but not necessarily. Based on the tonicity, crystalloid solutions can be divided into t...
What is a crystalloid solution?
Crystalloid solutions are intravenous solutions that contain small salt molecules and sugar molecules. Crystalloid molecules are small enough to pa...
What are the three types of Crystalloids?
Based on tonicity, crystalloids can be divided into three categories: isotonic crystalloid solutions, hypertonic crystalloid solutions, and hypoton...
Is lactated Ringer's an isotonic crystalloid?
Yes, lactated Ringer's is an isotonic solution. It resembles the concentration of blood plasma. It is used to treat low blood pressure or volume, a...
What is a crystalloid?
Crystalloid. Crystalloids are compositions of fluid and electrolytes in varying proportions that are divided generally into replacement fluids and maintenance fluids. From: Canine and Feline Gastroenterology, 2013. Download as PDF.
What is crystalloid solution used for?
In summary, crystalloid solutions are universally used for initial volume resuscitation in sepsis and septic shock, principally to “pay back” interstitial fluid debt. As sepsis proceeds, particularly into the hypofunctional phase, significant tissue accumulation of resuscitation fluid occurs, and this may result in adverse effects (see Chapter 12 ). Isotonic saline, when administered in large volume, is associated with hyperchloremic acidosis 51; this may affect splanchnic blood flow and may indeed be nephrotoxic. 47,52,53 Lactated Ringer solution and other isotonic crystalloid solutions may activate inflammation and result in cellular apoptosis, possibly worsening lung injury. 48
How much crystalloid is needed for resuscitation?
The quantity of crystalloid needed is in part dependent upon the parameters used to monitor resuscitation. If a urinary output of 0.5 cc/kg of body weight/hour is considered to indicate adequate perfusion, approximately 3 cc/kg/% burn will be needed in the first 24 h. If 1 cc/kg of body weight/hour of urine is deemed necessary, then of course considerably more fluid will be needed and in turn more edema will result. The Parkland formula recommends 4 cc/kg/% burn in the first 24 h, with one-half of that amount administered in the first 8 h 9 ( Table 9.1 ). The modified Brooke formula recommends beginning burn shock resuscitation at 2 cc/kg/% burn in the first 24 h ( Table 9.1 ). In major burns, severe hypoproteinemia usually develops with these resuscitation regimens. The hypoproteinemia and interstitial protein depletion may result in more edema formation.
What is crystalloid carcinoma?
Crystalloids are sharp, needle-like eosinophilic structures that are often present in the lumina of well- and moderately differentiated carcinoma 35 ( Fig. 3-4B) They are not specific for carcinoma and can be found in other conditions. The presence of crystalloids in metastatic adenocarcinoma of unknown site of origin is strong presumptive evidence ...
What is a collodion for dogs?
Crystalloids and colloids are the fluid types most commonly used in the treatment of dogs and cats with GI disease. Crystalloids are compositions of fluid and electrolytes in varying proportions that are divided generally into replacement fluids and maintenance fluids. Box 48-1 provides examples of each of these types of fluids. Replacement fluids, as the name suggests, are designed to replace water and electrolytes lost as a consequence of GI (or other) disease, and are characterized by higher concentrations of sodium than maintenance fluids, which have proportionally more water than replacement solutions. Colloids can be synthetic or natural. Box 48-1 also outlines examples of synthetic and natural colloids.
Can hemodilution cause postoperative bleeding?
Even so, hemodilution is rarely the sole cause of postoperative bleeding, because coagulation factor concentrations of 25% to 30% and platelet counts of 50,000 to 100,000/mm3 can be tolerated without excessive bleeding if platelet function is normal. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
Is crystalloid or colloid more expensive?
Crystalloid versus Colloid Replacement. Crystalloids distribute quickly into total body water and can cause peripheral and pulmonary edema, but are less expensive than colloid solutions. Colloid solutions primarily remain (at least initially) intravascular, but are more expensive and can cause allergic reactions.
What is crystalloid fluid?
Crystalloid fluids are a subset of intravenous solutions that are frequently used in the clinical setting. Crystalloid fluids are the first choice for fluid resuscitation in the presence of hypovolemia, hemorrhage, sepsis, and dehydration.
When was the mass based formula for maintenance crystalloid fluids developed?
The fluid requirements of patients were determined to be related to a patient's caloric demand by Drs. Holliday and Segar in 1957.[2] Since this time, their initial formula has been modified to provide clinicians with guidelines for administering maintenance crystalloid fluids. The mass-based formula uses what is known as the "4-2-1" rule:
How are crystalloid fluids administered?
Crystalloid fluids are administered parenterally via an intravenous infusion. Infusion rates depend on the clinical presentation and indication for administration. Fluid Resuscitation. In an acute setting, the clinical situation may indicate a rapid infusion of crystalloid fluids.
What is intravenous fluid?
Broadly, intravenous fluids can fall into two separate categories: crystalloids and colloids. In most clinical settings, crystalloids are the choice of fluid for many indications for fluid resuscitation, maintenance, or as a solvent for medication delivery.
Why are buffered solutions osmotically active?
Because of this discrepancy in concentration, these fluids are osmotically active and will cause fluid shifts. Their primary indication is for emergent replacement of serum solutes, such as in hyponatremia with neurologic symptoms. Buffered solutions contain molecules that metabolize in vivo to bicarbonate.
Can acetate buffered crystalloids increase serum concentration?
Studies performed on dogs have shown that even small volumes of acetate-containing crystalloids can significantly increase the serum concentration of acetate to 10 to 40 times the physiologic level.
Can crystalloid fluid cause pulmonary edema?
Patients with congestive heart failure are at elevated risk for serious adverse effects of crystalloid fluid administration. Fluid overload can cause life-threatening pulmonary edema and the worsening of diastolic or systolic heart failure, leading to end-organ damage or even death. It is vital for the clinician to monitor these patients carefully and administer the minimum required volume to maintain volume homeostasis.
What are crystalloids made of?
Ultrastructurally, crystalloids are composed of electron-dense material that lacks the periodicity of crystals. Radiographic microanalysis reveals abundant portions of sulfur, calcium, and phosphorus, and a small amount of sodium. 35 Hard proteinaceous secretions are almost always present in adjacent acini and are probably the source of the crystalloids.
When were crystalloids first used?
The use of crystalloids for blood replacement was first anticipated in the nineteenth century. In the 1880s, Ringer (1880) observed that salts of sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride in precise proportions and concentrations were necessary for cellular function; these observations led to the later development of balanced salt solutions. In 1899, Crile (1947) resuscitated animals subjected to hemorrhagic shock with warm intravenous infusions of saline and further refined the concept of treatment of shock with crystalloids. During World War I, battle casualties were treated with combinations of colloid and salt solutions. The effects of saline solutions alone were thought to be transient. Blalock, who first categorized shock as hemorrhagic, cardiogenic, neurogenic or septic ( Blalock, 1930 ), also demonstrated that tissue trauma resulted in the loss of extracellular fluid ( Blalock, 1940 ). Hartmann, in the early 1930s, added sodium lactate to saline to avoid hyperchloremic acidosis that he observed when treating children with saline for infantile diarrhea; ultimately, this innovation resulted in lactated Ringer’s (RL) or Hartmann’s solution ( Hartmann and Senna, 1932; Hartmann, 1934 ).
What are crystalloids in metastatic adenocarcinoma?
The presence of crystalloids in metastatic adenocarcinoma of unknown site of origin is strong presumptive evidence of prostatic origin, although it is an uncommon finding and not conclusive. 36 Special stains highlight crystalloids, which otherwise cannot be seen by light microscopy. 36 Crystalloids stain red with a trichrome stain, blue with a toluidine blue stain and violet with the Mallory's staining and appear argyrophilic with silver stain methods. Crystalloids do not stain with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), Alcian blue, Prussian blue, Congo red, or with immunohistochemical stains for PSA and prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP). The mechanism of crystalloid formation remains unknown, but crystalloids probably result from abnormal protein and mineral metabolism within benign and malignant acini.
How do crystalloids help with dehydration?
Crystalloids effectively replenish the interstitial space. Dehydration is defined as loss of water in the extravascular tissue (interstitial and intracellular). Tonicity of the interstitial compartment increases as fluid is lost, which promotes movement of fluid out of the intravascular space. Severe dehydration can result in poor tissue perfusion, but the terms dehydration and perfusion should not be used interchangeably. Crystalloids contribute to effective fluid resuscitation when used with colloids if dehydration also is present. Another consequence of large volumes of crystalloid fluids is decreased intravascular oncotic pressure caused by dilution of impermeant protein anions. 37 Decreased oncotic pressure impairs maintenance of intravascular volume and promotes extravasation of fluids into the interstitial space.
How much crystalloid is needed for resuscitation?
The quantity of crystalloid needed is in part dependent upon the parameters used to monitor resuscitation. If a urinary output of 0.5 cc/kg of body weight/hour is considered to indicate adequate perfusion, approximately 3 cc/kg/% burn will be needed in the first 24 h. If 1 cc/kg of body weight/hour of urine is deemed necessary, then of course considerably more fluid will be needed and in turn more edema will result. The Parkland formula recommends 4 cc/kg/% burn in the first 24 h, with one-half of that amount administered in the first 8 h 9 ( Table 9.1 ). The modified Brooke formula recommends beginning burn shock resuscitation at 2 cc/kg/% burn in the first 24 h ( Table 9.1 ). In major burns, severe hypoproteinemia usually develops with these resuscitation regimens. The hypoproteinemia and interstitial protein depletion may result in more edema formation.
When did Shires and al. add crystalloids to plasma?
In the 1960s, Shires et al. (1960, 1961, 1964) documented the necessity of adding substantial volumes of crystalloids to whole blood and plasma to achieve successful resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock. Shires et al. (1961) further extended the concept that extracellular fluid volume decreased also during major surgery.
Who first categorized shock as hemorrhagic, cardiogenic, neurogenic or septic?
Blalock, who first categorized shock as hemorrhagic, cardiogenic, neurogenic or septic ( Blalock, 1930 ), also demonstrated that tissue trauma resulted in the loss of extracellular fluid ( Blalock, 1940 ).
