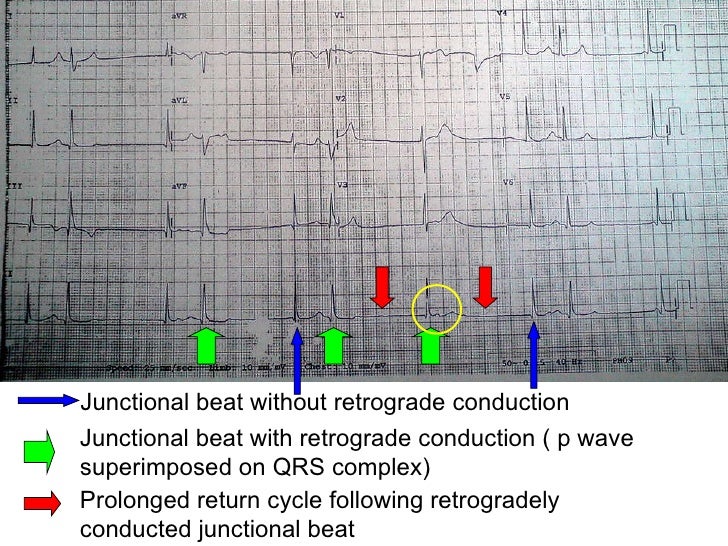
What is a junctional rhythm?
Junctional Rhythm: A comprehensive overview. A junctional rhythm is a protective heart rhythm that occurs when the atrioventricular node (AV node) takes over as the heart’s pacemaker. To fully understand a junctional rhythm, let’s first take a look at the cardiac conduction system and see how it operates in a normal, healthy heart.
What is premature junctional complex PJC?
Premature junctional complex (PJC) occurs when an irritable site within the AV node fires an impulse before the SA node. This impulse interrupts the sinus rhythm. The QRS complex will be narrow, usually measured at 0.10 sec or less.
What is included in the physical exam of junctional rhythm?
A significant component of an assessment for a patient who presents with signs and symptoms of junctional rhythm is history and physical exam. These should include vital signs (respiratory rate, blood pressure, temperature, and heart rate), review of the patient's medication list, and an electrocardiogram.
What is junctional tachycardia?
This is defined as either an accelerated junctional rhythm or junctional tachycardia, depending on the rate. A junctional rhythm is protective — the AV node serves as a backup for the SA node — so it should not be suppressed.

What is junctional activity in nevus?
The junctional nevus is composed of discrete nests of melanocytes/nevus cells at the dermoepidermal junction, usually located on the rete ridges, which often show some accentuation. The cells are oval to cuboidal in shape, with clear cytoplasm containing a variable amount of melanin pigment. Mitoses are rare or absent.
Is a junctional nevus cancerous?
The histologic findings of small, uniform, symmetrical, well circumscribed nests of melanocytes are reassuring for melanocytic nevi. Junctional Nevi are, by definition, benign and most remain benign throughout a person's lifetime. Therefore, most moles will never need to be treated.
Does melanocytic mean malignant?
Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the melanocytes. Other names for this cancer include malignant melanoma and cutaneous melanoma. Most melanoma cells still make melanin, so melanoma tumors are usually brown or black. But some melanomas do not make melanin and can appear pink, tan, or even white.
How do I get rid of junctional nevus?
Small nevi can be removed by simple surgical excision. The nevus is cut out, and the adjacent skin stitched together leaving a small scar. Removal of a large congenital nevus, however, requires replacement of the affected skin.
What does junctional mean?
1. The act or process of joining or the condition of being joined. 2. A place where two things join or meet, especially a place where two roads or railway routes come together and one terminates.
Is a junctional nevus a mole?
Junctional nevi. A junctional nevus is a mole that occurs between two layers of skin. This image shows two junctional nevi that appear as uniformly brown small macules, round in shape with smooth regular borders.
What are the warning signs of melanoma?
Other melanoma warning signs may include: Pigment, redness or swelling that spreads outside the border of a spot to the surrounding skin. Itchiness, tenderness or pain. Changes in texture, or scales, oozing or bleeding from an existing mole. Blurry vision or partial loss of sight, or dark spots in the iris.
Are melanocytes precancerous?
Compared with other clinically apparent, benign, but potentially precancerous lesions, melanocytic nevi are unique as they arise relatively early in life.
Where does melanoma usually start?
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer. While it can develop anywhere on the skin, it most commonly starts on the trunk (chest and back) in men and on the legs in women. Other common locations for melanoma include the face and neck, and on the scalp in men.
Can a nevus become cancerous?
Is it cancer? No. A dysplastic nevus is more likely than a common mole to become cancer, but most do not become cancer.
Does junctional nevus grow?
A junctional nevus will typically evolve over time into a compound nevus, which is a nevus with both epidermal and dermal melanocytes. Compound nevi become elevated and usually are more pale. Junctional nevi will typically grow to be 3 or 4 mm across, stop growing sideways, and begin to evolve into a compound nevus.
What does a nevus look like?
A common mole (nevus) is a small growth on the skin that is usually pink, tan, or brown and has a distinct edge. A dysplastic nevus is often large and does not have a round or oval shape or a distinct edge. It may have a mixture of pink, tan, or brown shades.
What is junctional rhythm?
Definition. Junctional rhythm describes a heart -pacing fault where the electrical activity that initiates heart muscle contraction starts in the wrong region. Heart rhythm is the result of electrical impulses sent from the pacemaker cells of the sinoatrial node (SAN) at the top of the right atrium. If the SAN fails to fire, an area located ...
What is the accelerated junctional rhythm?
Accelerated junctional rhythm (AJR) describes a depolarization rate of between 60 and 100 per minute with heart pacing initiated at the AV junction. The most common cause of accelerated junctional rhythm is digoxin (digitalis) toxicity.
What is the difference between AV junction and SAN?
The SAN activates contraction in the atria while the AV junction does the same for the larger, more powerful ventricles.
Where do junctional escape beats originate?
Junctional escape beats originate in the AV junction and are late in timing. They often occur during sinus arrest or after premature atrial complexes. The QRS complex will be measured at 0.10 sec or less. Rhythm will be regular with a rate of 40-60 bpm.
What is PJC in AV?
Premature junctional complex (PJC) occurs when an irritable site within the AV node fires an impulse before the SA node. This impulse interrupts the sinus rhythm. The QRS complex will be narrow, usually measured at 0.10 sec or less.
What is junctional rhythm?
A junctional rhythm is an abnormal heart rhythm that originates from the AV node or His bundle. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of junctional rhythm and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in educating patients about their prognosis.
Can junctional rhythm cause shortness of breath?
Patients with junctional rhythm may present with a varied array of symptoms or may be asymptomatic. Symptoms mostly depend on the underlying cause of the junctional rhythm, for instance, a patient presenting with heart failure exacerbation may present with shortness of breath, wheezing, and lower extremity edema.
Can Digoxin cause junctional rhythm?
Digoxin toxicity can also lead to an accelerated junctional rhythm. Epidemiology. Junctional rhythm is typical among individuals who have a sinus node dysfunction (SND), and 1 in every 600 cardiac patients above the age of 65 within the United States has SND.
What is junctional nevus?
Junctional nevi are benign melanocytic neoplasms in which nests are seen exclusively in the epidermis, predominantly at the dermoepidermal junction ( Figs. 2.4 to 2.6 ). Features of a benign junctional melanocytic proliferation include relatively small size, symmetry, ordered growth with relatively even placement of nests, sharp lateral demarcation, and bland cytology. The term lentiginous junctional nevus is used for junctional nevi in which the epidermis has lentigo-like features with elongated and pigmented epidermal rete ridges. In lentiginous nevi, there is typically a proliferation of solitary units and nests. The melanocyte nests are mainly aggregated to the tips of the rete ridges ( Fig. 2.5 ). Other junctional nevi may display a predominance of well-formed nests ( Fig. 2.6 ). In most lesions, there is a mix of solitary units and nests of melanocytes at the dermoepidermal junction. On occasion (e.g., with trauma, acral, or congenital nevi) melanocytes of junctional nevi may also be present in the spinous cell layer ( Table 2.1 ).
Why is it important to examine the junctional nevus?
Careful examination of the individual cells is extremely important in the junctional nevus, because a similar type of focal proliferation of melanocytes (junctional activity) occurs in the early phases of melanoma —a malignant neoplasm composed of atypical melanocytes.
What is lentiginous junctional nevus?
The term lentiginous junctional nevus is used for junctional nevi in which the epidermis has lentigo-like features with elongated and pigmented epidermal rete ridges. In lentiginous nevi, there is typically a proliferation of solitary units and nests.
Where is the junctional nevus located?
Histopathology. The junctional nevus is composed of discrete nests of melanocytes/nevus cells at the dermoepidermal junction, usually located on the rete ridges , which often show some accentuation. The cells are oval to cuboidal in shape, with clear cytoplasm containing a variable amount of melanin pigment.
Is junctional nevi round or oval?
Although most junctional nevi are round, elliptical, or oval and show a relatively uniform pigmentation, some may be slightly irregular in configuration and color. Most junctional nevi represent a transient phase in the development of compound nevi and are found only in children.
