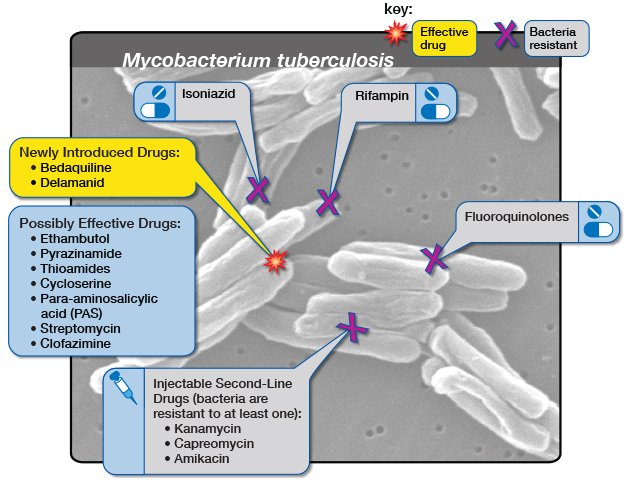
What is kanamycin A used to treat?
Kanamycin A belongs to the family of aminoglycoside antibiotics that target cellular RNA to inhibit bacterial and viral replication. Previous studies have shown that aminoglycosides bind to mammalian but disrupt bacterial membranes.
What is the difference between kanamycin and kanamycin A?
Kanamycin A is the major component of the kanamycin complex, an aminoglycoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces kanamyceticus, with antibacterial activity. Kanamycin A is a member of kanamycins. It has a role as a bacterial metabolite. It is a conjugate base of a kanamycin A (4+).
What type of antibiotic is Kanamycin sulfate?
Kanamycin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces kanamyceticus. It is D-Streptamine, 0-3-amino-3-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl - (1→6)-0- [6-amino-6-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl - (1→4)]-2-deoxy, sulfate 1:1 (salt).
What is the conjugate base of kanamycin A 4+?
It is a conjugate base of a kanamycin A (4+). Kanamycin (also known as kanamycin A) is an aminoglycoside bacteriocidal antibiotic, available in oral, intravenous, and intramuscular forms, and used to treat a wide variety of infections.
See 5 key topics from this page & related content

Does kanamycin target protein synthesis?
Mechanism. Kanamycin works by interfering with protein synthesis. It binds to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome.
What does kanamycin do to bacteria?
Kanamycin injection is used to treat serious bacterial infections in many different parts of the body. This medicine is for short-term use only (usually 7 to 10 days). Kanamycin belongs to the class of medicines known as aminoglycoside antibiotics. It works by killing bacteria or preventing their growth.
What is kanamycin mode of action?
Kanamycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat different types of bacterial infections. Kanamycin works by binding to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit, causing misreading of mRNA and leaving the bacterium unable to synthesize proteins vital to its growth.
How does kanamycin act on E coli?
kanamycin binds the decoding region at the 3' end of rRNA which may prevent tRNA from binding to the ribosomal A site [5]. This results in inhibition of protein translation by preventing protein elongation.
What bacteria is kanamycin resistant?
In Escherichia coli, mutations at positions 1408, 1409, and 1491 (equivalent to positions 1400, 1401, and 1483 of M. tuberculosis, respectively) caused resistance to kanamycin, paromomycin, and other aminoglycoside antibiotics (9, 20).
Is E coli resistant to kanamycin?
Kanamycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, can inhibit the peptide synthesis of E. coli by blocking the translocation process (Semenkov et al. 1982).
Is kanamycin the same as ampicillin?
The inhibition blocks the binary fission and leads to cell lysis, ampicillin is a BACTERICIDAL agent. On the other side kanamycin inhibits the protein synthesis by blocking the 30s subunit of the ribosome. Kanamycin acts as an BACTERISTATIC agent it arrests the growth and proliferation of cells.
Is kanamycin bacteriostatic or bactericidal?
Both kanamycin (t½ 2–4 h) and amikacin (t½ 2–4 h) are bactericidal drugs of the aminoglycoside class, valuable in patients with resistance to streptomycin.
Is kanamycin an antifungal?
A simple structural modification turns the clinically obsolete antibacterial kanamycin into an antifungal agent. Structure–activity relationship studies have led to the production of K20, an antifungal kanamycin that can be mass-produced for uses in agriculture as well as in animals.
What does the kanamycin resistance gene code for?
All hybrid plasmids contain the promoterless part of kanamycin resistance gene (which codes for aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase II) from transposon Tn5.
Is tetracycline and kanamycin same?
Kanamycin interacts with the 30S ribosomal subunit resulting in a significant amount of mistranslation and prevents translocation during protein synthesis [27, 28], whereas tetracyclines bind to the 16S part of the 30S ribosomal subunit and prevent amino-acyl tRNA to attach at A-site of mRNA-ribosome complex, ...
What bacteria do aminoglycosides cover?
Aminoglycosides are useful primarily in infections involving aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, and Enterobacter. In addition, some Mycobacteria, including the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, are susceptible to aminoglycosides.
Is kanamycin bacteriostatic or bactericidal?
Both kanamycin (t½ 2–4 h) and amikacin (t½ 2–4 h) are bactericidal drugs of the aminoglycoside class, valuable in patients with resistance to streptomycin.
Is kanamycin an antifungal?
A simple structural modification turns the clinically obsolete antibacterial kanamycin into an antifungal agent. Structure–activity relationship studies have led to the production of K20, an antifungal kanamycin that can be mass-produced for uses in agriculture as well as in animals.
Why is it necessary to grow the cells on plates containing kanamycin?
The presence of kanamycin in the media prevents all these other bacteria from growing and allows you to select only those containing the kanamycin resistance gene. Each bacterial cell that received a plasmid should grow up into a bacterial colony on a petri dish containing kanamycin media.
What does ampicillin do to bacteria?
Ampicillin is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It is a penicillin-type antibiotic. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections.
What is kanamycin injection?
Kanamycin injection is indicated in the short-term treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms below. Bacteriological studies to identify the causative organisms and to determine their susceptibility to Kanamycin should be performed. Therapy may be instituted prior to obtaining the results of susceptibility testing.
Why is kanamycin used in medicine?
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Kanamycin Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Kanamycin Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Why is it important to monitor renal function with kanamycin?
Because of high concentrations of Kanamycin in the urinary excretory system, patients should be well hydrated before treatment to prevent irritation of the renal tubules.
How long does it take for kanamycin to be absorbed?
The drug is rapidly absorbed after intramuscular injection and peak serum levels are generally reached within approximately one hour. Doses of 7.5 mg/kg give mean peak levels of 22 mcg/mL. At 8 hours following a 7.5 mg/kg dose, mean serum levels are 3.2 mcg/mL. The serum half-life is 2 1/2 hours. Intravenous administration of Kanamycin over a period of one hour resulted in serum concentrations similar to those obtained by intramuscular administration.
What nerves does Kanamycin affect?
As with other aminoglycosides, the major toxic effects of Kanamycin are its action on the auditory and vestibular branches of the eighth nerve and the renal tubules. Neurotoxicity is manifested by bilateral auditory toxicity which often is permanent and, sometimes, by vestibular ototoxicity. Loss of high frequency perception usually occurs ...
How long does kanamycin stay in your system?
The serum half-life is 2 1/2 hours. Intravenous administration of Kanamycin over a period of one hour resulted in serum concentrations similar to those obtained by intramuscular administration. Kanamycin diffuses rapidly into most body fluids including synovial and peritoneal fluids and bile.
What is the best way to remove kanamycin from the blood?
In the event of overdosage or toxic reaction, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis will aid in the removal of Kanamycin from the blood. In the newborn infant, exchange transfusion may also be considered.
How is this medicine (Kanamycin) best taken?
Use kanamycin as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
What are some other side effects of Kanamycin?
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if you have any side effects that bother you or do not go away.
How do I store and/or throw out Kanamycin?
If you need to store kanamycin at home, talk with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist about how to store it.
What to do if you have questions about kanamycin?
Check with your pharmacist. If you have any questions about kanamycin, please talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care provider.
What to do if you are allergic to kanamycin?
Tell all of your health care providers that you take kanamycin. This includes your doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and dentists. If you are allergic to sulfites, talk with your doctor. Some products have sulfites. Have blood work checked as you have been told by the doctor. Talk with the doctor.
Can you take kanamycin if you have kidney problems?
Do not use kanamycin if you are taking or have recently taken any drugs that can cause nerve, kidney, or hearing problems. This may be drugs like amphotericin B, bacitracin, cephaloridine, cisplatin, colistin, cyclosporine, ethacrynic acid, furosemide, paromomycin, polymyxin B, vancomycin, viomycin, or other drugs like this one.
Can kanamycin cause hearing loss?
This medicine may cause kidney problems, nerve problems, and hearing problems (like long-lasting hearing loss). This could even happen at normal doses. The risk of these problems may be higher if you already have kidney or hearing problems, if you get high doses of kanamycin, or if you get kanamycin for a long time.
What is kanamycin used for?
Kanamycin A. Kanamycin A, often referred to simply as kanamycin, is an antibiotic used to treat severe bacterial infections and tuberculosis. It is not a first line treatment. It is used by mouth, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle.
How does kanamycin work?
Kanamycin works by interfering with protein synthesis. It binds to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. This results in incorrect alignment with the mRNA and eventually leads to a misread that causes the wrong amino acid to be placed into the peptide. This leads to nonfunctional peptide chains.
What is the main product of Streptomyces kanamyceticus?
Biosynthesis. While the main product produced by Streptomyces kanamyceticus is kanamycin A, additional products are also produced, including kanamycin B, kanamycin C, kanamycin D and kanamycin X. The kanamycin biosynthetic pathway can be divided into two parts.
How long does kanamycin last?
It is used by mouth, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle. Kanamycin is recommended for short-term use only, usually from 7 to 10 days. As with most antibiotics, it is ineffective in viral infections. Common side effects include hearing and balance problems. Kidney problems may also occur.
Why does the Kanamycin pathway split into two branches?
At this point the kanamycin pathway splits into two branches due to the promiscuity of the next enzyme, which can utilize two different glycosyl donors - UDP-N-acetyl-α- D -glucosamine and UDP-α- D -glucose. One of the branches forms kanamycin C and kanamycin B, while the other branch forms kanamycin D and kanamycin X.
Which kanamycin is converted to kanamycin A?
One of the branches forms kanamycin C and kanamycin B, while the other branch forms kanamycin D and kanamycin X. However, both kanamycin B and kanamycin D can be converted to kanamycin A, so both branches of the pathway converge at kanamycin A.
What is the first part of an antibiotic?
The first part is common to several aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as butirosin and neomycin. In it a unique aminocyclitol, 2-deoxystreptamine, is biosynthesized from D -glucopyranose 6-phosphate in four steps.
What is the purpose of a kanamycin A?
Many antibacterial agents need to cross these membranes to reach their target and elicit specific effects. Kanamycin A belongs to the family of aminoglycoside antibiotics that target cellular RNA t …. Biological membranes are natural barriers to the transport of molecules and drugs within human bodies. Many antibacterial agents need ...
What is the family of kanamycin?
Many antibacterial agents need to cross these membranes to reach their target and elicit specific effects. Kanamycin A belongs to the family of aminoglycoside antibiotics that target cellular RNA to inhibit bacterial and viral replication.
What are the functional groups of Kanamycin A?
Both the computational and spectroscopic investigations provide information on specific functional groups involved in kanamycin A-membrane interactions at the molecular level. The MD simulations reveal the importance of hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl and amino groups of the aminoglycoside with specific lipid components of the membranes. The lipid phosphate, ester carbonyl (DMPC, DMPG) and hydroxyl (DMPG, cholesterol) groups were identified to be involved in the binding of the aminoglycoside. Kanamycin A quickly binds to the membrane and adopts a stable configuration within the head groups of the lipid bilayer which maximises its attractive electrostatic interactions. The hydroxyl groups of the aminoglycoside were directed towards the bilayer and formed hydrogen bonds with the phosphate and ester carbonyl groups of the lipids. Additional hydrogen bonds between the kanamycin A amino groups and the lipid ester carbonyl and phosphate groups further stabilised the bound configuration. IR spectroscopy confirmed the relevant role of the ester carbonyl, hydroxyl and phosphate groups of the lipids. Cholesterol, as a component of the mammalian membrane, was less involved in aminoglycoside binding, whereas the anionic DMPG, as negatively charged component of the bacterial membrane, made additional hydrogen bond interactions with kanamycin A. This supports the important role of negatively charged phospholipids for aminoglycoside activity. Differences in hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions and membrane fluidity present an important role for drug-membrane interactions. The bacterial membrane became disordered upon aminoglycoside addition whereas the mammalian membrane became stiffer and more ordered. This might indicate some mechanistic steps for bacterial membrane disruption observed by previous studies [27].
How was the kanamycin system simulated?
The equilibration of the systems was conducted using position restraints for kanamycin A to avoid drug-membrane interactions before the system stabilised. Each simulation was started in a canonical ensemble (NVT) using the Berendsen temperature coupling at 310 K [56]. The system was then run in an isothermal-isobaric ensemble (NPT) introducing the Berendsen semi-isotropic pressure coupling with a reference pressure of 1 bar and a compressibility of 4.5 · 10 − 5 bar. The final simulation was conducted without restraints to study specific kanamycin A-membrane interactions. It was run for 200 ns using the velocity rescale algorithm for temperature coupling [57] and the semi-isotropic Parrinello-Rahman algorithm for pressure coupling [58]. One repetition of each membrane system with 20 kanamycin A molecules was run for a further 800 ns (total 1000 ns).
What is DMPG in bacteria?
The bacterial membrane with DMPG as an anionic component formed more aminoglycoside-membrane interactions than the cholesterol-containing mammalian membrane. It also presented a more disordered membrane structure upon aminoglycoside interaction whereas the mammalian membrane became stiffer and ordered. This could explain the disruption of bacterial membranes previously shown in experimental studies [27], [79], [80]. Differences in membrane composition determine the selectivity of the aminoglycoside. Anionic phospholipids (e.g. DMPG) are typically found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and thus targeted by aminoglycosides [19], [29]. Our study supports the observation that aminoglycoside-resistant bacteria acquire its resistance through modifications and chemical substitutions that lead to an overall decreased negative charge. This results in a lower electrostatic attraction, a reduced sensitivity for cationic agents and thus a lower permeability [3], [13], [34].
How does Kanamycin A interact with the membrane?
Kanamycin A was observed to bind to the polar head groups of the membrane model systems on a short timescale (10 to 30 ns). Since periodic boundary conditions were applied, the aminoglycoside molecules were able to interact with either side of the bilayer. In the case of two aminoglycoside molecules in the system, kanamycin A could randomly bind to the same or opposing faces of the bilayer. After making initial contact with the membrane, the kanamycin A molecules bound and diffused within the head group region of the lipid bilayer, optimising their orientation. Plots of system energy versus time during kanamycin A-membrane binding show an energy decrease, primarily during the first 50 ns (see Fig. S2). The simulations containing one or two kanamycin A molecules presented a complete binding of all aminoglycoside molecules to both the bacterial and mammalian membrane models whereas only around half of the kanamycin A molecules bound to the mammalian membrane in the simulations with twenty aminoglycosides at any given time. This difference in binding for the mammalian membrane model may be attributed to a saturation of the membrane with positive charges of the bound aminoglycosides.
Does kanamycin bind to bacterial membranes?
Previous experimental studies using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) have shown that several aminoglycosides (including kanamycin A) bind to mammalian mimetic membranes without disruption but insert into and disrupt bacterial mimetic membranes, consistent with their antibiotic activity [26], [27], [28]. Clearly, detailed knowledge of the molecular interaction of kanamycin A with bacterial and mammalian membranes will enable the design of more effective and potent therapeutics with reduced toxicity towards mammalian cells.
Is kanamycin a hydroxyl or aminoglycoside?
In this study, we focus on kanamycin A as a representative aminoglycoside. It is an ideal candidate to be studied due to its structure with the hydroxyl and amino groups directed towards opposite sides (see Fig. 1) [11], [14]. This enables conclusions to be drawn about the role of both hydroxyl and amino functional groups for membrane action. Kanamycin A was first isolated from the bacterial species Streptomyces kanamyceticus from Japanese soil in 1957 [15], [16]. It binds to bacterial ribosomes and reduces mRNA translation hence reduces protein biosynthesis [17], [18]. However, it also exhibits some toxic effects towards mammalian cells [19], [20], [21].
Why is antimicrobial drug demand increasing?
The demand for new and potent antimicrobial drugs is rising because existing active substances face increased mutations leading to resistance [1], [2], [3]. Additionally, intense research efforts have been undertaken to develop a cure for viral diseases [4].
Identification
- Summary
1. Kanamycinis an aminoglycoside antibiotic agent used in the treatment of various infections caused by susceptible bacteria. - Generic Name
1. Kanamycin
Pharmacology
- Indication
1. For treatment of infections where one or more of the following are the known or suspected pathogens: E. coli, Proteus species (both indole-positive and indole-negative), E. aerogenes, K. pneumoniae, S. marcescens, and Acinetobacter species.Reduce drug development failure rates…
Interactions
- Drug Interactions information
1. This information should not be interpreted without the help of a healthcare provider. If you believe you are experiencing an interaction, contact a healthcare provider immediately. The absence of an interaction does not necessarily mean no interactions exist. - Food Interactions
1. No interactions found.
Categories
- ATC Codes
1. S01AA24 — Kanamycin
Chemical Identifiers
- UNII
1. EQK9Q303C5 - CAS number
1. 59-01-8
References
- Synthesis Reference
1. Hamao Umezawa, Shinichi Kondo, "Method for production of kanamycin C and its derivatives." U.S. Patent US4120955, issued December, 1975.US4120955 - General References
1. Not Available
Pharmacoeconomics
- Manufacturers
1. Not Available
Properties
- State
1. Solid
Spectra
- Mass Spec (NIST)
1. Not Available