What takes place after karyokinesis?
DNA replication occurs during the S phase; chromosome separation (karyokinesis) takes place during the M phase and is followed by cell division (cytokinesis); G1 and G2 are gap or growth phases when molecules required for DNA replication or mitosis are synthesized.
What happens first karyokinesis or cytokinesis?
The process of cell division during mitosis is called Karyokinesis. Karyokinesis is the first step that occurs during cell division.
What is karyokinesis also called?
Karyokinesis, also known as mitosis, is divided into a series of phases—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—that result in the division of the cell nucleus (Figure 10.2.
What is the correct order of stages in mitosis?
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase, and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis.
What happens when karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis?
If Karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis, then it will lead to multinucleate condition which is also known as “Syncytium”.
What would happen if a cell underwent karyokinesis but not cytokinesis?
The result of mitosis without cytokinesis will be a cell with more than one nucleus. Such a cell is called a multinucleated cell.
Does mitosis include karyokinesis?
Mitosis includes Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis. Karyokinesis is the division of the nucleus that occurs in four stages. They are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and Telophase. During prophase, the chromatin condenses to form chromosomes.
Why is it called karyokinesis?
Hint: The word Karyokinesis consists of two words- 'karyo' i.e. nucleus and 'kinesis' i.e. movement. Karyokinesis is followed by cytokinesis during cell division. Complete answer: Karyokinesis is the process of the division of a cell nucleus during mitosis or meiosis.
What is karyokinesis explain?
During mitosis or meiosis, the process of karyokinesis is the division of cell nucleus. It is succeeded by cytokinesis, which is the splitting of the cytoplasm and cell membrane. Karyokinesis is the process of dividing a cell's nucleus to from to nuclei for the two daughter cells during cell division.
What are the 7 steps of meiosis?
Stages of MeiosisProphase I. The nuclear envelope disintegrates. ... Prometaphase II. Spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes at the centromere.Metaphase I. The homologous chromosomes align at the equatorial plate ensuring genetic diversity among offspring.Anaphase I. ... Telophase I. ... Cytokinesis I. ... Prophase II. ... Metaphase II.More items...
What are the 5 stages of mitosis?
Mitosis is conventionally divided into 5 phases, which include prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase and cytokinesis.
What is the correct sequence of steps in cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).
What are the 5 stages of prophase 1?
Meiotic prophase I is subdivided into five stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
How many stages of karyokinesis are there?
Karyokinesis stage consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. During telophase stage, chromosomes that moved to the poles during anaphase become chromatin reticulum and two daughter nuclei are formed.
What happens during cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the physical process that finally splits the parent cell into two identical daughter cells. During cytokinesis, the cell membrane pinches in at the cell equator, forming a cleft called the cleavage furrow.
How are karyokinesis and cytokinesis connected in plants?
Karyokinesis is followed by the cytokinesis in the mitotic division. In plant cells, the cytoplasm of the parent cell is divided by the formation of a cell plate in the middle of the parent cell. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow is formed by the plasma membrane, separating the two daughter cells.
How does karyokinesis work?
Karyokinesis, in relation to organic life, comprises the division of cells through the transformation of their nucleus, which examines the division by budding, that is, the stem cell develops a protuberance or gem that will originate another cell. Sporulation also gives rise. It is here when the stem cell breaks its nucleus many times and the nucleoli are wrapped in cytoplasm creating spores that are thrown outside. Each will form a new cell. These two techniques are exhibited by single-celled organisms such as yeasts or lower vegetables, such as hydras.
What is the main function of karyokinesis?
Karyokinesis is continuous, uninterrupted, relatively fast, and its main function is to distribute chromosomes evenly among daughter cells. It occurs in four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Why is karyokinesis important?
It means that karyokinesis allows the growth and development of the multicellular organism, body growth and the regeneration of tissues exposed to cell destruction. That is why this complex process allows cells to survive over time, transmitting their characteristics from one generation to another. Day by day the dying cells are replaced.
What are the phases of mitosis?
Answer: The five phases of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
What is the meaning of the word "karyokinesis"?
Therefore, in a biological context, karyokinesis refers to the process by which the nucleus of a cell divides.
What stage of the cell cycle is the spindle disappearing?
Telophase: In this stage The spindle disappears, and nuclear membrane forms again around each group of chromosomes, and a nucleus is repeated in each new nucleus. Chromosomes also begin to condense. In telophase, the cell is almost complete and begins to regain its normal structure while cytokinesis, the segmentation of the cell compound, occurs.
What is the first stage of mitosis?
Also known as mitosis, karyokinesis, astral mitosis, or amphibian mitosis. This is the first stage of mitosis, which involves the precise distribution of genetic material from one stem cell to the two daughter cells.
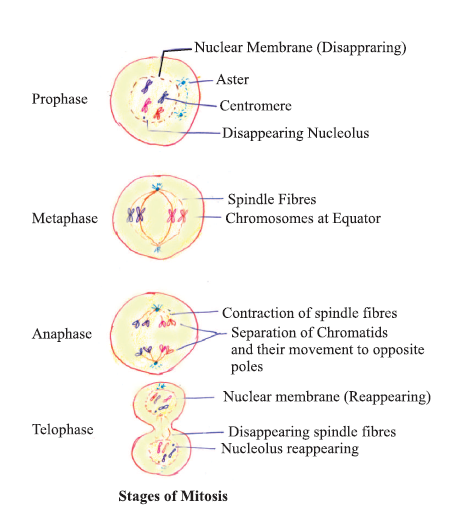
Prophase
The “first phase”. The nuclear envelope starts to dissociate into small vesicles. The Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and other membranous organelles fragment and disperse toward the periphery of the cell. First the nucleolus disappears and then the centrosomes begin to move to opposite poles of the cell.
Prometaphase
The “first change phase”. Many processes that began in prophase continue to advance. Remaining’s of the nuclear envelope fragment. “Mitotic spindle” continues to develop as more microtubules assemble and stretch across the length of the former nuclear area. By coiling more, chromosomes become more condensed and discrete.
Metaphase
The “change phase”. All the chromosomes are aligned on a plane called the metaphase plate, or the equatorial plane, midway between the two poles of the cell. Now also, the sister chromatids are still tightly attached to each other by cohesin proteins. The chromosomes are maximally condensed at this time.
Anaphase
It is the “upward phase”. In this the cohesin proteins degrade, and the sisterchromatids separate at the centromere. Each of the chromatids are now called a chromosome The are pulled rapidly towards the centrosome to which its microtubule is attached.
Telophase
The “distance phase”. The chromosomes reach the opposite poles and begin to decondense (unravel), relaxing into a chromatin configuration. Then the Mitotic spindles are depolymerized into tubulin monomers that will be used to assemble cytoskeletal components for each daughter cell.
What is the third stage of mitosis?
Anaphase (derived from the Greek terms, ἀνά, "up" and φάσις, "stage"), is the third stage of Mitosis after the metaphase.
What are the two processes involved in mitosis?
Mitosis or somatic cell division consists of two processes: Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis.
What is the first stage of cell division?
Prophase (derived from the Greek terms πρό, "before" and φάσις, "stage") is the first stage of cell division in both Mitosis and Meiosis. Beginning after Interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are:
What is Karyokinesis?
Karyokinesis is the step during cell division where the nucleus divides to form two daughter nuclei. It is usually followed by cytokinesis. In this process, the DNA condenses and the chromosomal material divides equally into two halves.
What is the difference between cytokinesis and karyokinesis?
Difference Between Karyokinesis And Cytokinesis. Karyokinesis is defined as the division of the nucleus during the M phase of the cell cycle. It is the first step in M phase. This process does not depend on cytokinesis. It divides the genetic material equally.
Which process occurs before cytokinesis?
Karyokinesis occurs before cytokinesis. The nucleus divides before the cytoplasm.
What is the second step of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis, on the other hand, is defined as the division of the cytoplasm during the M phase of the cell cycle. It is the second step in M phase. This process cannot occur without karyokinesis. It is also the final stage of mitosis, where the cytoplasm and other cell organelles divides between the two daughter cells.
