How many cartilages help stabilize the larynx?
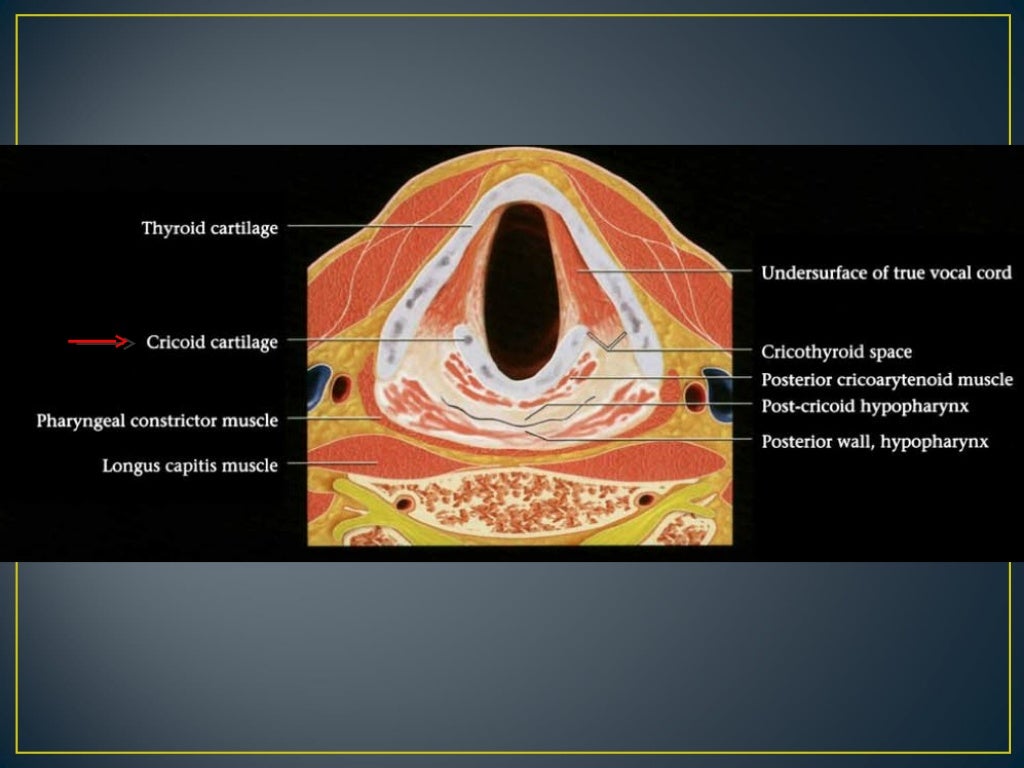
There are nine cartilages located within the larynx; three unpaired, and six paired. They form the laryngeal skeleton, which provides rigidity and stability. In this article, we shall examine the anatomy of the laryngeal cartilages. The three unpaired cartilages are the epiglottis, thyroid and cricoid cartilages.
What every patient should know about laryngeal cancer?
Signs and symptoms of laryngeal cancer include a sore throat and ear pain. These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by laryngeal cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following: A sore throat or cough that does not go away. Trouble or pain when swallowing.
What are the specific types of cartilage in the larnnx?
- Supraglottis - It is located just above the vocal cord which consists of the epiglottis cartilage.
- Subglottis - It is located beneath the vocal cord which consists of the cricoid cartilage.
- Glottis - It is located in the area of the vocal cord.
What type of cartilage is found in the larynx?
There are three types of cartilage:
- Hyaline – most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone.
- Fibro- is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments.
- Elastic – is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.

What is the function of the laryngeal cartilages?
It surrounds and protects the vocal chords, as well as the entrance to the trachea, preventing food particles or fluids from entering the lungs. The cartilages of the larynx make up its skeleton.
What are laryngeal cartilages made of?
The thyroid cartilage is the largest cartilage of the larynx and is composed of hyaline cartilage. It sits beneath the hyoid bone to which it connects by the thyrohyoid membrane. Inferiorly it articulates with the cricoid cartilage.
Where is laryngeal cartilage found?
Where is cartilage located? Almost any place where two bones meet in your body is cushioned by cartilage. It's also at the ends of all your bones that form joints.
What is the laryngeal?
Having to do with the larynx.
What are the 3 parts of the larynx?
The larynx is often divided into three sections: sublarynx, larynx, and supralarynx. It is formed by nine cartilages that are connected to each other by muscles and ligaments. The larynx plays an essential role in human speech.
What is cartilage called?
There are three types of cartilage: hyaline, fibrous, and elastic cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread type and resembles glass. In the embryo, bone begins as hyaline cartilage and later ossifies. Fibrous cartilage has many collagen fibers and is found in the intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis.
What are the 3 types of cartilage and their functions?
There are three types of cartilage:Hyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone.Fibro- is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments.Elastic - is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.
Does cartilage heal?
Sprains and minor cartilage damage may get better on their own within a few days or weeks. More severe cartilage damage probably will not improve on its own. If left untreated, it can eventually wear down the joint.
Why does damaged cartilage heal slowly?
Cartilage Healing Considerations Cartilage is avascular, meaning that it has no blood supply. The lack of blood circulation in cartilage means that it is a very slow-healing type of tissue. Nutrition to cartilage is maintained by fluid in the joints, which lubricates the tissue.
Where is the laryngeal?
Your larynx is inside the middle of your neck, at the level of the Adam's apple. It's located between your fourth to sixth cervical vertebrae (neck bones).
What are the 3 functions of the larynx?
The larynx serves to protect the lower airways, facilitates respiration, and plays a key role in phonation. In humans the protective and respiratory functions are compromised in favor of its phonatory function.
Can you speak without a larynx?
While your throat heals, you'll need to be fed through a tube that's passed through your nose and into your stomach. If you have had all of your larynx removed (total laryngectomy), you will not be able to speak normally, because you'll no longer have vocal cords.
What is an Adam's apple made out of?
The Structure of the Adam's Apple. The Adam's apple is made up of the thyroid cartilage. Cartilage is the same tissue that makes up your nose, ears, and windpipe (i.e., trachea). The voice box and windpipe have several kinds of cartilage, which work together to make sure your airways stay clear and you're able to speak ...
What tissue makes up the larynx?
The inside of the larynx is lined with mucous membrane tissue. Its walls are made of connective tissue, muscles and cartilage. The cartilage provides support and also keeps the larynx elastic. In men, it is clearly visible from outside the body and known as the “Adam's apple.”
What type of cartilage is found in the trachea?
HyalineHyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea.
What type of cartilage is cricoid cartilage?
hyaline cartilage ringThe cricoid cartilage is a hyaline cartilage ring which fully encircles the trachea and composes the inferior-most boundary of the laryngeal skeleton.
Which cartilage is located in the larynx?
There are three paired cartilages - the arytenoid , corniculate and cuneiform. They are situated bilaterally in the larynx. Arytenoid Cartilages. The arytenoid cartilages are pyramidal shaped structures that sit on the cricoid cartilage.
How many cartilages are there in the larynx?
There are nine cartilages located within the larynx; three unpaired, and six paired. They form the laryngeal skeleton, which provides rigidity and stability. In this article, we shall examine the anatomy of the laryngeal cartilages.
What is the only complete circle of cartilage in the larynx or trachea?
The cricoid is the only complete circle of cartilage in the larynx or trachea. This is of clinical relevance during emergency intubation – as pressure can be applied to the cricoid to occlude the oesophagus, and thus prevent regurgitation of gastric contents (known as cricoid pressure or Sellick’s manoeuvre).
What are the three unpaired cartilages?
The three unpaired cartilages are the epiglottis, thyroid and cricoid cartilages. Thyroid Cartilage. The thyroid cartilage is a large, prominent structure which is easily visible in adult males. It is composed of two sheets (laminae), which join anteriorly to form the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple).
What is the epiglottis?
The epiglottis is a leaf shaped plate of elastic cartilage which marks the entrance to the larynx. Its ‘stalk’ is attached to the back of the anterior aspect of the thyroid cartilage. During swallowing, the epiglottis flattens and moves posteriorly to close off the larynx and prevent aspiration.
What is the thyroid cartilage?
The thyroid cartilage is a large, prominent structure which is easily visible in adult males. It is composed of two sheets (laminae), which join anteriorly to form the laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple).
Where is the epiglottis located when swallowing?
Its 'stalk' is attached to the back of the anterior aspect of the thyroid cartilage. During swallowing, the epiglottis flattens and moves posteriorly to close off the larynx and prevent aspiration. There are three paired cartilages - the arytenoid, corniculate and cuneiform. They are situated bilaterally in the larynx.
What are the cartilaginous components of the larynx?
The final cartilaginous components of the larynx are the two small club-shaped cuneiform cartilages that lie superior and anterior to the corniculate cartilages. They do not directly attach to any other laryngeal cartilage but are suspended within and strengthen a fibro-elastic membrane called the aryepiglottic membrane. This membrane forms the free superior edge of the quadrangular membrane, which as described earlier, connects the arytenoid cartilages to the lateral borders of the epiglottis. It is covered by mucosa to form the aryepiglottic fold. On the posterior aspect of the aryepiglottic folds both the corniculate and cuneiform cartilages are seen as small nodules surrounding the laryngeal inlet.
How many cartilages are there in the larynx?
The larynx is composed of three large unpaired cartilages (cricoid, thyroid, and epiglottis) and three paired smaller cartilages (arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform), making a total of nine individual cartilages. The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the laryngeal cartilages and is composed of hyaline cartilage.
What is attached to the apices of the arytenoid cartilage?
Attached to the apices of the arytenoid cartilage are the small, paired and conical- shaped corniculate cartilages. The last unpaired cartilage, the epiglottis, is a large leaf-shaped elastic cartilage that is covered by mucous membrane.
Where is the epiglottis located?
As its name suggests (epi = above, glottis = mouth of windpipe), it sits above the laryngeal opening (inlet). During swallowing, as the larynx moves up and forwards, the epiglottis swings downward to close off the laryngeal inlet, and thus prevents materials from entering the airway.
Which part of the larynx is a V-shaped projection?
It forms the anterior and lateral portions of the larynx and has no posterior component. The broad flat right and left halves (laminae) of the cartilage fuse anteriorly in the midline to form a V-sha ped anterior projection called the laryngeal prominence (commonly called the “Adam’s apple”).
Where is the cricoid cartilage located?
The cricoid cartilage is a much smaller signet ring-shaped hyaline cartilage located directly below the thyroid cartilage. It forms the inferior aspect of the larynx and is connected to the trachea inferiorly. It is the only complete ring of cartilage that encircles the airway.
What is the organ of phonation?
It is commonly referred to as the “voice box” or the “organ of phonation” as it houses the structure responsible for sound production. It is quite mobile in the neck and can be seen and felt moving upward and forward during swallowing, closing off the trachea and opening the esophagus. Key facts about the larynx.
What is laryngeal cancer?
Laryngeal cancer is cancer of the larynx, part of the throat. Cancer happens when specific cells grow uncontrollably. As the cells multiply, they invade and damage the body. In laryngeal cancer, these cancerous (malignant) cells start in the larynx (voice box). Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Where is the larynx located?
The larynx is in your throat. It’s also known as the voice box. The larynx helps us speak, breathe and swallow. Our vocal cords are part of the larynx.
What is the difference between laryngeal cancer and advanced laryngeal cancer?
Early laryngeal cancer: In stages 0, 1 and 2, the tumor is small. Cancer has not spread beyond the larynx. Advanced laryngeal cancer: In stages 3 and 4, the tumor has grown larger. It’s affected the vocal cords or invaded the lymph nodes or other areas of the body.
What percentage of laryngeal cancer starts with a supraraglottis?
Supraglottis (upper part): More than one in three laryngeal cancers (35%) start here.
How long does it take for laryngeal cancer to come back?
But even advanced laryngeal cancer can be cured. If it comes back, it usually happens within the first two or three years after treatment. After five years, there’s very low risk of cancer returning.
How many people die from laryngeal cancer each year?
Laryngeal cancer is part of a group of head and neck cancers. Every year, approximately 13,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with laryngeal cancer. About 3,700 people die from it each year.
What is the name of the cancer that causes a sore throat and a sore throat?
Laryngeal Cancer. Laryngeal cancer is cancer of the larynx, or voice box. Laryngeal cancer symptoms include voice changes, such as hoarseness, and a sore throat or cough that doesn’t go away. Treatment may include surgery to remove part or all of the larynx, called a laryngectomy. You can reduce your risk of laryngeal cancer by avoiding tobacco ...
How many laryngeal cartilages are there?
There are 9 laryngeal cartilages: 3 paired and 3 unpaired
Where is the cricoid cartilage?
Just below the vocal cords at the cricoid cartilage
What is the role of the larynx in swallowing?
Protects the larynx from foreign body entry. During swallowing or laryngospasm, elevation of the larynx closses the epiglottis, sealing off the trachea
