What are the three functions of the larynx?
- The larynx helps provide smooth passage of air from the nasal cavity to the lungs
- Air enters through the nose and mouth when a person inhales, and travels through the pharynx, larynx, and bronchi
- When a person is breathing normally, the vocal cords are relaxed and partly open
What does the larynx do to help the body function?
Your larynx is made of:
- The cartilage that gives it structure.
- Ligaments that connect the areas of cartilage and attach your larynx to nearby structures.
- Membranes, which also help hold cartilage together.
- Muscles, which move your larynx while swallowing, help with breathing and produce vocal sounds.
What does the larynx do in the digestive system?
It acts as a switch between the larynx and the esophagus to permit air to enter the airway to the lungs and food to pass into the gastrointestinal tract. The epiglottis also protects the body from choking on food that would normally obstruct the airway.
What is the structure and function of the larynx?
larynx, also called voice box, a hollow, tubular structure connected to the top of the windpipe (trachea); air passes through the larynx on its way to the lungs. The larynx also produces vocal sounds and prevents the passage of food and other foreign particles into the lower respiratory tracts. The larynx is composed of an external skeleton of cartilage plates that prevents collapse of the structure.
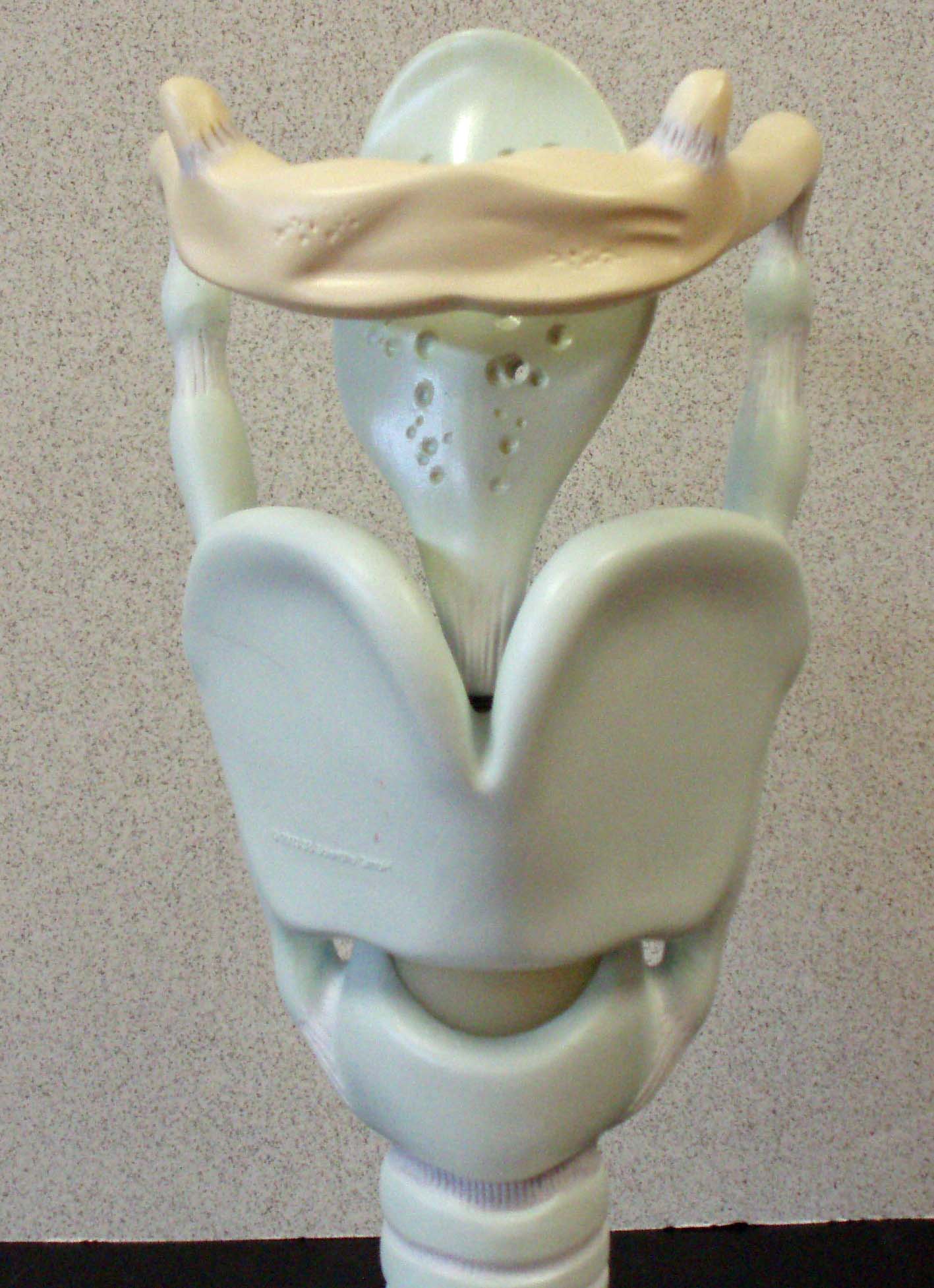

What is larynx short answer?
What is the larynx? Your larynx is part of your respiratory system. It's a hollow tube that lets air pass from your throat (pharynx) to your trachea on the way to your lungs. It also contains your vocal cords and is essential to human speech, so it's often called the voice box.
Where is a larynx?
neckThe larynx is a cartilaginous segment of the respiratory tract located in the anterior aspect of the neck. The primary function of the larynx in humans and other vertebrates is to protect the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing.
What is larynx Class 11?
Larynx is a hollow, tubular structure connected to the top of the trachea (windpipe). It serves as a passage for air to the lungs. Epiglottis a cartilaginous flap that covers the opening of Larynx & prevents the entry of food into the air passage. Complete answer: The larynx is known as a voice box or glottis.
What are the 3 parts of the larynx?
The larynx is often divided into three sections: sublarynx, larynx, and supralarynx. It is formed by nine cartilages that are connected to each other by muscles and ligaments. The larynx plays an essential role in human speech.
What is larynx and its function?
larynx, also called voice box, a hollow, tubular structure connected to the top of the windpipe (trachea); air passes through the larynx on its way to the lungs. The larynx also produces vocal sounds and prevents the passage of food and other foreign particles into the lower respiratory tracts.
Can you swallow without a larynx?
The connection between the mouth and the esophagus is usually not affected, so food and liquid can be swallowed just as they were before the operation. Removal of the vocal cords means that a laryngectomy patient will no longer have laryngeal speech.
Is larynx a bone?
The laryngeal skeleton consists of nine cartilages: three single (epiglottic, thyroid and cricoid) and three paired (arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform). The hyoid bone is not part of the larynx, though the larynx is suspended from the hyoid.
What is throat larynx?
larynx (plural larynges or larynxes) (anatomy, zootomy) A hollow muscular organ of the neck of mammals situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the oesophagus. It is involved in breath control and protection of the trachea, and, because it houses the vocal cords, sound production.
What is pharynx in simple words?
(FAYR-inx) The hollow tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and ends at the top of the trachea (windpipe) and esophagus (the tube that goes to the stomach). The pharynx is about 5 inches long, depending on body size. Also called throat.
Does larynx produce sound?
The larynx, or voice box, is located in the neck and performs several important functions in the body. The larynx is involved in swallowing, breathing, and voice production. Sound is produced when the air which passes through the vocal cords causes them to vibrate and create sound waves in the pharynx, nose and mouth.
Does the larynx move?
Movement of the larynx is controlled by two groups of muscles. The muscles that move the vocal folds and other muscles within the larynx are called the intrinsic muscles. The position of the larynx in the neck is controlled by a second set call the extrinsic muscles.
Is the larynx the Adam's apple?
You can find your larynx by touching the front of your throat and humming. When you feel vibrations under your fingers, you've found it! When the larynx grows larger during puberty, it sticks out at the front of the throat. This is what's called an Adam's apple.
Where is larynx pain?
It's the medical term for a sore throat. Your pharynx starts behind your nose and ends just above your voice box. Laryngitis refers to an inflamed larynx, or voice box. Your larynx is near your pharynx, just above your windpipe.
What causes larynx pain?
Risk factors for laryngitis include: Having a respiratory infection, such as a cold, bronchitis or sinusitis. Exposure to irritating substances, such as cigarette smoke, excessive alcohol intake, stomach acid or workplace chemicals. Overusing your voice, by speaking too much, speaking too loudly, shouting or singing.
Can you live without a larynx?
If you have had all of your larynx removed, the surgeon will need to create a permanent hole in your throat (a stoma) through which you will breathe. During the first few months after surgery, it's likely that your stoma will produce a lot of mucus, particularly if you have had radiotherapy.
How do you test your larynx?
The simplest form of laryngeal examination is called "indirect laryngoscopy". The examiner can place a small mirror in the back of the throat and angle it down towards the larynx. Light can be reflected downward and the larynx can be seen in the mirror.
Where is the larynx located?
The larynx is a small structure of cartilage that connects the throat to the windpipe. It is found in the front of the neck and houses the vocal cords, producing speech sounds and contributing to respiration. . Many conditions can affect it, including laryngitis.
How big is the larynx?
The larynx is about 4–5 centimeters in length and width. Trusted Source. . Many conditions can affect it, including laryngitis. This article will explore the location, anatomy, and purpose of the larynx. It will then list and explain several conditions that can affect it.
What is the tube shaped passageway that connects the throat (pharynx) to the windpipe (?
The larynx is a tube-shaped passageway that connects the throat (pharynx) to the windpipe (trachea).
Where is the epiglottis?
As a person matures, the larynx shifts backward and down the throat. In adulthood, it sits about halfway down the neck below the epiglottis and above the trachea, also known as the windpipe.
What is the cricoid cartilage?
Cricoid cartilage: This structure is also known as the cricoid ring. It forms a closed circle at the bottom of the larynx.
What are the soft tissue folds in the larynx?
Soft tissue folds. Finally, the hollow area inside the larynx contains two types of soft tissue folds: Vestibular folds: Also known as false vocal cords, these sit on top of the vocal folds and protect the larynx. As their name suggests, these folds do not produce sound.
What are the ligaments and membranes in the larynx?
Ligaments and membranes in the larynx include: Extrinsic ligaments and membranes: These ligaments and membranes attach the upper portion of the larynx to the hyoid bone and the lower part to the trachea. They sit on the outside of the larynx.
Overview
Your larynx is part of your respiratory system. It’s a hollow tube that lets air pass from your throat (pharynx) to your trachea on the way to your lungs. It also contains your vocal cords and is essential to human speech, so it’s often called the voice box.
Care
Many strategies can help you protect your larynx and voice, including:
Frequently Asked Questions
If you have certain symptoms that don’t go away or keep coming back, you should talk to a healthcare provider. They include:
What is the larynx made of?
The larynx is a complex band of cartilage, ligament , and muscle as well as a mucous membrane. A hollow structure, it’s formed of three large sections of cartilage that are unpaired—the thyroid, cricoid, and epiglottis—as well as six smaller cartilages. Here’s a quick breakdown of the large cartilages: 1
How many branches does the larynx have?
The primary laryngeal nerve has been observed to split into two or three branches, which affects where it accesses different structures, such as the cricothyroid joint. 2 These differences can have serious implications in surgery.
What is the voice box?
Commonly called the voice box, the larynx is located on top of the neck and is essential for breathing, vocalizing, as well as ensuring food doesn’t get stuck in the trachea and cause choking. Sitting just in front of the esophagus, the vocal folds are located here, making this organ absolutely vital for phonation (making speech sounds). 1 It visibly moves up and down when people swallow. This part of the body can be subject to a number of significant medical conditions, including bacterial infection (laryngitis), laryngeal cancer, and vocal fold paralysis (VFP), which can seriously compromise function.
Which membrane connects the arytenoid cartilage to the epiglottic cartilage?
Finally, there are a couple free-hanging cartilages, the cuneiform cartilages, located in a membrane called the aryepiglottic membrane, which represents the upper margin of the membrane that connects the arytenoid cartilages to the epiglottic cartilage. 1 This is covered in mucus and forms a structure called the aryepiglottic fold.
Which cartilage is the largest in the larynx?
Thyroid cartilage: This largest cartilage in the larynx composes the front and side portions of its structure. The right and left halves (laminae) fuse in the midline to create a projection forward—the laryngeal prominence, which is commonly known as the Adam’s apple.
How long does larynx inflammation last?
This inflammation of the larynx can be chronic—that is, lasting over three weeks —or acute, with the former being more common. Symptoms of this condition include hoarse voice, pain, couching, and, in some cases, fever. Acute laryngitis is often the result of either viral or bacterial upper respiratory tract infection, with a significant number of cases resulting from fungal growth. Chronic cases tend to be the result of smoking, allergies, or stomach acid reflux. Those who use their voices often, such as singers, teachers, and those in other professions, may experience inflammation of the larynx due to overuse.
What are the conditions that affect the vocal fold?
This part of the body can be subject to a number of significant medical conditions, including bacterial infection (laryngitis), laryngeal cancer, and vocal fold paralysis (VFP), which can seriously compromise function. SEBASTIAN KAULITZKI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images.
Where is the larynx located?
The ‘Adam's apple’ or voice box. The larynx is situated at the upper end of the wind-pipe ( TRACHEA ), just in front of the start of the gullet ( OESOPHAGUS ). At its inlet is a leaf-shaped flap of cartilage, the EPIGLOTTIS, that prevents entry of swallowed food.
What is the cavity of the larynx?
The cavity within the larynx comprises three consecutive chambers. The first chamber, the vestibule of the larynx, is a tube between the pharynx and a pair of folds, the vestibular folds (the "false vocal cords"), that protrude into the larynx. The second chamber, the ventricle of the larynx, is a short segment between the vestibular folds and the vocal folds; the ventricle has lateral recesses extending laterally under the vestibular folds. The third chamber, the infraglottic cavity (infraglottic larynx, subglottic space), is a tube between the vocal folds and the trachea.
What are the three paired cartilages in the larynx?
The three smaller paired cartilages are: the arytenoids, the corniculates, and the cuneiforms. These nine cartilages are held together by membranes and ligaments, usually named by the structures that are interconnected; for example, the cricothyroid membrane connects the front of the cricoid cartilage with the base of the thyroid cartilage in the midline.
How many cartilages are in the larynx?
The larynx is composed of nine cartilages that are held together by muscles and ligament: the single thyroid, cricoid, and epiglottic cartilages and the paired arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform cartilages. (See also color plates.) The largest of these, the thyroid cartilage, forms the Adam's apple, which protrudes in the front of the neck.
Which region of the throat contains vocal cords?
larynx. The region of the throat between the pharynx (tip of the epiglottis) and trachea (cricoid cartilage) which contains the vocal cords and is involved in breathing, swallowing, and speech. • Superolateral boundary—Tip of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds. • Inferior limit—Inferior rim of the cricoid cartilage.
How many specimens of larynx were obtained from embalmed cadavers of a tert?
Sixty specimens (51 males and 9 females) of apparently healthy larynxwere obtained from embalmed cadavers of a tertiary care teaching institute.
What is the flap that closes the larynx?
The epiglottis, a flap or lid at the base of the tongue, closes the larynx as it is lifted up during swallowing and so prevents passage of food or drink into the larynx and trachea. Larynx. artificial larynx an electromechanical device that enables a person after laryngectomy to produce speech.
Where is the larynx located?
Where is the Larynx (Voice Box) Located. The flexible structure is located at the anterior side of the neck, in front of the pharynx and above the windpipe [2]. Suspended from the hyoid bone, it extends from C3 to C6, opening into the laryngeal portion of the pharynx [3]. Larynx Diagram.
What is the larynx made of?
Anatomy of the Larynx. It is made up of multiple pieces of tough cartilage, surrounded and held together by fibrous tissues, membranes, and ligaments [3]. The largest cartilaginous segment is called the thyroid cartilage, with a prominent bulging known as Adam’s apple. The semicircular structure has a raised ridge on its anterior surface, ...
What is the voice box?
The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is a 2-inch long cartilaginous tube connecting the back of the nose ( pharynx) and the windpipe ( trachea) with each other. It is one of the most important structures of the respiratory system, also playing a crucial role in the production of speech in humans [1].
What is the function of the epiglottis?
Once the food passes into the esophagus, the epiglottis goes back to its original position to facilitate the passage of air [1]. Function in speech production: There are two pairs of vocal folds (mucous membrane structures) in the larynx, the false vocal folds and the true vocal folds.
What is the part above the vocal cords called?
Supraglotti s: The part above the vocal cords, containing the epiglottis [4] Glottis: The area consisting the vocal cords or folds; there are two pairs of vocal folds (mucous membrane structures) in the larynx, the false vocal folds and the true vocal folds [5]. The former is covered with respiratory epithelium, ...
Where does the inferior laryngeal artery enter the larynx?
Inferior laryngeal artery: Originating from the inferior thyroid artery (that arises from the thyrocervical trunk), it enters the larynx through the space between the trachea and esophagus, alongside the recurrent laryngeal nerve [2].
What is the function of the voice box?
Another primary function of the voice box is producing sounds and speech. Function in the respiratory system: Providing smooth passage of air from the nasal cavity to the lungs. During inhalation, air enters through ...
