Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switch
| Item | Layer 2 Switch | Layer 3 Switch |
| Routing Function | Mac address only | Supports higher routing such as static r ... |
| VLAN Tagging Based on IP Address | No | Yes |
| Inter-VLAN | No | Yes |
| Using Scenario | Pure Layer 2 domain | Aggregate multiple access switches |
Are Layer 3 switches faster than routers?
Within the LAN environment, a Layer 3 switch is usually faster than a router because it is built on switching hardware. In fact, many of Cisco's Layer 3 switches are actually routers that operate faster because they are built on "switching" hardware with customized chips inside the box.
Can a layer 3 switch be used as a router?
Simply put, a layer 3 switch combines the functionality of a switch and a router. It acts as a switch to connect devices that are on the same subnet or virtual LAN at lightning speeds and has IP routing intelligence built into it to double up as a router.
How are Layer 2 switches similar to Layer 3 switches?
Unmanaged Switch
- The unmanaged switch is a simple device with multiple LAN ports to connect the different device in the network.
- It is a plug and plays device and its interfaces are always active.
- Its port is not user-configurable.
- It has a fixed QoS to ensure it’s working well.
- It works at layer 2 of the OSI Model.
- It can maintain only a dynamic mac table.
Can you convert a layer 3 switch to Layer 2?
Yes, so here's a hypothetical example: Staff from accounting department is spread all over the building so this clients are all in VLAN 3 and VLAN 3 is configgured on every switch. <-- So this is layer 2 topology. But if I get more switches (with 200 ports per switch) and therefore more clients per VLAN, should this topology still be layer 2?

What is a Layer 2 router?
Layer 2 of the OSI model is known as the data link layer. The Layer 2 protocol you're likely most familiar with is Ethernet. Devices in an Ethernet network are identified by a MAC (media access control) address, which is generally hardcoded to a particular device and doesn't normally change.
What are Layer 2 routing protocols?
Layer 2 protocols or network L2 protocols are a list of communication protocols used by Layer 2 devices (such as network interface cards (NIC), switches, multiport bridges, etc.) to transfer data in a wide area network, or between one node to another in a local area network.
CAN Layer 2 switch do routing?
The layer 2 and Layer 3 differs mainly in the routing function. A Layer 2 switch works with MAC addresses only and does not care about IP address or any items of higher layers. Layer 3 switch, or multilayer switch, can do all the job of a layer 2 switch and additional static routing and dynamic routing as well.
What is Layer 2 Layer?
Layer 2 refers to a secondary framework or protocol that is built on top of an existing blockchain system. The main goal of these protocols is to solve the transaction speed and scaling difficulties that are being faced by the major cryptocurrency networks.
What is Layer 2 and Layer 3 networks?
A Layer 2 switch only works with MAC addresses and doesn't interact with any higher layer addresses, like an IP. A Layer 3 switch, on the other hand, can also do static routing and dynamic routing, which includes IP and virtual local area network (VLAN) communications.
Is a router Layer 2 or 3?
The most common Layer 3 device used in a network is the router. A router is able to look into the Layer 3 portion of traffic passing through it (the source and destination IP addresses) to decide how it should pass that traffic along.
Is VLAN a Layer 2?
VLANs are data link layer (OSI layer 2) constructs, analogous to Internet Protocol (IP) subnets, which are network layer (OSI layer 3) constructs. In an environment employing VLANs, a one-to-one relationship often exists between VLANs and IP subnets, although it is possible to have multiple subnets on one VLAN.
What is the difference between Layer 2 switch and router?
Layer 2 Switch Vs Router A switch learns all the MAC addresses of all the hosts connected to it in order to pass traffic between hosts in Layer 2. Routers on the other hand allow us the ability to take different networks and pass traffic to one another in Layer 3.
How does a Layer 2 switch differ from a router?
How does a layer-2 switch differ from a router? A layer-2 switch operates at the data link layer, and a router operates at the network layer.
What is the difference between layer 1 and Layer 2?
The term “Layer-1” refers to the basic main blockchain architecture. Layer-2, on the other hand, is a network that appears at the top of the underlying blockchain. Consider the Lightning Network and Bitcoin.
What is L2 VLAN and L3 VLAN?
I answered them, Layer 2 VLAN is a single broadcast domain. It works on layer 2 (Datalink Layer). They can communicate only within it. And L3 VLAN is an Interface, that works on Network Layer. In order to do inter VLAN routing/ communication we need L3 interface (SVI).
What is Layer 2 switching in networking?
A layer 2 switch is a type of network switch or device that works on the data link layer (OSI Layer 2) and utilizes MAC Address to determine the path through where the frames are to be forwarded. It uses hardware based switching techniques to connect and transmit data in a local area network (LAN).
What Does Layer 2 Mean?
Layer 2 refers to the second layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model, which is the data link layer.
Techopedia Explains Layer 2
Layer 2 provides the procedural and functional means for data transfer between network nodes and provides the means to detect and correct errors that may occur at the physical layer (Layer 1).
What layer of network is needed for enterprise?
Building enterprise networks with routers and switches requires interoperability of key protocols at Layer 2 and Layer 3. Without them, the network falls apart; with them, it’s a finely tuned and reliable service.
Why is STP layer 3?
While Layer 2 protocols such as STP operate within a LAN environment, routing between subnets requires Layer 3 dynamic routing to minimize management costs and maximize network uptime. Many dynamic routing protocols are being used, but most organizations rely on two for their internal routing of IP traffic: OSPF and Cisco Systems’ proprietary Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP).
Do OSPF routers have peering relationships?
In contrast, OSPF routers usually communicate without a specifically defined peering relationship (such as across a LAN), and the route interpretation rules are handled on a more macro scale, not one by one.
What are the parameters to check when buying a layer 2 switch?
If you are buying a Layer 2 or Layer 3 switch, there are some key parameters that you should check out, including the forwarding rate, backplane bandwidth, number of VLANs, memory of MAC address, latency, etc.
What is the difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3?
The main difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 is the routing function. This is also the biggest difference lies between Layer 2 switch and Layer 3 switch. A Layer 2 switch works with MAC addresses only and does not care about IP address or any items of higher layers. A Layer 3 switch, or multilayer switch, can do all the job ...
How many VLANs are needed for a Layer 2 switch?
Other important parameters are number of VLANs that can be configured. Generally, 1K = 1024 VLANs is enough for a Layer 2 switch, and the typical number of VLANs for Layer 3 switch is 4k = 4096. Memory of MAC address table is the number of MAC addresses that a switch can keep, usually expressed as 8k or 128k. Latency is the delay time that a data transfer suffers. It requires to be as short as possible, so the latency is usually expressed in nanosecond (ns).
What is the backplane bandwidth?
The next parameter is the backplane bandwidth or switch fabric capacity, which is the sum of speeds of all ports. The sum of speeds of all ports are counted twice, one for Tx direction and one for Rx direction. Backplane bandwidth is expressed in bits per second (bps or bit/s).
Can you use a layer 2 switch with a layer 3 switch?
When lingering between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches, you should think about where it will be used. If you have a pure Layer 2 domain , you can simply go for Layer 2 switch. A pure Layer 2 domain is where the hosts are connected, so a Layer 2 switch will work fine there. This is usually called access layer in a network topology.
What layer of OSI is routing?
Routing operates at layer 3 , where packets are sent to a specific next-hop IP address, based on destination IP address. Devices in the same layer 2 segment do not need routing to reach local peers. What is needed however is the destination MAC address which can be resolved through the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) as illustrated below:
Why use a layer 2 switch?
Large layer 2 broadcast domains can be susceptible to certain unintended problems, such as broadcast storms, which have the ability to cause network outages. Also, it may be preferable to separate certain clients into different broadcast domains for security and policy reasons. This is when it becomes useful to configure VLANs. A layer 2 switch can assign VLANs to specific switch ports, which in turn are in different layer 3 subnets, and therefore in different broadcast domains. VLANs allow for greater flexibility by allowing different layer 3 networks to be sharing the same layer 2 infrastructure. The image below shows an example of a multi-VLAN environment on a layer 2 switch:
What layer is broadcast traffic in?
Broadcasts are contained in the same layer 2 segment, as they do not traverse past a layer 3 boundary.
When you enable ip routing ip default-gateway command is ignored?
When you enable ip routing ip default-gateway command is ignored as this works only with L2 devices and you need to have a default route (which points to core switch) to have ip reachability to your 2960 switch.
What VLAN is used for 2960?
If you have a defualt route on you 2960 which point to your core that is all you need for your device to be accessed from any VLAN. Also if you are using vlan 25 as managment on 2960 then this vlans has to be trunked all the way to core for your 2960 to reach its gateway.
Is Cisco hosting the IT Blog Awards 2021?
The 2021 IT Blog Awards, hosted by Cisco, is now open for submissions. Submit your blog, vlog or podcast today. For more information, including category details, the process, past winners and FAQs, check out: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/t... view more
Can a 2960 switch be accessed from a LAN?
Thanks. So if ip routing is enabled on this switch, the 2960 shouldn't be accessible from the lan network ( assuming the administrative workstation is connected on vlan 15 with ip 1.1.15.15 & the 2960 has management vlan 25 with ip 2.2.2.25.
What is routing protocol?
A routing protocol is a protocol used for identifying or announcing network paths. The following protocols help data packets find their way across the Internet: IP: The Internet Protocol (IP) specifies ...
What is network routing?
Network routing is the process of selecting a path across one or more networks. The principles of routing can apply to any type of network, from telephone networks to public transportation. In packet-switching networks, such as the Internet, routing selects the paths for Internet Protocol (IP) packets to travel from their origin to their ...
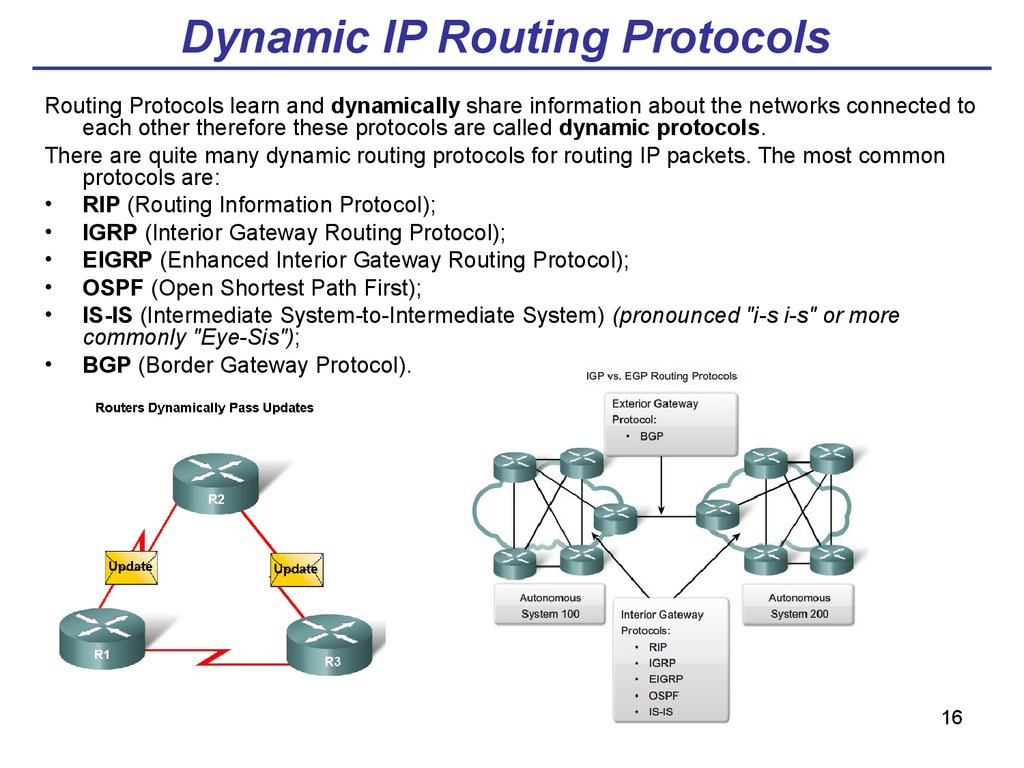
What is BGP routing?
BGP: The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing protocol is used to announce which networks control which IP addresses, and which networks connect to each other. (The large networks that make these BGP announcements are called autonomous systems .) BGP is a dynamic routing protocol. The below protocols route packets within an AS:
What is a router table?
Routers refer to internal routing tables to make decisions about how to route packets along network paths. A routing table records the paths that packets should take to reach every destination that the router is responsible for. Think of train timetables, which train passengers consult to decide which train to catch. Routing tables are like that, but for network paths rather than trains.
How does Cloudflare Argo work?
Cloudflare Argo uses smart routing to identify the fastest routes across the Internet, sending packets around highly congested networks rather than through them . The result is similar to when car traffic is routed around traffic jams: data packets arrive faster, accelerating the online experience for users.
What is RIP in network?
RIP: The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) uses "hop count" to find the shortest path from one network to another, where "hop count" means number of routers a packet must pass through on the way. (When a packet goes from one network to another, this is known as a "hop.")
What is dynamic routing?
Dynamic routing tables update automatically. Dynamic routers use various routing protocols (see below) to determine the shortest and fastest paths. They also make this determination based on how long it takes packets to reach their destination — similar to the way Google Maps, Waze, and other GPS services determine the best driving routes based on past driving performance and current driving conditions.
Why does routing add security?
It adds security because an only administrator can allow routing to particular networks only.
What is the purpose of routing?
Routing is a process which is performed by layer 3 (or network layer) devices in order to deliver the packet by choosing an optimal path from one network to another. There are 3 types of routing: 1. Static routing –. Static routing is a process in which we have to manually add routes in routing table. Advantages –.
What is R1 and R2?
In this topology, R1 and R2 are stub routers so we can configure default routing for both these routers.
What is static routing?
Static routing is a process in which we have to manually add routes in routing table. No routing overhead for router CPU which means a cheaper router can be used to do routing. It adds security because only administrator can allow routing to particular networks only. No bandwidth usage between routers.
What is the IP address of R1?
R1 having IP address 172.16.10.6/30 on s0/0/1, 192.168.10.1/24 on fa0/0.#N#R2 having IP address 172.16.10.2/30 on s0/0/0, 192.168.20.1/24 on fa0/0.#N#R3 having IP address 172.16.10.5/30 on s0/1, 172.16.10.1/30 on s0/0, 10.10.10.1/24 on fa0/0.
What layer of OSI is used for routing?
These packets are taken care of by the L3 layer of the OSI Reference Model’s network layer.
What are the two types of routing?
Types of Routing. There are two types: 1. Static Routing . This type is the optimal path between all possible pairs of sources & destinations in the given network is pre-defined and fed into the routing table of the network’s routers.
What is flooding in routing?
Flooding: In this, you send the packets to every other neighbouring router & they in-turn to the same, and by some path, the packet reaches its destination. This duplicates the packets, but the reliability is very high in a type of routing. This is mostly used in defense networks, distributed databases, wireless networks, and populating the routing tables.
What does it mean when a packet is introduced in the network and received by one of the routers?
When a packet is introduced in the network and received by one of the routers, it reads the packet’s headers to understand the destination and checks its routing table marked with its metrics to see what would be the next best hope for the packet to reach the destination optimally. Then, it pushes the packet to the next node, and the above process repeats at the new node too until the packet reaches the destination node.
How are packets exchanged?
Packets, which are the atomic unit of information in packet-switched communication networks, are exchanged between the nodes (a node might be an end device, a router or a data generating device, etc.). The process of transferring these packets of information from their source node to the destination node with one or more hops in between along the most optimum path is called as ‘Routing’. Routers and switches are the devices that are used for the purpose which work on the routing protocols and algorithms they are configured with. These packets are taken care of by the L3 layer of the OSI Reference Model’s network layer.
What is RIP in router?
This type gives the router the ability to discover the network by protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and RIP (Routing Information Protocol ), updates the routing table by itself and effectively decides upon the path that the incoming packet must follow to reach its destination.
What is delay in packet routing?
Delay: This is the measure of time it takes for the packet to route from source to destination. This depends on many factors like network bandwidth, the number of intermediate nodes, congestion at nodes, etc. Sooner the transfer, the better the Quality of Service (QoS).