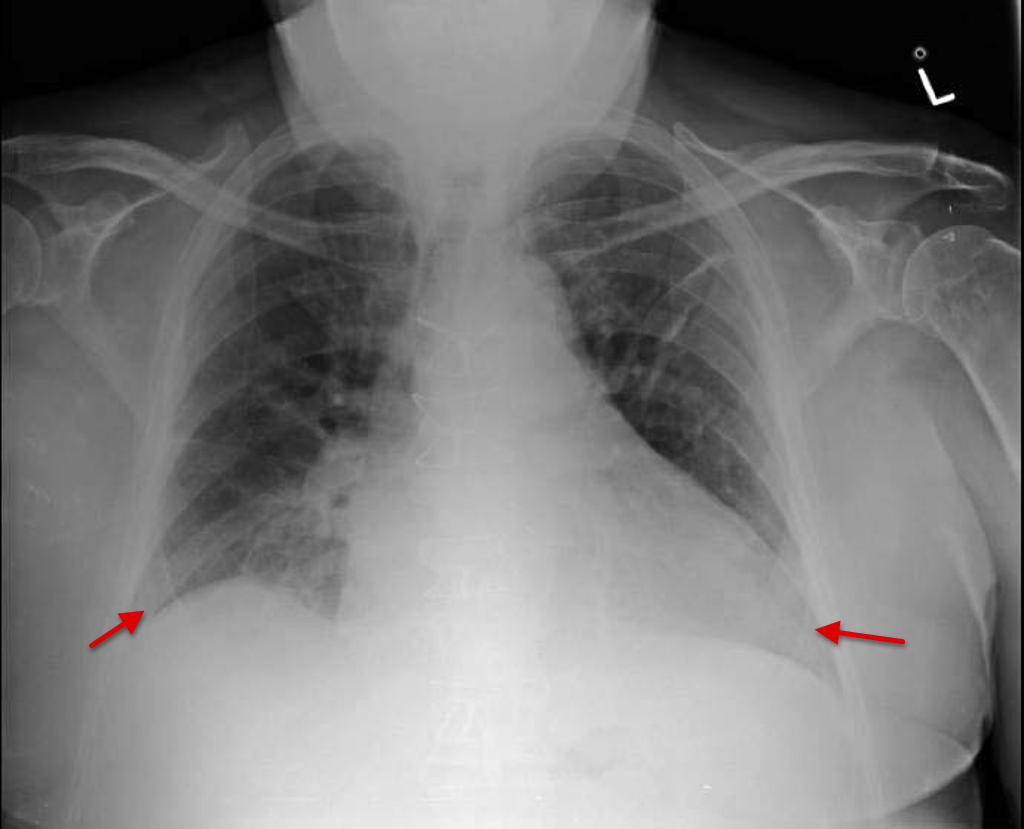
Symptoms
Pleural effusion, sometimes called fluid on the lung, can happen for various reasons, ranging from an infection to cancer. It does not usually have specific symptoms, but you may have signs of an infection or experience chest pain or difficulty breathing.
Causes
The seriousness of the condition depends on the primary cause of pleural effusion, whether breathing is affected, and whether it can be treated effectively. Causes of pleural effusion that can be effectively treated or controlled include an infection due to a virus, pneumonia or heart failure.
Prevention
The prognosis of the patient with a pleural effusion depends on the underlying condition. If due to heart failure, cirrhosis, or malignancy, the effusion is likely to recur. However, most patients with a pleural effusion have no long-term sequelae. Malignant effusions may change the staging and subsequent prognosis of the underlying cancer.
Complications
Pleural effusion has many causes. They include heart failure, pneumonia and other infections, cancer, pulmonary embolism, liver disease, and inflammation of the tissues around the lungs. How is it treated? A minor pleural effusion often goes away on its own without treatment.
What is pleural effusion and what does it feel like?
How serious is a pleural effusion?
What is the prognosis for pleural effusion?
Will pleural effusion clear on its own?

What causes left pleural effusion?
Results. The most common causes of pleural effusion are congestive heart failure, cancer, pneumonia, and pulmonary embolism. Pleural fluid puncture (pleural tap) enables the differentiation of a transudate from an exudate, which remains, at present, the foundation of the further diagnostic work-up.
What is the most common cause of pleural effusion?
Heart failure is the most common cause. Exudative effusion is caused by blocked blood vessels or lymph vessels, inflammation, infection, lung injury, and tumors.
Can pleural effusion go away on its own?
A minor pleural effusion often goes away on its own. Doctors may need to treat the condition that is causing the pleural effusion. For example, you may get medicines to treat pneumonia or congestive heart failure. When the condition is treated, the effusion usually goes away.
Is pleural effusion a serious problem?
Fluid around the lung (pleural effusion) is a potentially dangerous condition that can masquerade as something less worrisome. What may seem like chest pain or coughing due to a bad cold could actually have serious health ramifications.
How long can I live with pleural effusion?
Many patients with pleural effusions die within 30-days of admission to the hospital, and nearly 1/3 are dead within one year. A higher level of aggressive medical therapy may be warranted for those patients who present with pleural effusions in order to decrease their potential risk of death.
What happens if pleural effusion is left untreated?
Left untreated, pleural effusion can have serious medical complications. These include a partially collapsed lung, infections, bleeding, and pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs).
How do you treat pleural effusion?
TreatmentDraining fluid. One way to treat pleural effusion is by draining the fluid from the chest cavity, either with a needle or by inserting a small tube into the chest. ... Antibiotics. If you have a bacterial infection, the doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics or administer them intravenously. ... Pleurodesis. ... Surgery.
Can you survive pleural effusion?
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is a common but serious condition that is related with poor quality of life, morbidity and mortality. Its incidence and associated healthcare costs are rising and its management remains palliative, with median survival ranging from 3 to 12 months.
Can antibiotics treat pleural effusion?
(See "Society guideline links: Pleural effusion".) Antibiotics – All patients with suspected (or diagnosed) parapneumonic effusion or empyema should be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotic therapy should be administered promptly and not delayed for sampling or drainage procedures.
What foods to avoid if you have pleural effusion?
Limit sugar, fat and alcohol, and maintain a healthy weight. Healthy eating is important during and after treatment.
How can I reduce pleural effusion naturally?
Ways to clear the lungsSteam therapy. Steam therapy, or steam inhalation, involves inhaling water vapor to open the airways and may also help to loosen mucus. ... Controlled coughing. ... Draining mucus from the lungs. ... Exercise. ... Green tea. ... Anti-inflammatory foods. ... Chest percussion.
How fast does pleural effusion progress?
It is known that MPE recurs rapidly, sometimes within a month after an initial thoracocentesis in a considerable number of patients (7,8).
How long does it take for pleural effusion to resolve?
The time that it will take to recover can be dependent on the size, severity, cause, and your overall health. You will have to stay in the hospital overnight, but you will feel back to normal, on average, between 2-4 weeks.
What are the risk factors for pleural effusion?
Risk factors of pleural effusion may include: Smoking and drinking alcohol, as these can cause heart, lung and liver disease, which can lead to pleural effusion. History of any contact with asbestos.
How can I reduce pleural effusion naturally?
Ways to clear the lungsSteam therapy. Steam therapy, or steam inhalation, involves inhaling water vapor to open the airways and may also help to loosen mucus. ... Controlled coughing. ... Draining mucus from the lungs. ... Exercise. ... Green tea. ... Anti-inflammatory foods. ... Chest percussion.
What is the prevention of pleural effusion?
There is no established method for primary prevention of pleural effusion. However, avoidance of some risk factors, including smoke cessation, alcohol cessation, early treatment of pneumonia, and controlling heart failure, have demonstrated helpfulness.
What Is Pleural Effusion?
Pleural effusion is fluid buildup in the space between the layers of the pleura. The pleura are thin layers of tissue that form a 2-layered lining...
What Causes Pleural Effusion?
1. Heart failure or other heart and lung problems such as a pulmonary embolism (blockage of a blood vessel in the lungs) 2. Lung infections such as...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Pleural Effusion?
You may have no symptoms. A pleural effusion may cause you to cough or feel short of breath. You may breathe faster than usual. You may have mild t...
How Is Pleural Effusion Diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and listen to your heart and lungs through a stethoscope. You may need any of the following: 1. Blood tes...
How Is Pleural Effusion Treated?
Treatment depends on the cause of your pleural effusion and how bad your symptoms are. You may need any of the following: 1. Diuretics may help you...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have a fever. 2. Your breathing problems do not go away or get worse. 3. Your pain does not go away or gets worse. 4. You cough up yellow, g...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care Or Call 911?
1. You feel faint, or you cannot think clearly. 2. Your lips or fingernails turn blue. 3. You find it very hard to breathe.
What is pleural effusion?
A pleural effusion is an unusual amount of fluid around the lung. Many medical conditions can lead to it, so even though your pleural effusion may have to be drained, your doctor likely will target the treatment at whatever caused it.
Why do you need to drain pleural effusions?
Large, infected, or inflamed pleural effusions often need to get drained to help you feel better and prevent more problems.
What is a transudative effusion?
Transudative. This pleural effusion fluid is similar to the fluid you normally have in your pleural space. It forms from liquid leaking across normal pleura.
What is the membrane that lines the surface of the lungs and the inside of the chest wall?
The pleura is a thin membrane that lines the surface of your lungs and the inside of your chest wall. When you have a pleural effusion, fluid builds up in the space between the layers of your pleura. Normally, only teaspoons of watery fluid are in the pleural space, which allows your lungs to move smoothly in your chest cavity when you breathe.
How does talc work in pleural space?
Your doctor will tell you how and when to do that. Pleurodesis. Your doctor injects an irritating substance (such as talc or doxycycline) through a chest tube into the pleural space. The substance inflames the pleura and chest wall, which then bind tightly to each other as they heal.
How much watery fluid is in the pleural space?
Normally, only teaspoons of watery fluid are in the pleural space, which allows your lungs to move smoothly in your chest cavity when you breathe.
What is pleural decortication?
Pleural decortication. Surgeons can operate inside the pleural space, removing potentially dangerous inflammation and unhealthy tissue. To do this, your surgeon may make small cuts (thoracoscopy) or a large one ( thoracotomy ).
What causes pleural effusions?
Other causes of pleural effusions include: congestive heart failure (the most common cause overall) cirrhosis or poor liver function. pulmonary embolism, which is caused by a blood clot and is a blockage in the lung arteries. complications from open-heart surgery. pneumonia.
What is the first classification of pleural effusions?
The first classification of pleural effusions is either transudative or exudative.
What causes fluid to accumulate in the chest cavity?
This fluid accumulates in the chest cavity outside the lung, causing what’s known as a pleural effusion.
How to remove fluid from pleural membrane?
In a pleural fluid analysis, your doctor will remove fluid from the pleural membrane area by inserting a needle into the chest cavity and suctioning the fluid into a syringe. The procedure is called a thoracentesis. This also works as a common procedure to drain the excess fluid from the chest cavity. The fluid will then be tested ...
What is the term for the buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and chest cavity?
Pleural effusion , also called water on the lung, is an excessive buildup of fluid in the space between your lungs and chest cavity.
What is the treatment for pleural inflammation?
After drawing the excess fluid out of the chest cavity, a doctor injects a drug into the area. The drug is often a talc mixture. This medication causes the two layers of the pleura to stick together, which prevents the future buildup of fluid between them.
How long does it take for a pleural effusion to go away?
Treatment for some cases of pleural effusion may be managed with medication and other supportive care. Most people recover within a few days or weeks. Minor complications from more invasive treatments can include slight pain and discomfort, which often go away with time. Some cases of pleural effusion can have more serious complications, depending on the severity of the condition, cause, and treatment used.
How to treat pleural effusion?
Treatment depends on the cause of your pleural effusion and your symptoms. You may need any of the following: Diuretics may help you lose extra fluid caused by heart failure or other problems. Antibiotics help prevent or treat an infection caused by bacteria. NSAIDs help decrease swelling and pain or fever.
How is pleural effusion diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and listen to your heart and lungs through a stethoscope. You may need any of the following:
Why do you need surgery for pleural effusion?
Surgery may be needed if your pleural effusion keeps coming back or if it increases your risk for other problems.
How to get better after lung cancer?
Ask your healthcare provider for information if you need help quitting. Drink liquids as directed and rest as needed. Liquids help to keep your air passages moist and better able to get rid of germs and other irritants.
What is the pleura?
The pleura is a thin piece of tissue with 2 layers. One layer rests directly on the lungs. The other rests on the chest wall. There is normally a small amount of fluid between these layers. This fluid helps your lungs move easily when you breathe.
How to get rid of a lung infection?
Rest when you feel it is needed. Deep breathing and coughing will decrease your risk for a lung infection. Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can. Let the air out and then cough strongly. Deep breaths help open your airway. You may be given an incentive spirometer to help you take deep breaths.
What are the causes of heart failure?
Heart failure or other heart and lung problems such as a pulmonary embolism (blockage of a blood vessel in the lungs) Lung infections such as pneumonia or tuberculosis (TB) Cancer, injury, or problems with other organs in your chest or abdomen, such as cirrhosis or pancreatitis.
What is a pleural effusion?
Outlook. Pleural effusion refers to a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity. It can result from pneumonia and many other conditions. It can also be life threatening. Pleural effusion, or “water on the lung,” can resemble a respiratory infection. The cause is sometimes respiratory, ...
What is the difference between pleural effusion and uncomplicated effusion?
In complicated pleural effusion, signs of inflammation or infection will be present in the fluid. The person may need immediate treatment to prevent potentially serious complications. In uncomplicated effusion, there will be no sign of infection or inflammation in the fluid.
How to drain chest fluid?
To drain the chest, the healthcare professional will insert a tube into the pleural space and allow the fluid to leave the body.
What causes fluid to leak back into the chest?
Transudate effusion. Transudate effusion usually occurs when another condition causes a pressure imbalance in the blood vessels. As a result, fluid leaks back into the chest. The liquid in the effusion will likely consist of compounds from blood plasma.
How to take fluid from pleural space?
A healthcare professional may take a sample of fluid from the pleural space by inserting a needle between the ribs.
What is the lining of the lungs?
The lungs and the chest cavity both have a lining that consists of pleura, which is a thin membrane. In healthy lungs, these membranes ensure that a small amount of liquid is present between the lungs and chest. This prevents friction as the lungs expand and contract during breathing.
What are the conditions that affect the lungs?
pancreatitis. systemic conditions, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. infections, such as tuberculosis or pneumonia. pulmonary embolism, which occurs when a blood clot blocks the arteries of the lung. any cancer that affects or spreads to the lungs or pleura. asbestos exposure and mesothelioma.
What are the symptoms of pleural effusion?
The symptoms of pleural effusion can range from none to shortness of breath to coughing, among others. The greater the build-up of fluid, the more likely symptoms will be noticeable. In addition to excess fluid, the tissue around the lung may become inflamed, which can cause chest pain. In extreme cases, a person can have up to four liters of excess fluid in the chest. It's very uncomfortable. “Imagine trying to breathe with two soda bottles pushed up against your lungs,” Dr. Puchalski says.
Why do I have pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion occurs when fluid builds up in the space between the lung and the chest wall. This can happen for many different reasons, including pneumonia or complications from heart, liver, or kidney disease. Another reason could be as a side effect from cancer. “One of the most common reasons pleural effusion develops is due to congestive heart failure ,” says Jonathan Puchalski, MD, a pulmonologist at Yale Medicine.
How is fluid around the lung treated?
The best way is to treat the cause of the effusion. If the cause is pneumonia, a doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection, which may also cause the fluid to go away. If fluid build-up has been caused by congestive heart failure, a physician will likely prescribe diuretics, such as Lasix, for treatment.
What makes Yale Medicine’s approach to pleural effusion special?
At Yale Medicine, patients receive care from a team of physicians who specialize in dealing with pleural effusions. The clinical care team includes a physician assistant and an advanced practice registered nurse who are trained in this subspecialty. What makes Yale especially unique, Dr. Puchalski adds, is our ability to perform bilateral thoracenteses. This means that a patient can have fluid build-up removed from both lung areas in a single treatment, rather than scheduling two separate procedures. Patients can do this at Yale Medicine, Dr. Puchalski explains, due to a highly-trained staff.
How to drain fluid from pleural effusion?
This involves inserting a needle in the space between the lung and the chest wall and draining the liquid. In these cases, a doctor may also send a sample of fluid to be tested for other causes, such as lung cancer, for example. Some patients may require a pleural drain that is inserted through the skin so that the buildup of fluid can be drained repeatedly without the need for repeated thoracentesis.
How much fluid can cause chest pain?
In extreme cases, a person can have up to four liters of excess fluid in the chest. It's very uncomfortable.
Is fluid around the lung dangerous?
Fluid around the lung (pleural effusion) is a potentially dangerous condition that can masquerade as something less worrisome. What may seem like chest pain or coughing due to a bad cold could actually have serious health ramifications. It’s not that rare, either.
What Are Symptoms and Signs of Pleural Effusion?
Shortness of breath is the most common symptom of a pleural effusion. As the effusion grows larger with more fluid, the harder it is for the lung to expand and the more difficult it is for the patient to breathe.
Where is pleural effusion located?
A pleural effusion is a collection of fluid in the space between the two linings (pleura) of the lung.
What Causes a Pleural Effusion? What Are the Types?
A pleural effusion is not normal. It is not a disease but rather a complication of an underlying illness. Extra fluid (effusion) can occur for a variety of reasons.
When Should You Call a Doctor for Pleural Effusion?
Depending upon the circumstances and the severity of symptoms, call 911 or activating other emergency care services.
Can You Prevent Pleural Effusion?
Pleural effusions are caused by a variety of conditions and illnesses. Preventing the underlying cause will decrease the potential of developing an effusion.
What is a thoracentesis needle?
Thoracentesis is used to draw off the pleural fluid for analysis. A thin needle is inserted between the ribs into the fluid collection. Treatment of the pleural effusion depends upon the underlying illness.
Why do you need a chest X-ray before a thoracentesis?
Often, a chest X-ray is taken before the thoracentesis to confirm the presence of the effusion and afterward to make certain that the procedure did not cause a pneumothorax ( collapsed lung ). Analysis of the pleural fluid include: