
What does leptin mean?
Leptin is a hormone that helps regulate your body weight by controlling your appetite and energy level. Generally, the amount of leptin in your blood is related to the amount of fat tissue in your body. Leptin is released into your blood by your fat stores. Its main job is to tell your brain to stop eating.
What should leptin levels be?
ur fasting serum leptin level is 45 then it's a good idea to reduce that leptin level down 10-15 points in order for weight loss to occur. This drop in leptin still maintains a relatively high leptin level (which is required for fat burning) but one which is lower than your "old" leptin level.
How to stimulate a leptin response in your body?
- Drink at least eight to ten cups of water, or 64 to 80 ounces, every day.
- This may seem like a lot, but if you carry a refillable water bottle with you throughout your day, you'll be surprised at how quickly you can get your daily ...
- Avoid alcohol and beverages with caffeine. Do not count them to your daily water intake.
How to master leptin, your fat loss hormone?
- Limit your carb intake during the day, and time it as recommended in the Bulletproof Diet.
- Eat to eliminate food cravings and give your liver and hormones a rest. ...
- Allow 4-5 hours between food and sleep (not counting the sleep hacking recommendations for energy maintenance during sleep)

What is leptin simple words?
What is leptin? Leptin is a hormone your adipose tissue (body fat) releases that helps your body maintain your normal weight on a long-term basis. It does this by regulating hunger by providing the sensation of satiety (feeling full).
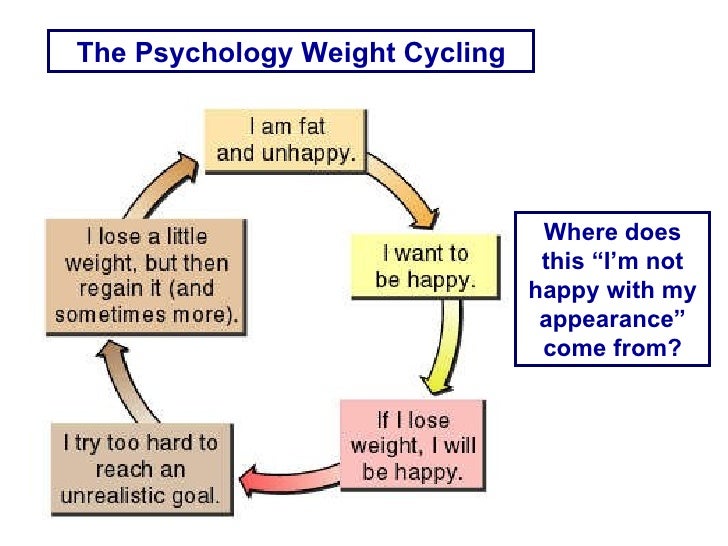
What is leptin AP Psych?
Also known as the "starvation hormone", leptin signals the hypothalamus that the body has enough fat stored to function normally. When leptin levels are high enough, appetite is inhibited. When leptin levels are low, it indicates that we need to consume more food and appetite increases.
How does leptin influence Behaviour?
Administration of leptin has been shown to modulate behaviors that are dependent upon the mesolimbic dopamine circuit. For example, leptin administration alters intracranial self-stimulation (10), suggesting an interaction with dopamine circuits that are thought to underlie the behavior (11).
Is leptin a stress hormone?
Conclusions: Leptin is a biomarker of stress, with a decrease following acute stress. Normal-weight individuals and women also have a higher variation of leptin levels after stress, suggesting that leptin may have implications in obesity development in response to stress in a sex-dependent manner.
What is leptin made of?
Leptin (from the Greek word leptos, meaning “thin”) is derived from the lep gene, located on chromosome 7, which transcribes a 167 amino acid peptide with a molecular weight of 16kD.
What is obesity in psychology?
the condition of having excess body fat resulting in overweight, variously defined in terms of absolute weight, weight–height ratio (see body mass index), distribution of subcutaneous fat, and societal and aesthetic norms.
What does leptin do to the brain?
Instead, leptin is a pleiotropic hormone that impinges on many brain areas, and in doing so alters food intake, motivation, learning, memory, cognitive function, neuroprotection, reproduction, growth, metabolism, energy expenditure, and more.
How does leptin regulate mood?
Leptin can affect mood and cognition via inducing structural and functional alterations in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Neural plasticity theories of depression may explain multiple aspects of brain plasticity changes associated with depression and antidepressant-like effects.
Does leptin affect mood?
The adipose-derived hormone leptin is well known for its function in the control of energy homeostasis. Recent studies suggest a novel role for this adipokine in the regulation of mood and emotion. Low levels of leptin have been found to be associated with depressive behaviors in rodents and humans.
What stimulates leptin?
Leptin secretion Insulin stimulates leptin secretion through a posttranscriptional mechanism that is mainly mediated by the PI3K-PKBmTOR pathway, or other unknown pathways. It has been suggested that the chronic effect of insulin is mediated by glucose metabolism.
Which hormone causes weight gain?
The hormones leptin and insulin, sex hormones and growth hormone influence our appetite, metabolism (the rate at which our body burns kilojoules for energy), and body fat distribution. People who are obese have levels of these hormones that encourage abnormal metabolism and the accumulation of body fat.
Why is leptin released?
What is leptin? Leptin is a hormone released from fat cells in adipose tissue. Leptin signals to the brain, in particular to an area called the hypothalamus. Leptin does not affect food intake from meal to meal but, instead, acts to alter food intake and control energy expenditure over the long term.
What is leptin quizlet?
Leptin is a hormone that acts to reduce food intake and to decrease body weight and body fat.
What type of hormone is leptin?
peptide hormoneLeptin is a peptide hormone synthesized by white adipose tissue. The leptin gene (LEP or ob) is on chromosome 7q31.
Is leptin a protein or hormone?
Leptin is the protein product encoded by the obese (ob) gene. It is a circulating hormone produced primarily by the adipose tissue.
How does leptin control appetite?
The hormone was discovered in 1994 and has been studied ever since for its function in weight regulation and obesity in both animals and humans ( 2 ). Leptin communicates to the brain that you have enough stored fat, which curbs your appetite, signals the body to burn calories normally and prevents excessive eating.
Leptin as adiposity signal
To date, only leptin and insulin fulfill the criteria of an adiposity signal:
Mechanism of action
It is unknown whether leptin must cross the blood-brain barrier to access receptor neurons, because the blood-brain barrier is somewhat absent in the area of the median eminence, close to where the NPY neurons of the arcuate nucleus are. If it does cross the blood-brain barrier, it is unknown whether this occurs via an active or passive process.
Leptin and reproduction
Leptin is produced by the placenta Leptin levels rise during pregnancy and fall at parturition. Leptin is also expressed in fetal mebranes and uterine tissue. Uterine muscle contractions are inhibited by leptin.
Recent Discoveries
Professor Cappuccio of the University of Warwick has recently discovered that short sleep duration may lead to obesity, through an increase of appetite via hormonal changes. Lack of sleep produces Ghrelin which, among other effects, stimulates appetite and creates less leptin which, amongst its many other effects, increases appetite.
What does leptin do to the brain?
Leptin is supposed to tell your brain that — when you have enough fat stored — you don’t need to eat and can burn calories at a normal rate ( 4 ). It also has many other functions related to fertility, immunity and brain function ( 5 ).
Why is leptin resistance important?
This condition — known as leptin resistance — is now believed to be one of the main biological contributors to obesity ( 12. Trusted Source. ). When your brain doesn’t receive the leptin signal, it erroneously thinks that your body is starving — even though it has more than enough energy stored.
What does it mean when your leptin levels go up?
). When you eat, your body fat goes up, leading your leptin levels to go up. Thus, you eat less and burn more.
What hormone is produced by fat cells?
But something is broken in the mechanism that is supposed to prevent us from overeating. Summary. Leptin is a hormone produced by the fat cells in your body. Its main role is to regulate fat storage and how many calories you eat and burn.
Why do people with obesity have high levels of leptin?
People who are obese have a lot of body fat in their fat cells. Because fat cells produce leptin in proportion to their size, people who are obese also have very high levels of leptin ( 10. Trusted Source. ). Given the way leptin is supposed to work, many obese people should naturally limit their food intake.
What hormone is involved in obesity?
However, modern obesity research disagrees. Scientists increasingly say that a hormone called leptin is involved ( 1. ). Leptin resistance, in which your body does not respond to this hormone, is now believed to be the leading driver of fat gain in humans ( 2 ).
How to reduce leptin resistance?
There are several things you can do: 1 Avoid processed food: Highly processed foods may compromise the integrity of your gut and drive inflammation ( 23#N#Trusted Source#N#). 2 Eat soluble fiber: Eating soluble fiber can help improve your gut health and may protect against obesity ( 24#N#Trusted Source#N#). 3 Exercise: Physical activity may help reverse leptin resistance ( 25#N#Trusted Source#N#). 4 Sleep: Poor sleep is implicated in problems with leptin ( 26#N#Trusted Source#N#). 5 Lower your triglycerides: Having high triglycerides can prevent the transport of leptin from your blood to your brain. The best way to lower triglycerides is to reduce your carb intake ( 27#N#Trusted Source#N#, 28 ). 6 Eat protein: Eating plenty of protein can cause automatic weight loss, which may result from an improvement in leptin sensitivity ( 29#N#Trusted Source#N#).
What is the function of leptin?
The primary function of the hormone leptin is the regulation of adipose tissue mass through central hypothalamus mediated effects on hunger, food energy use, physical exercise and energy balance.
Where is leptin expressed?
Subsequent studies in 1995 confirmed that the db gene encodes the leptin receptor, and that it is expressed in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain known to regulate the sensation of hunger and body weight.
What is the role of leptin receptors in the immune system?
It modulates the immune response to atherosclerosis, of which obesity is a predisposing and exercise a mitigating factor.
What hormones does leptin interact with?
Further, leptin interacts with other hormones and energy regulators, indirectly mediating the effects of: insulin, glucagon, insulin-like growth factor, growth hormone, glucocorticoids, cytokines, and metabolites.
How does leptin affect bone?
Leptin's role in regulating bone mass was identified in 2000. Leptin can affect bone metabolism via direct signalling from the brain. Leptin decreases cancellous bone, but increases cortical bone. This "cortical-cancellous dichotomy" may represent a mechanism for enlarging bone size, and thus bone resistance, to cope with increased body weight.
What is the function of leptin in the small intestine?
PDB. 1ax8 . Leptin (from Greek λεπτός leptos, "thin") is a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells and enterocytes in the small intestine that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger, which in turn diminishes fat storage in adipocytes.
Why did Leibel not receive the same level of recognition from the discovery of the gene?
Coleman and Friedman have been awarded numerous prizes acknowledging their roles in discovery of leptin, including the Gairdner Foundation International Award (2005), the Shaw Prize (2009), the Lasker Award, the BBVA Foundation Frontiers of Knowledge Award and the King Faisal International Prize, Leibel has not received the same level of recognition from the discovery because he was omitted as a co-author of a scientific paper published by Friedman that reported the discovery of the gene. The various theories surrounding Friedman's omission of Leibel and others as co-authors of this paper have been presented in a number of publications, including Ellen Ruppel Shell ’s 2002 book The Hungry Gene.
Leptin as adiposity signal
- To date, only leptin and insulin fulfill the criteria of an adiposity signal:
It circulates at levels proportional to body fat. - It enters the central nervous system (CNS) in proportion to its plasma concentration.
Its receptors are found in brain neurons involved in regulating energy intake and expenditure.
Mechanism of action
- It is unknown whether leptin must cross the blood-brain barrier to access receptor neurons, because the blood-brain barrier is somewhat absent in the area of the median eminence, close to where the NPY neurons of the arcuate nucleus are. If it does cross the blood-brain barrier, it is unknown whether this occurs via an active or passive process. It is generally thought that leptin …
Leptin and reproduction
- Leptin is produced by the placenta Leptin levels rise during pregnancy and fall at parturition. Leptin is also expressed in fetal mebranes and uterine tissue. Uterine muscle contractions are inhibited by leptin.
Recent Discoveries
- Professor Cappuccio of the University of Warwick has recently discovered that short sleep durat…
Next to a biomarker for body fat, serum leptin levels also reflect individual energy balance. Several studies have shown that fasting or following a VLCD diet lower
References
- ↑ Zhao J, townsend KL, Schulz LC, Kunz TH, Li C, Widmaier EP. leptin receptor expression increa…
↑ Moynihan AT, Hehir MP, Glavey SV, Smith TJ, Morrison JJ. Inhibitory effect of leptin on human uterine contractility in vitro. Amer J Obstet Gynecol (2006) 195:504-9.
External links
- A discussion of leptin in a bulletin by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI)
Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals - Leptin: Your brain, appetite and obesity
Leptin Hormone