What is a leukocyte alkaline phosphatase blood test?
The Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test helps determine the levels of LAP in a sample of blood containing neutrophils. The test is mainly used to differentiate between benign reactive increase in neutrophils and malignant conditions that show an increase in the number of neutrophils
Is it normal to have a low alkaline phosphatase level?
Seeing an abnormal test result can be stressful. Know that having a high or low level of alkaline phosphatase doesn’t necessarily mean you have a medical condition and need treatment. Approximately one in 20 healthy people have test results outside of the normal range.
How long should I fast for an alkaline phosphatase test?
If your alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test is part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), you’ll likely need to fast for 10 to 12 hours before your CMP blood test. Fasting means not eating or drinking anything other than water.
What is the LAP score for WBC?
The leukocyte alkaine phosphatase (LAP) score is often used in patients with an elevated WBC to differentiate a reactive process from chronic myelogenous leukemia.The score in the latter is low while it is within the normal reference range or elevated in the former condition.
See more

What does a high LAP score mean?
Scores for the LAP test can range from zero to 400, with those between 20 and 100 being considered normal. A score that's higher than normal may be caused by: leukemoid reaction. essential thrombocytosis. myelofibrosis.
What causes high leukocyte alkaline phosphatase?
High scores have been seen in polycythemia vera, myelofibrosis, aplastic anemia, mongolism, hairy cell leukemia, leukemoid reactions, and neutrophilia either physiological or secondary to infection. It is also increased in Hodgkin disease.
Why is leukocyte alkaline phosphatase low in CML?
In cases of CML, the LAP score is low (less than 13) due to the fact that these cells are not being produced in response to an infection or stress but rather due to the neoplasm.
What is mean by leukocyte acid phosphatase?
Abstract. Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) has been demonstrated during relapse in the cells in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) in a patient with the clinical features of acute T cell lymphocytic leukemia which suggests this isozyme may be a marker for malignant transformation of some types of lymphocytes.
What does a high alkaline phosphatase indicate?
An alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test measures the amount of ALP in your blood. Although ALP exists throughout your body, the two main sources of ALP in your blood are your liver and bones. High levels of ALP may indicate liver disease or certain bone disorders, but an ALP test alone cannot diagnose a condition.
Does leukemia cause high alkaline phosphatase?
Preliminary results obtained in our laboratory have shown that alkaline phosphatase can be expressed at high levels in leukemia.
What does it mean if your alkaline phosphatase is low?
Low levels Having lower-than-normal ALP levels in your blood can indicate a protein deficiency or Wilson's disease. It may also signal malnutrition, which could be caused by celiac disease or an insufficient amount of certain vitamins and minerals.
What are symptoms of low alkaline phosphatase?
Low ALP: Could it be HPP?Failure to thrive (in infants)Short stature.Bone and joint pain.Missed gross motor milestones (standing, sitting, crawling, turning over)Misshapen head, caused by craniosynostosis or chiari malformation.Brain fog.
Is CML lap positive?
If a myeloproliferative neoplasm is positive for the BCR/ABL-1 rearrangement, it is classified as CML, regardless of the LAP score. Just as a low LAP score does not make a diagnosis of CML, a normal or high LAP score doesn't exclude it.
What disease is diagnosed by monitoring acid phosphatase activity?
This resulted in recurrent infections. Prostate acid phosphatase (PAP) has been used extensively as a serum marker for cancer of the prostate....Table 2.Human acid phosphatase (AP)Clinical and laboratory importanceProstatic (PAP)Serum marker for cancer of the prostate157 more rows
What happens when acid phosphatase increased?
Traditionally, the serum prostatic acid phosphatase has been thought to originate in the prostatic cancer cell and has been used to stage the disease. Until recently, elevated serum values have been accepted as an indication of extraprostatic disease, and were thought to rule out lesions confined to the prostate.
What is the function of alkaline phosphatase in bone?
ALP increases inorganic phosphate local rates and facilitates mineralization as well as reduces the extracellular pyrophosphate concentration, an inhibitor of mineral formation.
What infections cause high alkaline phosphatase?
Extremely high elevations of alkaline phosphatase are most frequently seen in patients with sepsis, malignant obstruction, and AIDS. Patients with sepsis can have an extremely high alkaline phosphatase level and a normal bilirubin.
Should I worry about elevated alkaline phosphatase?
Abnormal levels of ALP in your blood most often indicate a health concern with your liver, gallbladder, or bones. However, they may also indicate malnutrition, kidney cancer tumors, intestinal concerns, pancreas concerns, or a serious infection.
What is the treatment for high alkaline phosphatase?
Reduction in serum alkaline phosphatase levels by treatment with active vitamin D (alphacalcidol) in primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism and in euparathyroid individuals.
What bone disorders cause high ALP?
High ALP levels can be caused by bone diseases, such as Paget's disease, osteomalacia, rickets, bone tumors, or tumors that have spread from another part of the body to the bone, or by overactive parathyroid glands (hyperparathyroidism). Normal healing of a bone fracture can also raise ALP levels.
Definition
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase is a test that tells how much of a protein called alkaline phosphatase (ALP) you have inside your white blood cells. Leukocyte means white blood cell.
How the test is performed
Blood is typically drawn from a vein, usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The site is cleaned with germ-killing medicine (antiseptic). The health care provider wraps an elastic band around the upper arm to apply pressure to the area and make the vein swell with blood.
How the test will feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain, while others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the test is performed
ALP is found in different forms throughout the body. This test is done to confirm a number of different medical conditions, including certain types of anemia and leukemia.
Normal Values
A staining score of 20 - 100 (out of a maximum of 400) is considered normal.
What the risks are
There is very little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one patient to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
What is the LAP score?
The aryl naphthylthalamide is coupled to diazonium salt (fast red violet LB) forming an insoluble blue dye within the cytolasm of the WBCs. Neutrophils and bands are scored (0 to 4+) and the total score of 100 of these cells is the LAP score. Variable intensity of blue staining can be seen in the leukocytes in this peripheral smear from a patient with a reactive leukocytosis.
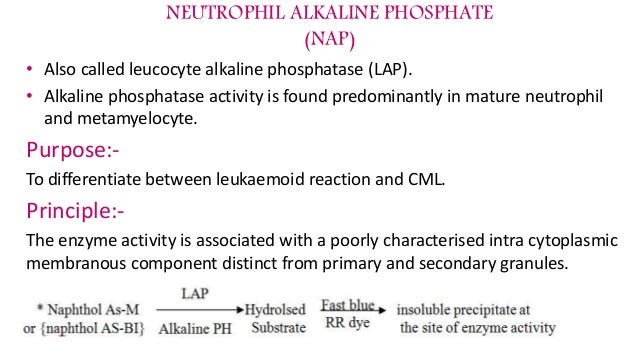
Is Naphthyl AS-B1 a phosphate?
Naphthyl AS-B1 phosphate is hydrolyzed to phosphate and an aryl maphthylthalamide by alkalline phosphatase in the cytoplasm of WBCs . The aryl naphthylthalamide is coupled to diazonium salt (fast red violet LB) forming an insoluble blue dye within the cytolasm of the WBCs.
What are the Clinical Indications for performing the Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test?
The clinical indicators for performing the Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test include differentiating between severe neutophilia (leukemoid reaction) and myeloproliferative neoplasms from chronic myeloid leukemia.
How is the Specimen Collected for Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test?
Following is the specimen collection process for Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test:
How many neutrophils are in a leukocyte alkaline phosphatase test?
The Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test is scored by counting 100 neutrophils in a blood sample and assigning a grade based on the amount of dye they take up as part of the test, which indicates the abundance of leukocyte alkaline phosphatase.
What is the enzyme that makes up the leukocytes?
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) is an enzyme present in a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) called a neutrophil
Why is the LAP blood test used?
The test is mainly used to differentiate between benign reactive increase in neutrophils and malignant conditions that show an increase in the number of neutrophils. Because there are advanced tests to diagnose blood cancers, currently the LAP Blood Test is only occasionally used in medical practice.
Is the Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test ordered?
More advanced medical tests have largely replaced the Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Test, making it a rarely ordered test
Clinical Use
Aids in the differential diagnosis of chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML) versus leukemoid reaction; aids in the evaluation of polycythemia vera, myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Test Information
Low scores have been associated with CML, PNH, thrombocytopenic purpura, and hereditary hypophosphatasia. In CML regardless of the total white count, the score remains low. In CML, it has been demonstrated that the mRNA for leukocyte alkaline phosphatase by Northern blotting is undetectable.
Specimen Type
Smears made from fingerstick or heparinized specimen; heparin (green-top) tube − slides must be made within 24 hours of collection.
Container Type
Slides; green-top (heparin) tube − slides must be made within 24 hours of collection.
Collection
Prepare smears on six (frosted end) slides from either fingerstick blood or immediately after drawing into heparin Vacutainer® and mixing. Air dry the slides and label with patient’s name. Submit all. Note: Do not use EDTA anticoagulant. Do not fix slides with any type of fixative prior to submission.
Rejection Criteria
Improper labeling; heparin tube specimen more than 24 hours old; frozen slides; slides more than seven days old; slides made from any anticoagulant other than heparin
What is the difference between a CML and a benign left shift?
A benign left shift usually presents with a mild to moderate leukocytosis (the neutrophil count is often just above normal; it’s generally nowhere near the magnitude often seen in CML), and the neutrophils are shifted back to the metamyelocyte or myelocyte stages (you’ll very rarely see promyelocytes, and you’ll virtually never see myeloblasts). Also, CML tends to have a “bulge” at the metamyelocyte stage, whereas a benign left shift does not (the cells are more or less present in decreasing amounts by stage of maturation, i.e., there are more segmented than band neutrophils, more bands than metamyelocytes, more metamyelocytes than myelocytes, more myelocytes than promyelocytes…and blasts are basically nonexistent). Finally, CML has a basophilia, whereas a benign left shift does not.
Is LAP a good test?
But it’s still a good test, and it would be a good thing to do if you couldn’t look for the Philadelphia chromosome. Here’s the principle behind the test. LAP is an enzyme present in normal neutrophils, but absent (or present at very low concentrations) in malignant neutrophils (i.e., the ones in CML).
Can you do a leukocyte phosphatase test for CML?
But if you wanted more proof that your case was CML, you could do a leukocyte (or neutrophil) alkaline phosphatase (LAP). This test is not done as much as it used to be, because now everyone goes right to cytogenetics or molecular testing in order to find the Philadelphia chromosome or the bcr-abl translocation.
Ordering Recommendation
Recommendations when to order or not order the test. May include related or preferred tests.
Reported
Expected turnaround time for a result, beginning when ARUP has received the specimen.
New York DOH Approval Status
Indicates test has been approved by the New York State Department of Health.
Specimen Required
Patient Preparation: Instructions patient must follow before/during specimen collection.
Reference Interval
Normal range/expected value (s) for a specific disease state. May also include abnormal ranges.
Interpretive Data
Background information for test. May include disease information, patient result explanation, recommendations, details of testing, associated diseases, explanation of possible patient results.
CPT Codes
The American Medical Association Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes published in ARUP's Laboratory Test Directory are provided for informational purposes only. The codes reflect our interpretation of CPT coding requirements based upon AMA guidelines published annually.
Overview
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme that’s found throughout your body. An enzyme is a type of protein in a cell that acts as a catalyst and allows certain bodily processes to happen. There are thousands of enzymes throughout your body that have important functions.
Test Details
A healthcare provider called a phlebotomist usually performs blood draws, including those for an ALP blood test, but any healthcare provider who is trained in drawing blood can perform this task. The samples are sent to a lab where a medical laboratory scientist prepares the samples and performs the test on machines known as analyzers.
Results and Follow-Up
Blood test reports, including alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test reports, usually provide the following information: