What percentage of the gait cycle is loading response?
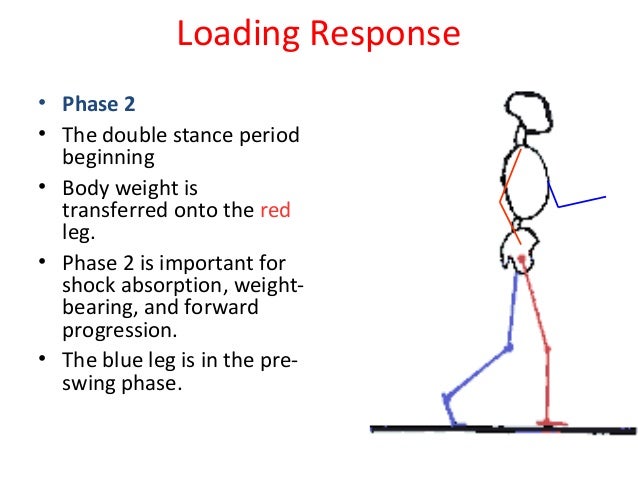
Loading response goes from 3-12% of the gait cycle. In this portion, the knee flexes slightly in order to absorb shock as the foot falls flat on the ground, stabilizing in advance of single limb support. 2. Single limb support (12-50%):
What is the biomechanics of gait?
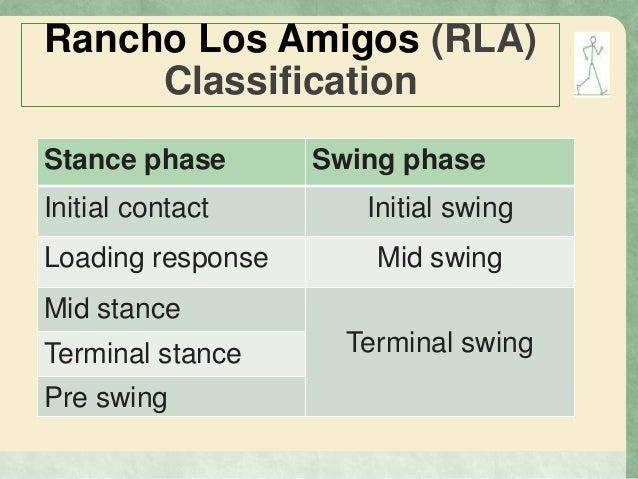
Biomechanics of Gait and Running I. Normal Gait STANCE(60-62% gait cycle) Initial Contact: The moment the foot contacts the ground. Loading Response: Weight is rapidly transferred onto the outstretched limb, the first period of double-limb support. Midstance: The body progresses over a single, stable limb.
How does the gait cycle work?
The gait cycle begins when one foot contacts the ground and ends when that foot contacts the ground again. Thus, each cycle begins at initial contact with a stance phase and proceeds through a swing phase until the cycle ends with the limb's next initial contact.
What is the loading response phase of foot flat?
In foot flat, or loading response phase, the body absorbs the impact of the foot by rolling in pronation. The hip moves slowly into extension, caused by a contraction of the adductor magnus and gluteus maximus muscles. The knee flexes to 15° to 20° of flexion.

What is the functional aspect of the loading response phase?
The foot-flat phase or “loading response” phase has an important function since body weight is transferred to the lead leg at this point and thus must absorb this weight while maintaining forward momentum.
What muscles are active during loading response?
Following initial floor contact, the loading response is an increase in the intensity of these hip and knee extensor muscles to stabilize the trunk and limb against the rapid transfer of body weight. To ensure knee stability, the hamstrings and single joint hip extensors exchange their intensities.
What is RLA gait?
RLA terminology divides gait phases into initial contact, loading response, mid-stance, terminal stance, pre-swing, initial swing, mid-swing and terminal swing. In this work, our aim is to enhance the rehabilitation of hemiplegic patients who have only one dysfunctional leg.
What are the 3 parts of of the swing phase of the gait cycle?
The swing phase can be broken down into 4 sub-phases.Pre-swing takes place during 50-62% of the gait cycle. ... Initial swing goes from 62-75% of the gait cycle. ... Mid-swing goes from 75-87% of the gait cycle. ... Terminal swing is the final phase of the gait cycle going from 87-100% of the cycle.
Which muscle action produces knee flexion during loading response of the normal gait cycle?
The quadriceps role is to eccentrically control the knee during flexion through the stance phase. If these muscles are weak the hip extensors will compensate by bringing the limb back into a more extended position, reducing the amount of flexion at the knee during stance phase.
What muscles are activated during gait?
These include the tibialis anterior, the quadriceps, the hamstrings, the hip abductors, the gluteus maximus, and the erector spinae (1,4,5).
What are the 4 phases of the gait cycle?
Stance phase of gait is divided into four periods: loading response, midstance, terminal stance, and preswing.
What are the 7 kinds of gait?
What are some types of gait disorders?Propulsive gait. This type of gait is seen in patients with parkinsonism. ... Scissors gait. This type of gait gets its name because the knees and thighs hit or cross in a scissors-like pattern when walking. ... Spastic gait. ... Steppage gait. ... Waddling gait.
What are the 4 phases of walking?
A more convenient and precise way to think about the stance phase (foot on the ground) of walking is to consider the five sub-stages that a single foot undergoes (Figure 1). They are as follows: Heel strike, Early flatfoot, Late flatfoot, Heel rise, and Toe off.
What are the 8 phases of gait?
8 Phases of the gait cycleABSWING PHASE 1INITIAL SWING/ACCELERATIONSWING PHASE 2MIDSWINGSWING PHASE 3TERMINAL SWING/DECELERATIONSTANCE PHASE 1INITIAL CONTACT/HEEL STRIKE22 more rows
What is the difference between the stance phase and the swing phase?
During walking, the gait cycle is usually subdivided into a stance phase and a swing phase. The swing phase is the period of time when the foot under consideration is not in contact with the floor. The stance phase is the period of time when the foot under consideration is in contact with the floor.
What is Trendelenburg gait?
A trendelenburg gait is an abnormal gait resulting from a defective hip abductor mechanism. The primary musculature involved is the gluteal musculature, including the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscles. The weakness of these muscles causes drooping of the pelvis to the contralateral side while walking.
What is the preswing phase of the gait cycle?
Thus, preswing corresponds to the gait cycle's second period of double limb support.
When does the gait cycle begin?
The gait cycle begins when one foot contacts the ground and end s when that foot contacts the ground again. Thus, each cycle begins at initial contact with a stance phase and proceeds through a swing phase until the cycle ends with the limb's next initial contact.
What percentage of the gait cycle is double limb support?
The two periods of double limb support account for 20 to 24 percent of the gait cycle's total duration.
How many periods are there in gait?
Stance phase of gait is divided into four periods: loading response, midstance, terminal stance, and preswing. Swing phase is divided into three periods: initial swing, midswing, and terminal swing. The beginning and and ending of each period are defined by specific events.
What is the period from knee flexion to midswing?
Initial swing begins at toe off and continues until maximum knee flexion (60 degrees) occurs. Midswing is the period from maximum knee flexion until the tibia is vertical or perpendicular to the ground. Terminal swing begins where the tibia is vertical and ends at initial contact. References: Gage, J.R. (1990).
What is the human gait?
Introduction. Human gait depends on a complex interplay of major parts of the nervous, musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems. The individual gait pattern is influenced by age, personality, mood and sociocultural factors.
What is the gait cycle?
The gait cycle is a repetitive pattern involving steps and strides. A step is one single step. A stride is a whole gait cycle. Step time - time between heel strike of one leg and heel strike of the contralateral leg. Step width - the mediolateral space between the two feet.
What is 30° flexion?
30° flexion of the hip: full extension in the knee: ankle moves from dorsiflexion to a neutral (supinated 5°) position then into plantar flexion. After this, knee flexion (5°) begins and increases, just as the plantar flexion of the heel increased.
What is Trendelenburg gait?
Trendelenburg gait, the gait characteristic of paralysis of the gluteus medius muscle, marked by a listing of the trunk toward the affected side at each step. Hemiplegic gait a gait involving flexion of the hip because of footdrop and circumduction of the leg.
What causes plantar flexion?
Flexion is caused by a contraction of the hamstrings, Flexion of the hip is caused by the contraction of the rectus femoris.
What is the normal forward step?
Generation of ground reaction forces. The normal forward step consists of two phases: stance phase; swing phase, The Stance phase occupies 60% of the gait cycle, during which one leg and foot are bearing most or all of the bodyweight.
What is diplegic gait?
Diplegic Gait (Spastic gait). Spasticity is normally associated with both lower limbs. Contractures of the adductor muscles can create a ‘scissor’ type gait with a narrowed base of support. Spasticity in the lower half of the legs results in plantarflexed ankles presenting in ‘tiptoe’ walking and often toe dragging.
What are the phases of gait?
Two Primary Phases of the Gait Cycle 1 Stance phase: Consists of the entire time that a foot is on the ground. 2 Swing phase: Consists of the entire time that the foot is in the air.
How is gait measured?
A single gait cycle can be measured from any gait event to the same subsequent event on the same foot, but the conventional tacit model considers gait cycle is measured from one foot strike to the subsequent foot strike of the same foot. Quantifying aspects of the gait cycle, such as time and spatial measures, allow for analysis of gait symmetry, ...
What is single limb support?
Single limb support involves progression of the body over the foot and weight-bearing stability. The first sub-phase of single limb support is midstance, which is seen during the 12-31% of the gait cycle. During midstance, the shank rotates forward over the supporting foot, creating the second rocker motion of the cycle.
What is the transition phase between stance and swing?
Pre-swing is the transition phase between stance and swing, in which the foot is pushed and lifted off of the ground. Initial swing goes from 62-75% of the gait cycle. During initial swing, the hip, knee, and ankle are flexed to begin advancement of the limb forward and create clearance of the foot over the ground.
What is the beginning instant of the gait cycle?
Heel - strike: The beginning instant of the gait cycle is represented as initial contact of one foot with the ground , usually termed HS or foot-strike. ii. Foot - flat: The instant that the rest of the foot comes down to contact the ground and usually is where full body weight is being supported by the leg. iii.
How many times does the foot touch the ground during the gait cycle?
As noted earlier, within one gait cycle, each foot performs one ground contact (stance phase), respectively, and stays on the ground for about 60 to 62% of the entire gait cycle. consequently, the period where the foot is lifted off the ground (swing phase) accounts for about 38 to 40% of the entire gait cycle. in contrast to running, where both feet never touch the ground at the same time, there are two double contact periods during walking. Both feet are on the ground during the first and last 10% of the walking stance phase. The exact duration depends on individual walking velocity.
What are the steps of the gait cycle?
Two main steps of the gait cycle—the heel strike (HS) and the loading response (LR) steps, were simulated with the LS-DYNA software (LSTC, Livermore, CA). The initial position of the lower limb model corresponded to the HS configuration as defined by the multibody rigid model (i.e., multibody kinematic optimization). First, the HS activation levels computed from the multibody rigid model (i.e., static optimization) were applied to the fiber muscles of the deformable model according to a ramp function. From the previous configuration, the LR kinematics of the segments (corresponding to a 15 degree knee flexion) and the LR activation levels, both computed from the multibody rigid model, were applied to the rigid bones and the muscle fibers of the deformable model, also through a ramp function. The kinematics and the activation levels were maintained to stabilize the mechanical behavior of the explicit integration scheme. A slight mass scaling was added to increase the time step from 10−6 to 10 −5 s.
What is the swing period of a single limb support?
The four intervals include loading response, mid stance, terminal stance and pre-swing. 2.1.2 Swing period. The swing period constitutes approximately 40% of the gait cycle.
What is the human walking cycle?
Human walking can be described as a cyclic pattern of body movements which advances an individual’s position. Assuming that all walking cycles are about the same, studying the walking process can be simplified by investigating one walking cycle.
What is the stance phase?
The stance phase represents about 60% of the gait cycle. Describes the entire time the foot is in contact with the ground and the limb is bearing weight. This phase is begins with the initial contact of the foot on the ground, and concludes when the ipsilateral foot leaves the ground.