/images/library/2638/Sperm___Egg.jpg)
In simple terms, locomotion is the entire displacement of a body from one place to the other. It includes acts like crawling, running, walking, etc. during this process actions take place in the wings, limbs, and flagella
Flagellum
A flagellum is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals a…
What is locomotory movement of the body?
The movement and locomotion of body parts are carried out by specialised muscles that are muscular and non-muscular by nature. Human locomotory movement involves the interaction and movements of tissues and joints such as cartilage, muscles, ligaments, bones etc. Is this page helpful? Q1: What is Meant by Locomotion?
What is locomotion in living things?
All the living organisms exhibit a special characteristic feature of moving the whole or a part of the body from one place to another. What is Locomotion? Various kinds of motions such as walking, running, jumping, swimming, etc. by the body is known as locomotion.
Which muscles are responsible for movement and locomotion?
These skeletal muscles are mainly responsible for the movement and locomotion in the human body. Smooth muscles are also called involuntary muscles and controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
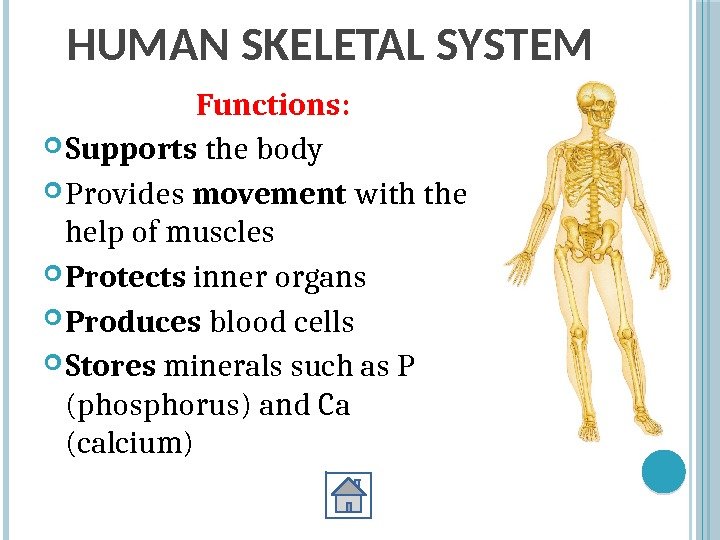
How does the skeletal system assist the body with locomotory movements?
The skeletal system assists the body with locomotory movements from one place to another The skeletal system helps in the movement of the sternum and the ribs, thus helping in the process of breathing. Based on elasticity, excitability and extensibility, there are three types of muscles involved in human locomotion.
What is the locomotion of a human?
Various kinds of motions such as walking, running, jumping, swimming, etc. by the body are known as locomotion. Movement is one of the characteristic features of all living organisms. Locomotion helps us to move from one place to other.
Why is locomotion important to humans?
Locomotion helps us in running through various conditions of the environment around us. The movement of limbs, trunk and head helps in changing the posture of the human body and maintaining equilibrium against gravity.
What is locomotion answer in short?
Locomotion is the ability to move and the act of moving from one place to another.
What is a locomotion in medical terms?
: an act or the power of moving from place to place : progressive movement (as of an animal body)
What are three types of locomotion?
Locomotion is the ability to move from one place to another and the three types of locomotion which are performed by living organisms include flight locomotion, swimming locomotion and land locomotion.
What organ system is responsible for locomotion?
the musculoskeletal systemThe locomotor system is also known as the musculoskeletal system. It is made up of the skeleton, skeletal muscles, ligaments, tendons, joints, cartilage and other connective tissue. These parts work together to allow your body to move.
What is locomotion explain with example?
Locomotion is the ability of an organism to move. Walking, running, swimming, jumping are the different types of locomotion.
What is the process of locomotion?
Locomotion in biology pertains to the various movements of organisms (single-celled or multicellular organisms) to propel themselves from one place to another. In multicellular animals, these movements include walking, running, jumping, crawling, climbing, swimming, flying, galloping, slithering, and so on.
What is type of locomotion?
The three types of locomotion are flight, swimming, and land locomotion. These types of locomotion are used by different animals and the type of locomotion is dependent on the environment.
What is locomotion in biology?
locomotion, in ethology, any of a variety of movements among animals that results in progression from one place to another.
What is the role of muscles in locomotion?
Muscles function in locomotion by 1, exerting torques which coiiper- ate with the other forces present in determining the movements of the body; 2, regulating energy exchange, by transmitting, absorbing, releasing and dissipating energy.
Which bone in man is concerned with locomotion?
Locomotion is the movement of organisms from one place to another. The femur and the acetabulum form the hip joint. Hence, the rotation of head of femur in acetabulum will lead to the movement of the legs and thereby, be help in locomotion.
What does locomotion indicate in a living thing?
Locomotion is the ability of an organism to move. Walking, running, swimming, jumping are the different types of locomotion.
Why is locomotion important to animals?
Animals move for a variety of reasons, such as to find food, a mate, a suitable microhabitat, or to escape predators. For many animals, the ability to move is essential for survival and, as a result, natural selection has shaped the locomotion methods and mechanisms used by moving organisms.
Is locomotion a characteristic of life?
Locomotion, reproduction, and growth are all characteristics of living things but they aren't the defining characteristics. This is because there are living things like plants, which cannot move and yet are living.
What is locomotion and movement in biology?
Movement is when the living organism moves a body part or parts to bring without a change in the position of the organisms. Locomotion is when the movement of a part of the body leads to change in the position and location of the organism.
1. What is Meant by Locomotion?
Locomotion: In simple terms, locomotion means the ability of moving from one place to another. The human walk has been explained as striding and is...
2. What is Meant by a Locomotory?
Locomotory Meaning: In medical terms, locomotory means an organ having the power of locomotion. Examples of locomotory organs are flagella, cilia,...
3. Write a Note on Skeleton Movement and Location with Respect to Locomotion Muscles
Please refer to the section above.
4. What is locomotion in plants?
Like organisms, plants also move from one position to the other. The change in their position is called locomotion. It can be bending, turning, twi...
5. What are the different stages of locomotion in a child’s development?
Locomotion is the activity to move from one place to the other. Different stages of locomotion in a child’s development are :Crawling and creeping...
6. What are non-locomotor movements?
When a human body moves around without traveling any distance, it is called a non-locomotor movement. For eg, the swinging of arms and legs, should...
7. What is the difference between locomotion and movement?
There is some fundamental difference between the two:In locomotion, the body changes its positions while in movement the body doesn't necessarily c...
8. Are the three systems that are muscular, nervous, and skeletal systems sufficient for locomotion?
Although the three systems are the muscular, nervous, and skeletal systems are very crucial in the function of movement, however, they are not suff...
Why do animals need locomotion?
Locomotion helps us to move from place to other. In general, animals require locomotion for defence, searching for food and shelter. The locomotory movement is the coordinated movement of various bones, tissues and joints such as cartilage, muscles, bone, ligaments, and tendons, etc.
What is the name of the movement of the body?
What is Locomotion ? Various kinds of motions such as walking, running, jumping, swimming, etc. by the body is known as locomotion. Movement is one of the characteristic features of all the living organisms. Locomotion helps us to move from place to other.
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
Functions of Skeletal System in Locomotion and Movement 1 The skeletal system provides a definite shape and posture to organisms 2 They provide a structural framework 3 It imparts protection to the internal organs that are delicate such as the spinal cord, Human brain, and the lungs 4 It assists the body in the locomotory movements from one place to another 5 The skeletal system also helps in the breathing process by the movement of the sternum and the ribs
What are cardiac muscles?
Cardiac muscles. The cardiac muscles consist of muscle fibres which are in short and striated form. The cardiac muscles are in the form of the branch and are found in the heart of the body. These muscles are also called involuntary muscles. Also Read: Muscular System.
What is the role of the skeletal system in the body?
The skeletal system plays a vital role in the locomotion and movement. The coordinated movement of skeletal muscles, bones, ligaments help in locomotion. The skeletal system provides a definite shape and posture to organisms. They provide a structural framework.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscles. Smooth muscles are also called involuntary muscles and controlled by the autonomic nervous system. These smooth muscles consist of a non-striated, slender type of tapering fibres. These muscles are found in the walls of the internal organs such as reproductive tract, blood vessels, alimentary canal, etc.
How many types of muscles are there in the human body?
Types of Muscles in the Human Body. There are three types of muscles in the human body based on the contractibility, elasticity, excitability, and extensibility. They are as explained below-.
Which muscle bends one part of a limb on another at a joint?
This muscle bends one part of a limb on another at a joint, e.g., biceps. It brings the fore arm towards the upper arm.
Which muscle presses the entire arm against the side?
This muscle brings a limb towards the mid line of the body, e.g., latissimus dorsi. It presses the entire arm against the side.
How are muscles attached to bones?
A muscle may be attached to a single bone or different bones by one end or by both the ends, either directly by epimysium or by way of inelastic connective tissue cords , the tendons.
How much of the body weight is muscle?
In humans muscles constitute about 40 to 50 percent of the total body weight.
Where does glycolysis occur?
It was proposed by Cori and Cori, who got Nobel prize with Houssay in 1947. This cycle occurs in the muscles and liver. During glycolysis lactic acid is produced from pyruvic acid in the muscles.
Which muscle turns the palm downward or to the posterior?
This muscle turns the palm downward or to the posterior, e.g., pronatorteres.
Where are the muscles found?
These muscles are found in the limbs, body wall, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus. These muscles are under the control of animal’s will. These muscles are normally attached to the skeleton. The major component of muscles is water.
What is active locomotion?
Active Locomotion. is based on a combination of Newton’s Laws. A body will move with a constant velocity until it experiences a net force ( . ). A change in body motion is achieved by initiating muscle contraction in order to apply a force against another object , such as the floor or the wall.
How is locomotion created?
Locomotion in cars is created by the reactionary friction force on the car tires from the road in response to the friction force from the tires on the road. Forward acceleration occurs when the force on the tires from the road is larger than the drag force, providing a net force in the forward direction.
How does walking at constant speed work?
Walking at constant average speed is achieved by alternating of forward acceleration caused when the floor pushes forward on your back foot, and backward acceleration caused by the floor pushing back on your front foot. These accelerations average out to zero so appears , but if you use a sensor capable of taking several measurements per second, then you can see the#N#oscillatory#N#nature of walking motion:
What is the meaning of "movement"?
movement or the ability to move from one place to another. an object's motion will not change unless it experiences a net force. for every force applied by an object on a second object, a force equal in size, but opposite in direction, will be applied to the first object by the second object.
What is the outward force supplied by an object in response to being compressed from opposite directions?
the outward force supplied by an object in response to being compressed from opposite directions, typically in reference to solid objects. the force of gravity on on object, typically in reference to the force of gravity caused by Earth or another celestial body.
Is the normal force greater than the body weight?
pushing up from the ground is equal to their . In order to jump, the muscles of the leg contract to push down against the floor. This downward push results in an equal reactive normal force from the floor, so that now the normal force is greater than body weight a there is an upward .
How much gravity does locomotion have?
On the other hand, it is contemplated that locomotion can occur under forces of up to 4.6g, since with a gravity greater than 5g, a well-trained athlete would no longer be able to get up from the bed or from a chair.
What is the function of the bones in the human body?
As the concept itself encloses in its terminology, it is easy to guess that the function of this system is locomotion . The bones are responsible for providing the mechanical basis for movement, since they are the places of insertion for the muscles (through the tendons) that serve as “lever” to perform the movement.
How many muscles are there in the human body?
Depending on whether the expert in question takes into account involuntary movement tissues or not, the human musculature can range from 639 pieces to 840.
What is the structure that attaches muscles to bone called?
Tendons: structures that attach muscles to bone.
What are some diseases that affect movement?
Some pathologies such as fibromyalgia, lumbar disc herniation, arthritis, osteoarthritis or lumbago are diseases that affect movement and are widespread in the population. For example, did you know that up to 80% of the global population will suffer at least one episode of low back pain in their lifetime? The prevalence, that is, the number of cases at any given time in Spain, is almost 15%.
Do humans have to deal with friction?
Luckily, humans do not have to deal with intense friction as the air is a homogeneous mixture of gases that is easy to navigate, but for other living beings the friction of the water or the ground is the main obstacle when it comes to moving. All these data, apparently anecdotal in nature, show how specialized the locomotor system of our species is: we are prepared to overcome the force of earth’s gravity, stand up, and perform movements in a medium composed mainly of air.
What is the meaning of locomotion?
Locomotion, in ethology, any of a variety of movements among animals that results in progression from one place to another.
What are the two types of locomotion?
Movement in animals is achieved by two types of locomotion, axial and appendicular. In axial locomotion, which includes the hydraulic ramjet method of ejecting water (e.g., squid), production of a body wave (eel), or the contract–anchor–extend method (leech), the body shape is modified, and the interaction of the entire body with the surrounding environment provides the propulsive force. In appendicular locomotion, special body appendages interact with the environment to produce the propulsive force.
What are the propulsive mechanisms of animals?
The diverse propulsive mechanisms of animals involve a contractile structure —muscle in most cases—to generate a propulsive force. The quantity, quality, and position of contractions are initiated and coordinated by the nervous system: through this coordination, rhythmic movements of the appendages or body produce locomotion.
What are the physical restraints of locomotion?
The physical restraints to movement—gravity and drag —are the same in each environment: they differ only in degree. Gravity is here considered as the weight and inertia (resistance to motion) of a body, drag as any force reducing movement. Although these are not the definitions of a physicist, they are adequate for a general understanding of the forces that impede animal locomotion.
How do aquatic animals overcome inertia?
To initiate movement, a sufficient amount of muscular work must be performed by aerial, fossorial, and terrestrial animals to overcome inertia. Aquatic animals must also overcome inertia; the buoyancy of water, however, reduces the influence of gravity on movement. Actually, because many aquatic animals are weightless—i.e., they possess neutral buoyancy by displacing a volume of water that is equal in weight to their dry weight—little muscular work is needed to overcome inertia. But not all aquatic animals are weightless. Those with negative buoyancy sink as a result of their weight; hence, the greater their weight, the more muscular energy they must expend to remain at a given level. Conversely, an animal with positive buoyancy floats to and rests on the surface and must expend muscular energy to remain submerged.
What causes a strong backward pull on an animal?
If the animal is streamlined (e.g., has a fusiform shape), the turbulence is low; if, however, the water layers from the sides meet abruptly and with different speeds, the turbulence is high, causing a strong backward pull, or drag, on the animal. Aerial locomotion also encounters resistance from drag, but, because the viscosity and density ...
What are some examples of passive locomotion?
There are also many animal species that depend on their environment for transportation, a type of mobility called passive locomotion. Some jellyfish, for example, have structures called floats that extend above the water’s surface and act as sails. A few spiders have developed an elaborate means of kiting; when a strand of their web silk reaches a certain length after being extended into the air, the wind resistance of the strand is sufficient to carry it away with the attached spider. In one fish, the remora, the dorsal fin has moved to the top of the head and become modified into a sucker; by attaching itself to a larger fish, the remora is able to ride to its next meal.
How many types of movements are there in the human body?
The human body exhibit four types of movements, they are as follows:
What is Movement?
The act of moving or changing one’s position is referred to as movement. When a live organism moves a bodily part or parts without changing its location, it is said to be moving. Locomotion occurs when a portion of the body moves, causing an organism’s position to change.
Does the saddle joint allow rotation?
iii. Although the saddle joint does not allow for rotation, it does allow for movement back and forth as well as side to side. The joint is present at the base of our thumb and helps in the movement of the thumb.