
How many loci in DNA?
- Count the frequency of alleles. For each allele in the genotype, examine a random sample of the population and count the proportion of matching alleles—that is, alleles that would be ...
- Calculate the frequency of the genotype at each locus. ...
- Calculate the frequency of the complete multilocus genotype. ...
- c1. ...
What does locus D3S1358 represent?
The D3S1358-locus belongs to the compound STRs where the repeat units are composed of two or more different repeat sequences. The test involves identifying the genetic profiles of the recipient and of the donor and then evaluating the extent of mixture in the recipient’s blood or bone marrow.
Is DNA found on genes?
Genes are made up of DNA. Some genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins. However, many genes do not code for proteins. In humans, genes vary in size from a few hundred DNA bases to more than 2 million bases.
What is locus biology?
What is a locus biology? In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait.
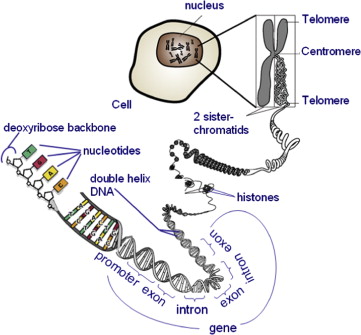
What is locus and allele?
Locus is the position of a gene on the chromosome. The alleles of a particular gene can be found in the same loci of the homologous chromosome pair. An allele describes a nucleotide sequence of a gene while a locus describes the position of that allele on the chromosome. This is the difference between allele and locus.
What is a locus vs gene?
A specific position along a chromosome is called a locus. Each gene occupies a specific locus (so the terms locus and gene are often used interchangeably). Each locus will have an allelic form (allele). The complete set of alleles (at all loci of interest) in an individual is its genotype.
Where is locus of a gene?
chromosomeA locus is a spot or “address” on a chromosome at which a gene for a particular trait is located in all members of a species. It can also refer to the location of a mutation or other genetic marker. A given locus can be found on any pair of homologous chromosomes (Brown, 2009).
How many locus are in a gene?
An allele is a variant form of a gene. Some genes have a variety of different forms, which are located at the same position, or genetic locus, on a chromosome. Humans are called diploid organisms because they have two alleles at each genetic locus, with one allele inherited from each parent.
How do you define locus?
1 : a place or site of an event, activity, or thing the integrity of the tissues determines the extent and locus of the damage— Sylvia E. Hines. 2 : the position in a chromosome of a particular gene or allele. locus. noun.
How do you describe a locus?
Definition. A locus, as related to genomics, is a physical site or location within a genome (such as a gene or another DNA segment of interest), somewhat like a street address. The plural of locus is loci.
What is locus made of?
Locus or loci (noun, “LO-kuss” and “LO-sigh”) Chromosomes are pieces of coiled DNA. They contain many individual genes — segments of DNA carrying instructions for making proteins. Together those genes help make a cell run.
What can a locus do?
Locust swarms devastate crops and cause major agricultural damage, which can lead to famine and starvation. Locusts occur in many parts of the world, but today locusts are most destructive in subsistence farming regions of Africa.
How do you find a locus?
Steps Involved in Finding Equation of Locus:Assume the locus point P(x, y)Write given geometrical condition.Use distance, section, centroid, and other formulae as per condition.Substitute in geometrical condition. Simplify to get the equation of locus.
How do you read a locus?
So, how exactly does one decipher the gene location? A universal code is followed for naming a locus. For example, the locus 11p15, read as 'Eleven-P-One-Five', tells us that the gene is on chromosome 11, on its 'p' arm or the short arm.
Is allele and gene same?
The short answer is that an allele is a variant form of a gene. Explained in greater detail, each gene resides at a specific locus (location on a chromosome) in two copies, one copy of the gene inherited from each parent. The copies, however, are not necessarily the same.
How many alleles are at a loci?
two allelesBecause loci are located on chromosomes, and we inherit one chromosome from each of our parents, each locus has two alleles. These alleles can recombine from generation to generation to produce different genotypes.
What is the plural of locus?
Locus. =. A locus is the specific physical location of a gene or other DNA sequence on a chromosome, like a genetic street address. The plural of locus is "loci".
What do we think about when we think about genes and chromosomes?
And one of the things that we think about when we're thinking about genes and chromosomes is we may think of the chromosome as a country, and then a region of a chromosome would maybe be the city, and then we'll get down to a very specific area, which is the locus, and that would be equivalent to, say, a person's street address.
What is the name of the site in a DNA test?
Sixteen of these sites are tested, each site is called a “locus”, (“loci” – plural).
What happens if DNA is not consistent?
If the DNA is not consistent, it will conclude that the alleged father can be excluded as the biological father of the child. * Each locus used in the testing is composed of a variable number of repeating short sequences of the bases A,C,T, and G; such as ACGACGACGACG.
What is an allele in a report?
The columns marked “allele” on the report contain numbers indicating the two alleles found at each locus (or one number if they are the same size). If, for example, a child has two alleles that are designated 12.1 and 18, and if the mother has alleles 12.1 and 16, then the child inherited the 12.1 allele from the mother.
Can you interpret DNA results?
A DNA result report can look confusing at first glance. If you read the statement of result under the genetic profile chart, then you should be able to interpret the outcome of the test.
Can a father be excluded from a child's DNA?
If the DNA of the alleged father is consistent (to a degree of mathematical certainty) with that of the child, then the report will conclude that the alleged father cannot be excluded as the biological father of the child. If the DNA is not consistent, it will conclude that the alleged father can be excluded as the biological father of the child.
Is a homozygous allele homozygous or heterozygous?
These two alleles are sometimes identical ( homozygous), but usually they are not the same size (heterozygous). During parentage testing, the laboratory identifies the length of the two alleles found at each locus.
What is the locus of a chromosome?
Locus (genetics) In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set ...
What is the order of loci in a genome called?
The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait .
How are chromosome bands visible?
The bands are visible under a microscope when the chromosome is suitably stained. Each of the bands is numbered, beginning with 1 for the band nearest the centromere. Sub-bands and sub-sub-bands are visible at higher resolution. A range of loci is specified in a similar way.
What is the shorter arm of a chromosome called?
The shorter arm of a chromosome is termed the p arm or p-arm, while the longer arm is the q arm or q-arm. The chromosomal locus of a typical gene, for example, might be written 3p22.1, where:
Where is the locus of OCA1?
For example, the locus of gene OCA1 may be written "11q1.4-q2.1", meaning it is on the long arm of chromosome 11, somewhere in the range from sub-band 4 of region 1 to sub-band 1 of region 2. The ends of a chromosome are labeled "pter" and "qter", and so "2qter" refers to the terminus of the long arm of chromosome 2.
How many genes are in a human chromosome?
Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000.
What is it called when a cell has the same allele?
Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map.
Definition
A locus is the specific location of a gene on a chromosome. Chromosomes are structures characterized by exhibiting complex packaging, made up of DNA and proteins.
Nomenclature
Biologists need to be able to refer to a locus precisely and their colleagues to understand the address.
What are genetic maps?
Techniques exist to determine the location of each gene on chromosomes, and this type of analysis is crucial for understanding genomes.
Linkage disequilibrium
What does it mean that one gene is "linked" to another? In recombination events, we say that a gene is linked if they do not recombine and stay together in the process. This occurs due to the physical closeness between the two loci.
Markers for the construction of genetic maps
Suppose we want to determine the position of a certain gene on the chromosome. This gene is the cause of a fatal disease, so we want to know its location. Through pedigree analysis, we have determined that the gene has traditional Mendelian inheritance.
How do we build a genetic map?
Continuing with our analysis, we choose a series of markers that are separated from each other by about 10 cM - this is the unit in which we measure the separation and it is read centimorgans. Therefore, we assume that our gene is located at a distance no greater than 5 cM from the markers.
What is the locus of a chromosome?
Together those genes help make a cell run. Locus is the word we use for the precise place where a gene is located on a chromosome. Figuring out the locus of a gene can be very important to understanding what it does.
What is DNA in biology?
DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid) A long, double-stranded and spiral-shaped molecule inside most living cells that carries genetic instructions. In all living things, from plants and animals to microbes, these instructions tell cells which molecules to make.
What is the name of the piece of DNA that contains the genes that make up a cell?
Chromosomes are pieces of coiled DNA. They contain many individual genes — segments of DNA carrying instructions for making proteins. Together those genes help make a cell run. Locus is the word we use for the precise place where a gene is located on a chromosome.

Content
Definition
- A locus is the specific location of a gene on a chromosome. Chromosomes are structures characterized by exhibiting complex packaging, made up of DNA and proteins. If we go from the most basic levels of organization in chromosomes, we will find a very long DNA strand wrapped in a special type of protein called histones. The union between both molecu...
Nomenclature
- Biologists need to be able to refer to a locus precisely and their colleagues to understand the address. For example, when we want to give the address of our houses, we use the reference system we are used to, be it house number, avenues, streets - depending on the city. Similarly, to deliver information about a specific locus, we must do so using the correct format. The compon…
What Are Genetic Maps?
- Techniques exist to determine the location of each gene on chromosomes, and this type of analysis is crucial for understanding genomes. The location of each gene (or its relative position) is expressed on a genetic map. Note that genetic maps do not require knowing the functioning of the gene, only its position needs to be known. In the same way, genetic maps can be constructe…
Linkage Disequilibrium
- What does it mean that one gene is "linked" to another? In recombination events, we say that a gene is linked if they do not recombine and stay together in the process. This occurs due to the physical closeness between the two loci. In contrast, if two loci inherit independently, we can conclude that they are far apart. The linkage disequilibrium is the central point for the constructi…
Markers For The Construction of Genetic Maps
- Suppose we want to determine the position of a certain gene on the chromosome. This gene is the cause of a fatal disease, so we want to know its location. Through pedigree analysis, we have determined that the gene has traditional Mendelian inheritance. In order to find the position of the gene, we will need a series of marker loci that are distributed throughout the genome. Then, we …
How Do We Build A Genetic Map?
- Continuing with our analysis, we choose a series of markers that are separated from each other by about 10 cM - this is the unit in which we measure the separation and it is read centimorgans. Therefore, we assume that our gene is located at a distance no greater than 5 cM from the markers. Then, we rely on a pedigree that allows us to obtain information about the inheritance …
References
- Campbell, N. A. (2001).Biology: Concepts and Relationships. Pearson Education.
- Elston, R. C., Olson, J. M., & Palmer, L. (Eds.). (2002).Biostatistical genetics and genetic epidemiology. John Wiley & Sons.
- Lewin, B., & Dover, G. (1994).Genes V. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- McConkey, E. H. (2004).How the human genome works. Jones & Bartlett Learning.