
What are the two uses of lubricating oil?
- It prevents the metal surface corrosion- Lubricating oil prevents the metal surface from any type of corrosion and roughness. ...
- It helps in controlling the friction between load-bearing surfaces- ...
- Helps in reducing the temperature by carrying away heat from friction and combustion of fuel-
What makes a good lubricant?
What to Look for in a Lube
- Natural Ingredients. Similar to most products, it’s beneficial to have all-natural labels. ...
- Water. If all else fails, pick a water-based lube. It’s a safe choice that won’t harm your body. ...
- Multipurpose. The lube you choose has to fit all your needs. If you’re hoping to get pregnant, that’s what the Pre-Seed Fertility Friendly Lubricant is for.
What is the main function of a lubricant?
The five basic functions of lubricating oil
- Basic Functions of Lubricating Oil. Friction is the resistance of a body or a substance that opposes a certain movement. ...
- Oil analysis and predictive maintenance. Predictive maintenance is a methodology that allows us to determine the actual operating conditions of each machine.
- Conclusion. ...
Which can be used as a lubricant?
What are things you can use as lube?
- Aloe vera. Surprisingly, a number of commercial lubricants contain aloe vera, a known skin soother, especially after a sunburn.
- Coconut oil. Oh coconut oil, let us count the ways we love you: your amazing smell, your antimicrobial and anti-fungal properties, and your slipperiness as a lube for anal and ...
- Actual lubricant. ...
What element is used as a lubricant?
Types of lubricants
- Mineral oil. The term " mineral oil " is used to refer to lubricating base oils derived from crude oil. ...
- Synthetic oils. Petroleum-derived lubricant can also be produced using synthetic hydrocarbons (derived ultimately from petroleum), " synthetic oils ".
- Solid lubricants. ...
- Aqueous lubrication. ...
- Biolubricant. ...
What is lubricant oil?
Lubricating oil, sometimes simply called lubricant/lube, is a class of oils used to reduce the friction, heat, and wear between mechanical components that are in contact with each other. Lubricating oil is used in motorized vehicles, where it is known specifically as motor oil and transmission fluid.
Why do we use lubricating oils in cars?
Use in Vehicles. The use of lubricating oils in vehicles is vital to their operation. When an engine is properly lubricated, it needs to put less work into moving pistons as the pistons glide easily. In the long run, this means that the car is able to operate while using less fuel and run at a lower temperature.
How is lubricant oil recycled?
Used lubricating oil is recycled at "re-refineries", where water is removed from the oil in a process of dehydration. Impurities within the used oil - such as industrial fuel - are separated out and the oil is captured using vacuum distillation. This leaves behind a heavy waste that contains oil additives and byproducts. The extracted lubricating oil then undergoes a series of refining processes to remove other impurities. Once refined, the oil is separated into three different viscosities for a variety of uses.
What happens to oil after it is refined?
Once refined, the oil is separated into three different viscosities for a variety of uses .
Why are mineral oils used?
Mineral lubricating oils are currently the most commonly used type because of the low cost of extracting the oils from crude oil. Additionally, mineral oils can be manufactured to have a varying viscosity, therefore making them useful in a wide range of applications.
Can you blend different oils together?
Lubricating oils of different viscosities can be blended together, and it is this ability to blend them that makes some oils so useful. For example, common motor oil - shown in Figure 1 - is generally a blend of low viscosity oil to allow for easy starting at cool temperatures and a high viscosity oil for better performance at normal running temperatures.
What is lubricating oil?
Background Information. Lubricating oil is a generic name for a wide range of products that are characterized by hundreds of base chemicals and additives. The most common lubricating oils are crude oil distillate fractions although both synthetic and plant-based lubricating oils are used.
What are the environmental releases of lubricating oil?
Environmental releases of unused lubricating oil have been reported. The largest releases have been associated with lubricating oil manufacture and storage. These oils, stored in large above-ground tanks, have been the subject of large releases similar to other petroleum hydrocarbon materials (e.g., fuels).
How does lubricant oil deteriorate?
Lubricating oils deteriorate in service in two primary ways: they become contaminated and they undergo physical and chemical changes due to oxidation.2 In engines the common contaminants are airborne dust and wear products, unburnt fuel, fuel combustion products, and water. The oxidation products are mainly acidic materials and asphaltenes. Asphaltenes in association with fuel contaminants and water tend to form solids such as sludges and lacquers that can coat component parts and become entrained in the lubricant. The acidic materials resulting from oxidation of the lubricant oil are generally weak organic acids. However, contamination by fuel combustion products (i.e., oxides of sulfur and nitrogen) is the source of almost all strong-acid contamination in lubricants. Recent trends in fuel compositions have resulted in the amount of sulfur, particularly in diesel fuels for automotive use, being reduced considerably. However, heavy fuel oils and residual diesel fuels can contain several percent of sulfur by weight. This sulfur is oxidized to sulfur acids, and sulfuric acid condensate may be encountered on the cooler surfaces. In petrol (gasoline) the sulfur content is now generally very small to negligible. Historically, halogen compounds added to gasoline as scavengers for lead-based antiknock compounds could be oxidized to halogen acids; however, with the general elimination of lead in this role, this is no longer of significant concern.
How does viscosity affect mineral oil?
The viscosity of a mineral oil depends strongly on its composition, with higher viscosity being associated with higher molecular weight. Generally, paraffinic oils have a higher VI than naphthenic oils, but the VI can be modified considerably by the use of suitable polymer additives, such as polybutene or polyacrylics. These increase the viscosity index of an oil and are often used as viscosity index improvers. As the temperature rises, these long-chain molecules occupy progressively larger volumes and increase the viscosity of the oil-polymer blend, thus increasing the value of VI. Under conditions of high shear rate, however, certain VI improvers may lose their effectiveness, and the viscosity will then drop sharply. Figure 4.4 illustrates this effect for two mineral oils which have the same value of viscosity at low shear rate, but differ in their behaviour at high rate. Prolonged shearing of the additive molecules can also lead to chain scission in some VI improvers, with permanent reduction in their effectiveness. Resistance to shear thinning and degradation varies between different VI improvers.
Why is lubricant oil unsuitable?
A lubricating oil may become unsuitable for its intended use as a result of one or several processes, notably oxidation, water and air contamination (foaming, air release, demulsibility), partial evaporation, additive depletion, accumulation of contaminants, including wear debris, thermal or biological degradation.
What happens if water is dissolved in oil?
Water contamination is a problem for machine health. Water affects viscosity, promotes oil degradation and equipment corrosion, and interferes with lubrication. More precisely, water contamination (from leaking heat exchangers and seals, condensation, etc.) in fluid systems may cause fluid breakdown (such as additive precipitation and oil extraction), reduced fluid viscosity and lubricating film thickness, accelerated metal surface fatigue, galvanic corrosion, loss of dielectric strength in insulating oils, etc. Even low concentrations of moisture (< 100 ppm) can have a meaningful negative impact on machine components such as bearings [24]. In particular, it has been observed that the fatigue life of bearings can be extended considerably by reducing the amount of water in petroleum-based lubricants. Typical water saturation levels are 30–50 ppm for transformer oils and 100–1000 ppm for hydraulic fluids, depending on the specific grade. Below the saturation level water will completely dissolve in the oil. The saturation level increases at higher operating temperatures. Water contamination is a common occurrence for hydraulic fluids because of their hygroscopic nature. Hydraulic system operation may be compromised when water contamination reaches 1–2%. The separation of small droplets of water can be assisted using centrifuges or coalescers. Dissolved air (and other gases) in oil systems may cause foaming, slow system response with erratic operation, higher fluid temperatures, pump damage due to cavitation, inability to reach full system pressure, and acceleration of oil oxidation.
How does oxidation affect lubrication?
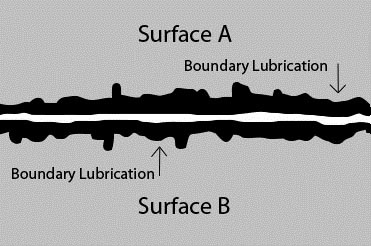
Oxidation has an impact on the lubrication performance of vegetable oils (see Table 14.6) and quite possibly also plays a role in the lubrication process itself. Correlating studies of oxidation with lubrication performance will lead to greater understanding into the role of oxidation in the lubrication mechanism of vegetable oils [25]. Controlling the consequences of oxidation degradation (deposits, varnish and residue formation) begins with controlling the oxidative processes within the system. Additives are used to help stop, or at least postpone, oxidation. As antioxidants are meant to be gradually consumed by chemical reaction with oxygen, this determines reduced oxidation protection and stability with time. Once antioxidant additives are consumed, oxidation can continue unabated. Additive depletion is thus a cause of degradation of lubricants. Also water may react with additives. For example, zinc dialkyldithiophosphate (ZDDP), an AW additive commonly used for boundary lubrication applications in high-pressure pumps, gears and bearings, is destroyed by chemical reaction with water at operating temperatures above 60 °C. The end result is premature component failure due to metal fatigue. The effects of additive depletion may also be illustrated for turbine lubricating oil where R&O-inhibiting agents are essential. Water may deplete such inhibitors and increase the rate of rusting.
What is lubricating oil?
Continue Reading. Lubricating oil is also called the blood of an engine. It is the class of oils used to reduce the friction, heat, and wear between mechanical components that are in contact with each other. The lubrication system has consisted of the oil pan, oil pump, oil filter, and oil passages.
Why do machines use lubricating oil?
Machines which have rotating/sliding components use lubricating oil to reduce friction in moving parts. For simplest example consider an old rusty pad lock, it is very inconvenient to use because its shackle is very hard to press and once locked it is very hard to turn the key.
What is the property of reducing friction?
The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. Lubricant oil manufacturers use 90% base oil and less than 10% additives. Vegetable oils or synthetic liquids such as hydrogenated polyolefins, esters, silicones, fluorocarbons, and many others are sometimes used as base oils.
What is liquid lubricant used for?
Synthetic lubricants are used in turbines, vacuum pumps, and semiconductor devices. Liquid lubricants are also used in certain medicines.
What is engine oil used for?
Another example is an automobile engine, engine oil/lubricating oil is used to reduce friction between pistons and cylinders so that pistons may slide up and down in the cylinders smoothly thereby avoiding wastage of fuel energy in overcoming friction.
What is oil based lubricant?
so, in any conceivable situation where metal touches metal, you will likely find some type of oil based lubricant, often specifically formulated to address the existing condition where contact occurs. 26 views.
Why is coolant used in engines?
Coolant in engine is used to absorb the heat of the engine. It is used in radiator and circulated outside the engine. Water is used as coolant but now a days chemicals are used along with water. They prevent the rusting, cool engine fast and doesn't freeze.
What is lubricating oil?
Lubricating oil is an oily substance that is used to cover or treat machinery so as to lessen friction. It is a class of oils used to reduce the friction, heat, and wear between mechanical components that are in contact with each other. Lubricating oil is used in motorized vehicles, where it is known as motor oil and transmission fluid.
What is lubricant in machinery?
Lubricants are materials that help reduce the wear and tear in machines, equipment, industrial gears and other industry machinery. They are usually liquids, fluids, oils, which complement easy functioning and smooth running of these equipment. Time-to-time lubrication with the best industrial or specialty lubricants is necessary for a machine’s long life.
Why is lubricant oil so thin?
Since the function of a lubricant oil is to prevent metal parts from coming in direct contact with each other, if it becomes too thin because of the heat and the motion of the parts inside the engine, friction points might be created.
What is multi grade oil?
Multi-grade oil is oil that has viscosity modifier additives in it. These additives allow the oil to flow differently under cold and hot conditions. Multi-grade, or multi-weight oil is designated with two numbers. The first one is followed by the letter “W”. This first number indicates the viscosity (weight) of the oil in Winter (cold), and the second number indicates the viscosity (weight) of the oil under normal engine temperature (hot).
Why is engine oil important?
When it comes to longer and healthier life of your vehicle's motor, engine oil plays a vital role in it. High quality oil is important and fundamental characteristics of your vehicle depends on it like smooth running, fuel efficiency, performance and emissions
Is lubricant oil volatile?
Lubricating oils are flammable, but they are not volatile, so are not easy to ignite unless heated.
Can engine oil have high viscosity?
If you are talking about engine lubrication oil, it cannot have too high a viscosity, as it must flow easily through the filter and through the tiny ducts inside the engine,
