Top 3 Dynamic Lumbar Stabilization Exercises
- Working on Three Planes. Dynamic lumbar stabilization exercises are essential for strengthening your core muscles to protect your back and prevent back pain.
- Dynamic and Static Stabilization Exercises. Your body moves on three anatomical planes. ...
- The Three Progressive Exercises. ...
What are the best exercises for the lumbar spine?
This exercise will help strengthen the muscles in your lower back:
- Lie on your back on the floor or an exercise mat.
- Activate your core and butt muscles to flatten your back on the floor, tilting your pelvis slightly forward.
- Hold the position for five seconds.
What exercises to do after a lumbar microdiscectomy?
To perform the exercise:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent.
- Slowly lift your bent knees up towards your chest, and grasp your knees with both hands.
- Gently pull your knees toward your chest, and hold the position for 1 or 2 seconds.
- Slowly lower your knees back down to the starting position.
- You can perform the supine lumbar flexion exercise for 10 repetitions.
What is the best workout to strengthen core stability?
What Are 5 Exercises For The Core?
- Plank. The king of static core exercises, the starting position simple. ...
- Ab wheel rollout. Set up kneeling for this one and take the ab wheel by the handles. ...
- Pallof press. This one is best done with a resistance band. ...
- Windshield wipers. ...
- Alternating V-ups. ...
What are the best exercises to strengthen back?
6 Exercises To Strengthen Your Lower Back And Core
- Bird Dog (Alternate both sides)
- Glute Bridge
- Prone Leg Raises
- Plank
- Side Plank
- Dead Bug (Alternate both sides)

What is stabilizing the spine?
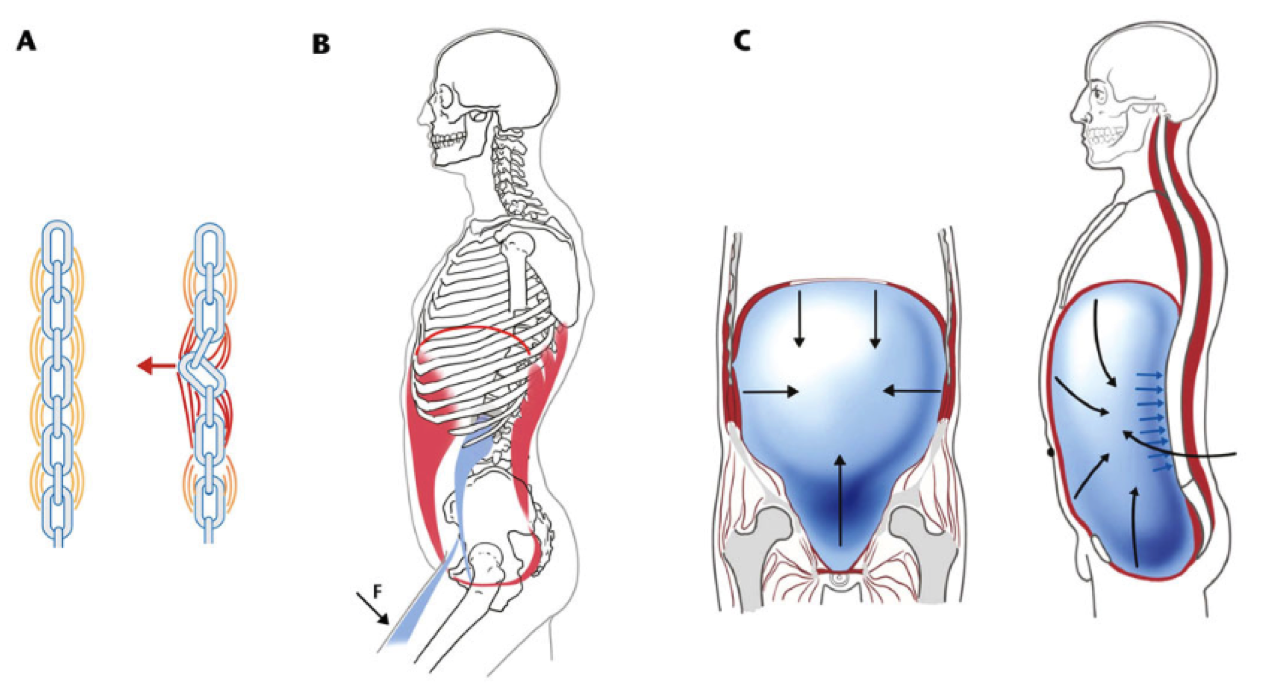
In normal trunk function, co-contraction of the TrA and MF muscles stabilizes the spine when the limbs are moved and occurs independently of contraction of the larger, multisegmental, superficial muscles of the trunk, such as the erector spinae and rectus abdominis, which move the trunk.
What is dynamic lumbar stabilization?
Dynamic lumbar spine stabilization is a surgical technique that stabilizes the spine with flexible materials to allow for more mobility in the spine than traditional spinal fusion surgery.
How do you treat lumbar instability?
TreatmentsPhysical therapy can help treat mild cases of spinal instability by strengthening the muscles in the spine.Prescription painkillers and anti-inflammatory medicines.Microdiscectomy — a surgical procedure that removes the intervertebral disc impinging on the spinal nerve.More items...•
Why is lumbar stabilization important?
Lumbar stabilization is an active form of exercise used in physical therapy. It is designed to strengthen muscles to support the spine and help prevent lower back pain.
What is the lumbar stability test?
The patient is in supine position and then the examiner asks the patient to lift both lower extremities. The knees must be extended. Then the examiner asks the patient to return slowly to the start position. If the lower extremities fell down instantly because of the low back pain , the test was positive.
What are the symptoms of lumbar instability?
Symptoms of Lumbar Instability Pain may also be accompanied by weakness in the leg or foot. Abnormal movement can also trigger extremely painful muscle spasms. Signs of spinal macro-instability may start with spine pain, or weakness and/or numbness of the arms or legs.
How can I make my lumbar stronger?
Step 1: Lie on the back with the knees bent and the arms down by the sides of the body. Step 2: Keep the spine in a neutral position and pull the bellybutton toward the spine. Step 3: Inhale. Step 4: Exhale while tightening the abdominal muscles, drawing the bellybutton toward the spine.
How do you strengthen your lumbar?
1. BridgesLie on the ground with your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.With your hands by your sides, press your feet into the floor as you slowly lift your buttocks off the ground until your body is in one straight line. Keep your shoulders on the floor. ... Lower down.Repeat 15 times.Perform 3 sets.
What does dynamic stabilizer mean?
Dynamic stabilization is a surgical technique designed to allow for some movement of the spine while maintaining enough stability to prevent too much movement. This type of operation is considered an alternative to lumbar fusion surgery in some situations.
What's another term for dynamic stabilization?
Dynamic stabilization, also called flexible or soft stabilization, is a growing area of spine surgery that potentially can reduce some of the problems inherent with metal implants.
What is dynamic muscular stabilization?
Dynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization (DNS) is an assessment and treatment modality in physical therapy, chiropractic and personal training fields. DNS works by stimulating the central nervous system to retrain the neurophysiological aspect of the locomotion system.
What is Dynamic Stability in exercise?
Dynamic core stability physiotherapy refers to the ability to stabilise the lower back and pelvis region during complex movements through the correct recruitment of the deep muscles of the abdomen, lower back and pelvic floor.
What are some exercises to stabilize the lumbar muscles?
Lumbar Stabilization Exercises #1: Hamstring Stretches. Advertisement. Tightness of the hamstring muscles leads to increased stress in your lower back. Stiff hamstring muscles can ruin your posture, affect balance and cause back pain.
Why do we do lumbar stabilization exercises?
Lumbar stabilization exercises are done in an effort to improve muscle balance and flexibility of your back. However, lumbar stabilization exercises are not as simple as a set of exercises to follow at home and must be done under the supervision of an expert. Back pain or other problems arising due to lumbar instability often need proper medical ...
How to do hamstring stabilization?
They can be done anywhere and at any fitness level. Lay down on your back. Keep your knees bent and your soles on the ground. Maintain your neutral spine position.
How to relax your back?
These lumbar stabilization exercises are a great way to relax your back and improve your balance and co-ordination. Lie on your back, on a yoga mat with arms by your sides. Keep your knees bent at 90 degrees and soles touching the mat. Inhale and engage your abdominal muscles throughout the exercise.
Why do lumbar vertebrae stay in neutral position?
Regular movements and your daily activities get compromised with back-pain. In order to maintain a healthy and stable spine, it is necessary for the lumbar vertebrae to stay in the ‘neutral spine position’, which means they should be perfectly balanced. Lumbar stabilization exercises are done in an effort to improve muscle balance ...
What is lumbar stabilization?
Lumbar stabilization exercises are a part of such a therapeutic program and are advised according to the condition of the patient. Lumbar stabilization exercises are imparted through a complete lumbar stabilization program, which includes proper medical consultation and evaluation to plan an individual exercise system.
What is hip bridge exercise?
While being an excellent exercise for your posterior and your thighs, the hip bridges exercise is also great for stretching and strengthening the lumbar spine. Apart from being a superb lumbar stabilization exercise, it also helps you to work on your balance.
What are the goals of lumbar stabilization exercises?
The goals of lumbar stabilization exercises include: Reduce amount of back pain. Gain control over the movements of—and forces acting on—the spine during daily activity. Heal soft-tissue injury, such as muscle strain and torn ligaments.
What is lumbar stabilization?
Lumbar stabilization is an active form of exercise used in physical therapy. It is designed to strengthen muscles to support the spine and help prevent lower back pain. Through a regimen of exercises, and with the initial help of an experienced physical therapist, the patient is trained to find and maintain her/his "neutral spine" position.
Why is a neutral spine important?
The benefits of the neutral spine include: Allows the various forces acting on the discs and vertebrae to be distributed in a more balanced manner. Keeps the patient's posture near his/her "center", enabling the patient to react more quickly (either forward or backward) when necessary.
What is the role of posture in a patient?
Keeps the patient's posture near his/her "center", enabling the patient to react more quickly (either forward or backward) when necessary
Is lumbar stabilization exercise one size fits all?
Each patient will present different problems, and there is no "one-size-fits-all" in lumbar stabilization exercise. The physical therapist will then work with the referring physician and the patient to develop a therapy plan. This process begins with helping the patient find her/his neutral spine through positioning, discussion, and feedback.
Why do we do stabilization exercises?
There are different reasons why we might give stabilisation exercises to patients with lumbar instability. The most important considerations are our treatment goals and the likelihood of a positive response to treatment. An important study by Hicks et al shows that during the examination of lumbar instability positive and negative determinants can be found indicating whether a subject will benefit from a low back stabilization program.#N#There are indications that stabilization exercise programs are used to improve the strength, endurance and/or motor control of the abdominal and lumbar trunk musculature. Stabilisation exercise programs exist of general exercises, educational and workplace-specific back school classes, increase of workload tolerance, psychological interventions and segmental stabilization exercises. The stabilizing exercises focus on the re-education of a precise co-contraction pattern of local muscles of the spine.#N#It had been shown that stabilizing exercises along with routine exercises help with the reduction of pain intensity while increasing functional ability and muscle endurance. Stabilizing exercises are therefore recommended in the treatment of patients with lumbar segmental instability.
What is lumbar instability?
Lumbar instability - is a significant decrease in the capacity of the stabilizing system of the spine to maintain the intervertebral neutral zones within the physiological limits so that there is no neurological dysfunction, no major deformity, and no incapacitating pain.
Why use repeated movements of the lumbopelvic region?
Use repeated movements of lumbopelvic region, in non-weightbearing positions initially, to improve position sense. Implications for practice of the local muscle system with the global muscle system. Training the local and weightbearing muscles is likely to reverse impairments in the non-weightbearing muscles.
What is the phase of a squat?
Prone kneeling with shoulders directly above the hands and hip above the knees. Phase 1 (a): no lumbar or pelvic movement should occur. Phase 2 (b): posterior pelvic tilt and hip flexion occur. Phase 3 (c) :Lumbar flexion and some thoracic flexion finish the action.
What muscles are used to stabilize spinal cord?
Optimal spinal stabilization can be achieved by strengthening the deep back and abdominal muscles. These include the transversus abdominus, quadratus lumborum, oblique abdominals, multifidus and erector spinae. Exercises targeting these specific muscles should be done in a progression, usually beginning with transversus abdominus which provides the patient with initial stabilization that is helpful during subsequent exercises and daily activities.
How much muscle intensity is required for transversus abdominus?
Progression: Gradually build up the duration of the contraction. Only when the patient can activate transversus abdominuswith minimal muscle intensity (10 repetitions each 30-40%) over a period of time, should more advanced exercises be added. [6]
How to self palpate L4-L5?
Self-palpate the L4-L5 level by placing the thumbs on the lower lumbar spinous process and moving them outward slightly into the spinal tissue. Place the weight onto the front leg and then onto the back leg alternately. Feel the muscles beneath the thumbs switching on and off. YouTube. daney20.
What Are Stabilization Exercises and Why Are They Important?
The purpose of stabilization exercises is to activate the muscles you normally don’t target when you train on a stable surface. The muscles in your body can be divided into two main types: movers and stabilizers. The job of the movers is pretty obvious: they’re designed for movement.
Which muscle is the main stabilizer of the shoulder?
Several ligaments provide stability but the major stabilizers are the rotator cuff muscles – the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor. These muscles work as a team to keep the shoulder stable. The lower trapezius muscle also helps stabilize and protect the rotator cuff muscles from injury.
Why do squats work more than leg extensions?
For example, squats work stabilizing muscles far more than leg extensions because your stabilizers are activated to keep you balanced. When you do leg extensions on a bench or machine, your body is already stable because you’re sitting during the exercise and the stabilizing muscles don’t have to work harder.
How does stance affect stabilizing muscles?
Another tip – your foot stance can impact how hard your stabilizing muscles work. By placing your feet closer together, your body is less stable and the trusty stabilizer muscles have to kick in. Placing one foot directly in front of the other when doing an exercise creates the same lack of balance that forces the stabilizer muscles to work harder.
What happens if you stand on one leg and your hip is off the ground?
That might not seem like a problem until you consider that a strong gluteus medius stabilizes your pelvis when one leg is off the ground. Without this stability, you’re at higher risk of knee injury. In fact, if you have a weak gluteus medius and you stand on one leg, your hip may drop on the opposite side.
Why do you need a stabilizing muscle?
Stabilizers hold things in place when you move so that that you don’t get injured when you train.
What is the deep stabilizing muscle called?
These include the deep muscles in your core and back that hook directly to your spine. One of the most important deep stabilizing muscles is called the multifidus, a stabilizer that supports your spinal column. Dysfunction of this muscle is strongly linked with back pain. No wonder!
What muscles support and stabilize your spine?
There is evidence that not only do your back and abdominal muscles contribute to the stability of your spine and pelvis, they also support your low back when the stability of your spine is challenged. Therefore, achieving control and coordination of these muscles is critical to achieving fully sufficient stability of your back.
Tabletop Isometric Hold
Lie on your back with bent knees and the soles of your feet on the floor. In this position, the natural curve of your lumbar spine will lift the lower back slightly off the floor.
Segmental Bridge
Lie on your back with bent knees and the soles of your feet on the floor. In this position, the natural curve of your lumbar spine will lift the lower back slightly off the floor.
Dead Bug
Lie on your back with bent knees and the soles of your feet on the floor. In this position, the natural curve of your lumbar spine will lift the lower back slightly off the floor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Sit-ups – this exercise puts a lot of pressure on your spine, increasing the risk of disc herniation injuries.
Conclusion
There are multiple layers of short, long, and thick muscle groups supporting each segment of your vertebrae throughout the length of your spine. As you can see, your spine is structurally and anatomically strong and can withstand the strain and stress of your everyday activities.