Full Answer
How do you calculate residual volume?
Residual volume – represents the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a forced expiration and is more complex to determine, being measured indirectly. Average value is around 1.2 L for males and 1.1 L for females. Functional residual capacity = Expiratory reserve volume + Residual volume. In short: FRC = ERV + RV
How to measure residual volume?
Residual volume is the amount of air that remains in a person's lungs after fully exhaling. Doctors use tests to measure a person's residual air volume to help check how well the lungs are functioning. Residual volume is measured by: A gas dilution test.
What is the formula for residual volume?
what is the formula for measuring residual volume using the helium dilution method? V2=V1(C1-C2)/C2 (V=volume; C=helium concentration) ______ are the sum of two or more lung volumes
What is normal residual volume?
Residual volume (RV) is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximum forceful expiration. In other words, it is the volume of air that cannot be expelled, thus causing the alveoli to remain open at all times. The residual volume remains unchanged regardless of the lung volume at which expiration was started. Reference values for residual volume are 1 to 1.2 L, but these values are ...
See more
What is residual volume in the lungs?
Residual volume is the amount of air that remains in a person's lungs after fully exhaling. Doctors use tests to measure a person's residual air volume to help check how well the lungs are functioning. It is normal to have some air remain after exhaling to keep the lungs from collapsing.
Why is residual volume important for the lungs?
Residual volume is necessary for breathing and proper lung function. This air that remains in the lungs is also important for preventing large fluctuations in respiratory gases—oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Why would a patient have high residual volume?
Increased lung volumes, particularly residual volume (RV), are commonly observed in airway obstruction. TLC may be normal, but is frequently increased in the late stages of COPD. Hyperinflation and air-trapping are terms commonly used to reflect these changes, but are not well standardized.
What does low residual volume mean?
Residual volume is the only lung volume that is not decreased with respiratory muscle weakness. Residual volume is the amount of air left in the lungs at the end of a maximal expiration and is typically increased due to the inability to forcibly expire and remove air from the lungs.
Why is residual volume above normal in a patient with emphysema?
Why is RV above normal in a patient with emphysema? The lungs empty slower than normal. Why did the asthmatic patient's inhaler medication fail to return all volumes and capacities to normal values right away? The smooth muscle in the bronchioles didn't return to normal plus mucus still blocks the airway.
What is residual volume quizlet?
Residual Volume (Definition) Volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum expiration.
Why does residual volume increase in COPD?
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exhibit increases in lung volume due to expiratory airflow limitation. Increases in lung volumes may affect upper airway patency and compensatory responses to inspiratory flow limitation (IFL) during sleep.
What is the function of residual volume?
Function. The residual volume functions to keep the alveoli open even after maximum expiration. In healthy lungs, the air that makes up the residual volume is utilized for continual gas exchange to occur between breaths. Inspiration draws atmospheric oxygen into the lungs to replenish the oxygen-depleted residual air for gas exchange in ...
What is residual volume used for?
An interesting clinical use for residual volume is applied during post-mortem autopsies of drowning victims. The residual volume of air in the lungs can only be removed if it is replaced by another substance. In the case of drowning victims, water will replace the residual air in the lungs. During autopsies, medical examiners can clamp the trachea and submerge the lungs in water. If the lungs sink, no residual air remains, so it is likely the person drowned after inhaling large amounts of water. However, if the lungs float, the residual volume of air remains in the lungs. The residual volume was not replaced by water, so it is likely the person died before entering the water.
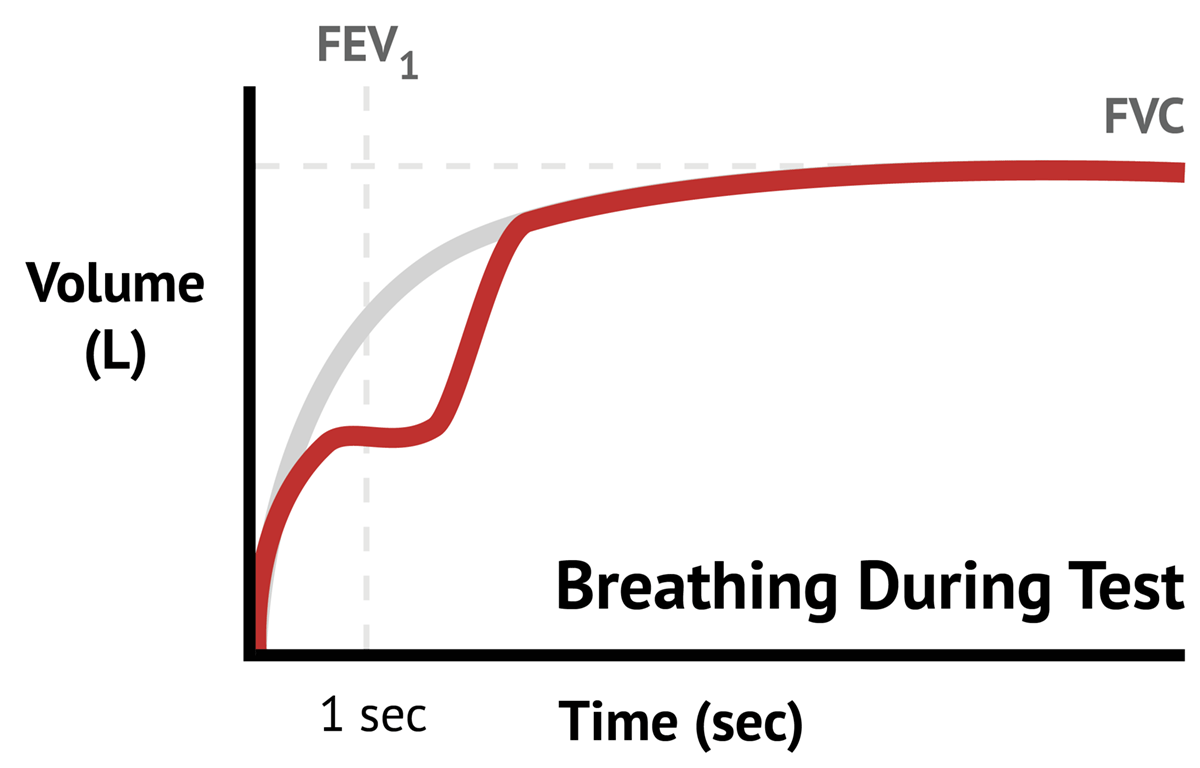
What is the FRC of a spirometry?
FRC is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after a normal, physiologic expiration (Figure 1A). The TLC, FRC, and RV are absolute lung volumes and cannot be measured directly with spirometry. Instead, they must be calculated using indirect measurement techniques such as gas dilution or body plethysmography.
What causes airway closure?
In obstructive lung disease, inflammation and decreased elastic recoil cause increase airway resistance and lead to earlier small airway closure during expiration. The premature airway closure increases the volume of air retained in the lungs at the end of expiration; this is referred to as air trapping.
What is the volume of air entering and leaving the lungs called?
During tidal breathing, the inspiration and expiration at physiologic rest, the volume of air entering and leaving the lungs is known as the tidal volume (TV).
How to measure FRC?
To conduct the test, a patient is placed inside an enclosed chamber and breathes through a spirometer that can measure changes in pressure and volume. After a period of tidal breathing, the spirometer is closed at end-expiration, and the patient breathes against it. Changes in pressure at the mouthpiece are recorded. As the patient exhales, the volume of the thoracic cavity can be calculated by recording the change in pressure of the entire chamber. This test is the most accurate measure of FRC, but also the most expensive.
Why does pressure decrease in the alveoli?
The pressure inside the airways (Paw) slowly decreases as you move up from the alveoli to the trachea as a result of increased airway resistance. In sections of small, non-cartilaginous airways, pleural pressure is greater than airway pressure and causes a collapse of the airway (Figure 1B).
What is RV in a person's lungs?
Residual volume (RV) is the amount of air that remains in a person’s lungs after maximum exhalation. In other words, this is the volume of air that we can’t possibly get out of our lungs, meaning that the lungs are never completely empty of air. Otherwise, they would collapse as the tissue sticks together. On average, a person’s RV is about a liter and doctors can run special tests to find a person’s RV, as it can indicate lung health.
What is minute ventilation?
Minute ventilation – The volume of air that is breathed in and out within a minute.
Can a restrictive lung disease expand the lungs?
In a restrictive lung disease, lungs can’t be expanded to the normal amount. What we find usually is a RV that is ordinary, because the flow of air in the airways is not hindered.
Is residual volume higher than normal?
D is correct. The residual volume in obstructive lung diseases is higher than normal due to the difficulty of complete exhalation.
How to measure lung volume?
The method for measuring lung volumes is based on the equilibration of gas in the lung with a known volume of gas containing helium. This technique involves the subject being connected to a spirometer filled with 10% helium in oxygen.
What is the volume of air in the lungs called?
Lung volumes are also known as respiratory volumes. It refers to the volume of gas in the lungs at a given time during the respiratory cycle. Lung capacities are derived from a summation of different lung volumes. The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air.
What is the normal ERV value?
It is the volume of air that can be exhaled forcibly after exhalation of normal tidal volume. The normal adult value is 700-1200ml. ERV is reduced with obesity, ascites or after upper abdominal surgery
What is the purpose of measuring lung volume?
Measurements of lung volume are important for a correct physiological diagnosis, however, its role in the assessment of disease severity, functional disability, the course of disease and response to treatment remains controversial. Measurement can be done using Spirometry see..., Body plethysmography, Nitrogen washout and Helium dilution with the latter three techniques used in measuring static lung volumes .
What is the tidal volume?
Lung Volumes. Tidal Volume (TV) It is the amount of air that can be inhaled or exhaled during one respiratory cycle. This depicts the functions of the respiratory centres, respiratory muscles and the mechanics of the lung and chest wall.
What is the normal value of FRC?
It is calculated by adding together residual and expiratory reserve volumes. The normal value is about 1800 – 2200 mL. FRC = RV+ERV.
Why is lung volume important?
Measurements of lung volume are important for a correct physiological diagnosis, however, its role in the assessment of disease severity, functional disability, the course of disease and response to treatment remains controversial.
What is the volume of air inhaled or exhaled during resting breath?
The volume of air inhaled or exhaled during this rest breathing is the tidal volume. So, tidal volume is defined as “The volume of gas inhaled or exhaled during the resting breath is called tidal volume ”.
What is lung capacity?
Actually, lung capacity is measured in volume. Lung volume is the volume of gas during each phase/ part of respiration. For example, there is a certain volume of gas we all inhale during our normal respiration (i.e respiration during rest).
What is the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled during a forceful inspiration?
Inspiratory reserve volume is the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled during a forceful inspiration. Actually, it is the additional air to the tidal volume that can be inspired during the forceful inspiration.
What is the difference between restrictive and obstructive pulmonary disease?
The difference between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disease. Obstructive and Restrictive pulmonary disease shows different lung volume and capacities. In restrictive pulmonary disease, all the capacities of lung reduces and in obstructive pulmonary disease it all increases. Let us try to understand it through this graph.
What is the volume of air that can be inspired from the end of the tidal expiration?
Inspiratory capacity is the volume of air that can be inspired from the end of the tidal expiration or volume of air that can be inspired forcibly after a normal inspiration.
What is the measure of the amount of air in the lungs when we breathe normally and forcefully?
Lung volume and capacity. Lung volume and capacities are the measures of the amount of air in the lungs when we breathe normally and forcefully. During respiration, there occurs the movement of air in and out of the pulmonary system. When we respiration is normal, the lesser amount of air moves in and out which increases when we rate ...
What is the expiratory reserve volume?
Expiratory Reserve Volume is defined as the amount of air that can be expelled during forceful expiration. Now, close your eyes and after taking normal inspiration, try to exhale the maximum amount of air possible. This extra amount of air in addition to normal expiration is ERV.
What Determines Residual volume?
- Residual volume is determined by two competing factors. 1. The strength of the expiratory muscles and the inwards pull of the lungs tends to decrease residual volume. 2. The outward pull of the chest wall tends to increase residual volume.
Why Do We Need Residual volume?
- The lungs are never completely empty; there is always some air left in the lungs after a maximal exhalation. The air that remains in the lungs is needed to help keep the lungs from collapsing. If this residual volume did not exist and the lungs were completely empty, the tissues that make up the lung would could and stick together, making it almost impossible for us to re-inflate and forc…
How Is Residual Volume Measured?
- There is no way to measure residual volume directly, but it can be calculated indirectly with a pulmonary function test. Other lung volumes and capacities must first be measured directly, usually with spirometry, before RV can be calculated. The first step in calculating RV is to determine the functional residual capacity (FRC). Measurement of the FRC can be done using on…