
What is macrodactyly?
A child's hand with large fingers present in macrodactyly Macrodactyly is a congenital condition in which a baby is born with abnormally large fingers or toes due to an overgrowth of the underlying bones and soft tissue. Macrodactyly occurs more often in hands than the feet. One or more fingers or toes may be involved.
Is there a treatment for macrodactyly of the foot?
Macrodactyly of the foot Toe amputation, which is cosmetically unappealing, is not effective for treating macrodactyly of the lesser toes and does not address the enlargement of the forefoot. Ray resection results in the best cosmetic and functional outcomes in feet with involvement of the lesser toes. When the great toe is …
What does static macrodactyly look like in children?
If your child has static macrodactyly, their affected fingers or toes will generally be about one-and-a-half times the length and width of the unaffected digits. If their condition is progressive, the involved fingers or toes can become enormous. What causes macrodactyly?
How is macrodactyly diagnosed in children?
Most children are born with obvious signs of macrodactyly. Occasionally, this condition presents a bit later, when the child is a year or two old. At Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), diagnosing macrodactyly typically begins with a physical examination of your child’s affected hand or foot.
What is macrodactyly?
What is macrodactyly in the fingers?
What is a static finger?
When do macrodactyly affected fingers grow?
What are the conditions that cause macrodactyly?
How old is a child when they have macrodactyly?
Can a macrodactyly be a benign condition?
See 4 more
About this website
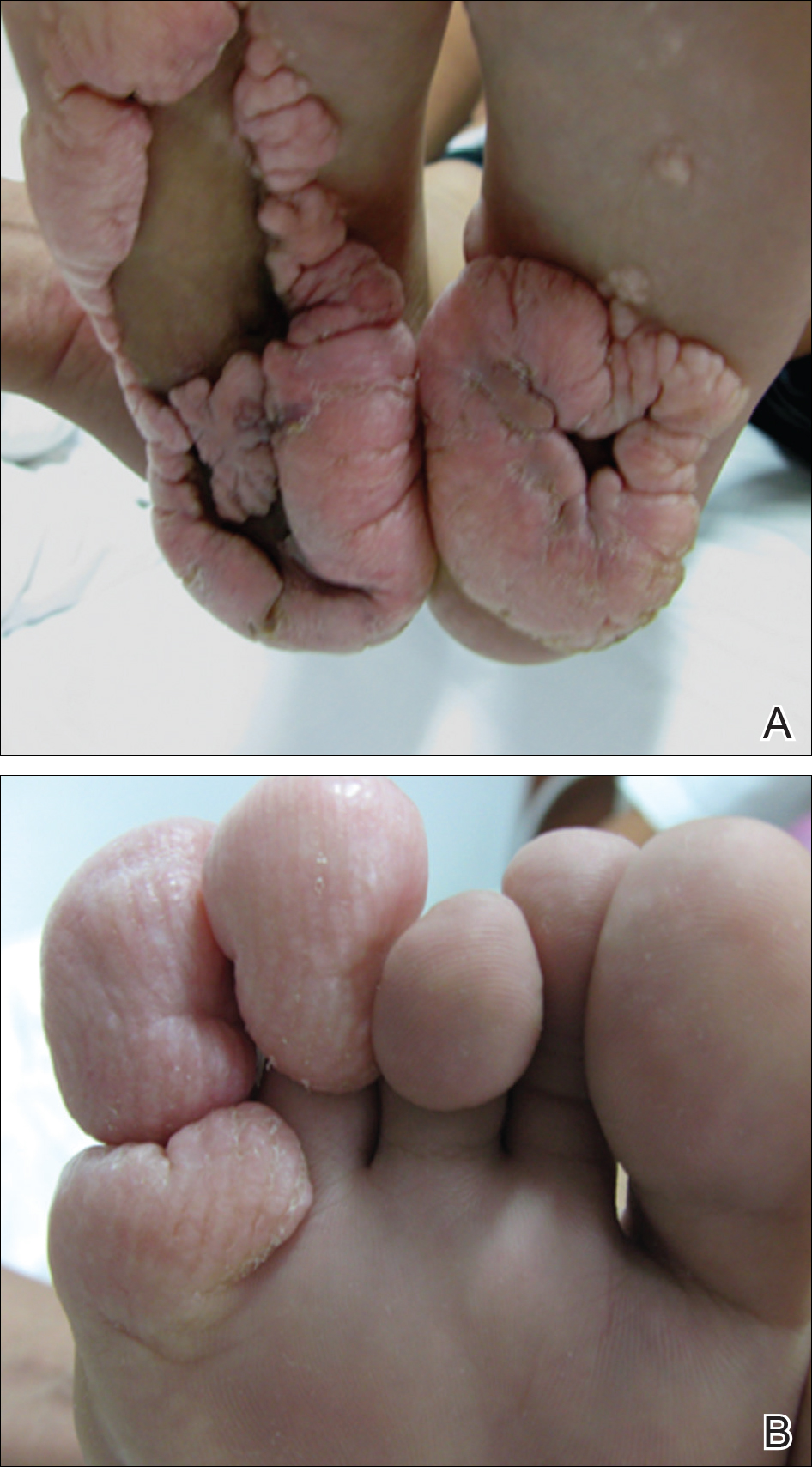
How common is macrodactyly?
Macrodactyly is a rare, nonhereditary and congenital deformity, accounting for about 1% of upper extremity congenital anomalies and affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 live births. Macrodactyly can appear alone (ie, the isolated form) or as part of a congenital deformity syndrome (ie, the syndromic form).
What is Ray resection of foot?
Ray resection for localized necrosis, infection, and osteomyelitis is an accepted procedure allowing removal of the diseased toe and metatarsal. The traditional approach involves a rather lengthy incision and dissection that can compromise the vascular supply to the remaining forefoot.
What causes cleft feet?
What causes cleft foot? Cleft foot is generally understood to have a genetic cause. Cleft foot can occur by itself; with cleft hand (ectrodactyly, also called split hand-split foot malformation); or as part of a genetic syndrome.
What does Brachymetatarsia mean?
What is Brachymetatarsia? Brachymetatarsia is a condition in which one of the bones in the front of the foot is significantly shorter than the others. This usually affects both feet and although it may affect any of the five metatarsals, it most commonly affects the fourth metatarsal.
What is a first ray amputation of the foot?
Partial first-ray resections are used to help salvage the foot and maintain bipedal ambulation. Losing the first metatarsophalangeal joint has biomechanical consequences that lead to further foot deformities and result in more proximal amputations of the ipsilateral limb, such as a transmetatarsal amputation.
What is 2nd ray amputation foot?
Second ray amputation surgical technique With a skin marker, a dorsal longitudinal incision following the shaft of the second metatarsal and then curving around the base of the 2nd toe at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint (racquet-type incision) was planned (Figure 3A).
Can cleft foot be corrected?
Even with treatment, clubfoot may not be totally correctable. But in most cases, babies who are treated early grow up to wear ordinary shoes and lead full, active lives.
Is cleft foot a birth defect?
A cleft foot is a birth defect that involves a deep space missing from the foot that extends toward the ankle. It is often V-shaped and may involve missing toes and other problems.
Can clubbed feet be fixed?
How Is Clubfoot Treated? Clubfoot won't get better on its own. It used to be fixed with surgery. But now, doctors use a series of casts, gentle movements and stretches of the foot, and a brace to slowly move the foot into the right position— this is called the Ponseti method.
Is brachymetatarsia serious?
In many cases, though, concerns go beyond the cosmetic, and brachymetatarsia can cause problems with your feet. Your toe impacted by brachymetatarsia is at risk of not touching the ground like toes usually do. When your metatarsal lifts, it might also move to the side, crossing over either of the toes next to it.
Is brachymetatarsia inherited?
The causes of brachymetatarsia are genetic or situational, meaning that you can be born with it or it can be induced by premature closure in the metatarsal growth plate due to a trauma.
Can brachymetatarsia cause foot pain?
Also, certain cases of brachymetatarsia can alter the alignment in your foot resulting in faulty biomechanics. Both of these instances can lead to pain, discomfort, and additional foot problems.
What is 5th ray amputation?
Bone resection for partial fifth toe amputation. ( a, b) Toe amputation was performed through the base of the proximal phalanx. Ray amputation is typically at the neck of the fifth metatarsal although partial or complete fifth toe amputation is an option under special circumstances including gangrene.
What are the metatarsal bones?
The metatarsal bones are the bones of the forefoot that connect the distal aspects of the cuneiform (medial, intermediate and lateral) bones and cuboid bone to the base of the five phalanges of the foot.
Macrodactyly of the foot - PubMed
Background: The purpose of this study was to focus on the problems associated with macrodactyly of the foot and to formulate guidelines for optimum treatment. Methods: Seventeen feet (fifteen patients) with macrodactyly formed the basis of this retrospective review. The feet were classified into one of two groups, depending on whether the macrodactyly involved only the lesser toes (group A) or ...
What is macrodactyly in the foot?
Macrodactyly is usually a benign condition, but it can result in foot or hand deformities —often affecting appearance and function. Macrodactyly Diagnosis and Treatment. Macrodactyly is usually visible at birth, ...
What is static macrodactyly?
Static macrodactyly occurs when the affected fingers or toes are roughly one-and-a-half times the size of normal fingers and toes. They grow at the same rate as the unaffected fingers or toes.
What is the condition where one or more fingers are larger than the other?
The main symptom of macrodactyly is having one or more fingers or toes that are much larger than the others. Macrodactyly is usually a benign condition, but it can result in foot or hand deformities—often affecting appearance and function.
What causes macrodactyly in the fingers?
The cause of macrodactyly is unknown. Some believe an abnormal nerve or blood supply in the affected fingers or toes causes the condition. The condition isn’t inherited and isn’t caused by anything the mother did during pregnancy. Macrodactyly is associated, however, with other conditions, such as vascular malformations and neurofibromatosis.
How is macrodactyly corrected?
In most cases, macrodactyly is corrected with surgery. Often, the surgery is complex, involving multiple procedures and long-term planning.
When is macrodactyly visible?
Macrodactyly is usually visible at birth, unless it is the progressive type, which might not be detected until later in early childhood, when fingers or toes start getting larger.
How to correct macrodactyly?
In most cases, macrodactyly is corrected with surgery. Often, the surgery is complex, involving multiple procedures and long-term planning. Your child’s customized treatment plan might include: Soft Tissue Debulking. Removes the thickened layers of skin and fat to reduce the width of the fingers or toes.
What is Macrodactyly?
Macrodactyly is a rare congenital disorder in which the fingers or toes become extremely large as a result of overgrowth of the bones and tissues. 1 As this condition is congenital, a child is born with it. Macrodactyly normally is present in the hands than the toes. In majority of cases, this condition is unilateral which means only one hand or foot is affected but in some cases it is seen bilaterally as well. Macrodactyly is seen to occur in the presence of another similar condition called syndactyly in which two fingers or toes are joined together at the time of birth. Macrodactyly is a benign condition but can be a factor of displeasure due to cosmetic reasons. This condition generally is treated surgically.
What are the Symptoms of Macrodactyly?
The defining characteristic of Macrodactyly is that one or more of the child’s fingers or toes are abnormally large than the other fingers or toes. If a child has Macrodactyly, then it does not mean that the affected finger or toe will not grow, in fact the affected finger or toe also grows in the same way as other fingers and toes of the child, although the affected fingers or toes may grow faster than the normal fingers or toes. If the condition progressively worsens then the affected finger or toe will become gigantically large compared to the static condition in which the affected finger or toe is about two times larger than the normal finger or toe.
How is Macrodactyly Treated?
The goal of the treatment for Macrodactyly is to provide maximal function of the affected hand or toe. The treatment modalities differ for the hands and foot. The function of the hand may not be affected if a finger is enlarged however if the toe is enlarged then wearing shoes becomes difficult. For mild cases of Macrodactyly, for the fingers no specific treatment is required and for the foot treatment may involve shoe wear modifications in the form of shoes with a wider toe box. In cases where the condition is quite severe, then the route for treatment is surgery. The surgical procedure is quite complicated as it usually involves multiple layers of tissue and may require more than one procedure to correct the deformity. The surgical procedure will have to be planned precisely keeping in mind the growth rate of the fingers which will involve close observation. Some of the surgical procedures done for correction of Macrodactyly are:
Is macrodactyly an inherited disorder?
2 It definitely does not occur due to anything done by the mother during pregnancy. Macrodactyly is not an inherited disorder. Macrodactyly seems to occur in conjunction with some other congenital conditions to include neurofibromatosis, vascular abnormalities, tuberous sclerosis etc.
Can a child have macrodactyly?
The overall prognosis of the child suffering from Macrodactyly varies from case to case depending on the severity of the condition. Post surgery, there may be a significant improvement in the overall appearance of the affected finger or toe but the child may still be left with some sort of deformity and still be left with some dysfunction of the affected region as a result of Macrodactyly.
What is macrodactyly?
A child's hand with large fingers present in macrodactyly Macrodactyly is a congenital condition in which a baby is born with abnormally large fingers or toes due to an overgrowth of the underlying bones and soft tissue. Macrodactyly occurs more often in hands than the feet. One or more fingers or toes may be involved. This condition can occur on one side only, or may affect both hands or both feet.
What is macrodactyly in the fingers?
The main symptom of macrodactyly is the appearance of one or more abnormally large fingers or toes. The larger digits may grow at the same rate as other non-affected fingers/toes, or have much faster growth.
What is a static finger?
Static — the enlargement of the fingers or toes is present at birth, and the affected digits grow at the same pace as unaffected fingers or toes.
When do macrodactyly affected fingers grow?
In some cases, a child’s macrodactyly-affected limb may appear to have a static growth pattern during infancy, but then can rapidly progress when the child is about 2 years old. In these cases, the affected fingers or toes grow very quickly, and often involve abnormally growth in the adjacent palm or forefoot.
What are the conditions that cause macrodactyly?
Macrodactyly can occur in conjunction with other conditions and syndromes, including neurofibromatosis, lipofibromatous hamartoma, vascular conditions, and tuberous sclerosis complex.
How old is a child when they have macrodactyly?
Most children are born with obvious signs of macrodactyly. Occasionally, this condition presents a bit later, when the child is a year or two old. At Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), diagnosing macrodactyly typically begins with a physical examination of your child’s affected hand or foot. A referral to the genetics team is sometimes necessary.
Can a macrodactyly be a benign condition?
Though macrodactyly is a benign condition, it does cause deformities, appear cosmetically different, and may affect your child’s normal hand or foot function. Treatment for macrodactyly varies, but generally includes surgery.
