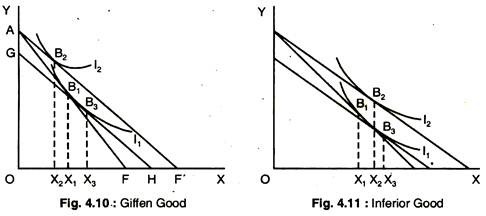
The equimarginal principle states that consumers will choose a combination of goods to maximise their total utility. This will occur where The consumer will consider both the marginal utility MU of goods and the price. In effect, the consumer is evaluating the MU/price.
What is the relationship between marginal utility and equilibrium?
A consumer attains equilibrium at such level where marginal utility derived from the consumption of a commodity is equal to its one unit price. Marginal utility is the change in the total utility of a commodity. It is expressed as MU = TUn+1 - TUn Here, MU stands for Marginal Utility
What is a marginal benefit?
A marginal benefit is the added satisfaction or utility a consumer enjoys from an additional unit of a good or service. Utility is an economic term referring to the satisfaction received from consuming a good or service.
What is economic equilibrium?
Charles has taught at a number of institutions including Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Societe Generale, and many more. What is Economic Equilibrium? Economic equilibrium is a condition or state in which economic forces are balanced. In effect, economic variables remain unchanged from their equilibrium values in the absence of external influences.
What is the law of demand and marginal benefit?
The law of demand states that quantity purchased varies inversely with price. In other words, the higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded. A marginal benefit is the added satisfaction or utility a consumer enjoys from an additional unit of a good or service.
What is marginal equilibrium in economics?
According to the law of equi-marginal utility, a consumer will be in equilibrium when the ratio of marginal utility of one commodity to its price is equal to the ratio of marginal utility of another commodity to its price. Let us assume that consumers buy two goods i.e. X and Y.
What is marginal utility in simple words?
What Is Marginal Utility? Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. The concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an item consumers are willing to purchase.
What is consumer equilibrium with example?
Consumer's Equilibrium means a state of maximum satisfaction. A situation where a consumer spends his given income purchasing one or more commodities so that he gets maximum satisfaction and has no urge to change this level of consumption, given the prices of commodities, is known as the consumer's equilibrium.
How do you calculate equilibrium marginal utility?
At the time of purchasing a unit of a commodity, a consumer compares the price of the given commodity with its utility. The consumer will be at equilibrium when marginal utility (in terms of money) equals the price paid for the commodity say 'X' i.e. MUx = PX.
Why is marginal utility Important?
Importance of Marginal Utility In economics, this law helps one to understand how consumers are able to reach an equilibrium where a single commodity applies. In most cases, a consumer can make use of a commodity until the marginal utility equals the market price, which ensures the consumers maximum satisfaction.
What are the 3 types of marginal utility?
The main types of marginal utility include positive marginal utility, zero marginal utility, and negative marginal utility. Consumers often experience higher marginal utility when marginal cost is lower.
What are the three conditions of consumer equilibrium?
Conditions of Consumer's Equilibrium The state of equilibrium for consumers is possible under the following conditions: The (MU)marginal utility of commodity X cost of product in terms of cost is equal to the cost of the commodity X in cost (MUx = Px).
How does a consumer reach equilibrium?
The law of equi-marginal utility states that a consumer will attain equilibrium when the ratio of marginal utility of one commodity to its price is equal to the ratio of the marginal utility of another commodity to its price.
How do you find the equilibrium price?
To find the equilibrium price a mathematical formula can be used. The equilibrium price formula is based on demand and supply quantities; you will set quantity demanded (Qd) equal to quantity supplied (Qs) and solve for the price (P). This is an example of the equation: Qd = 100 - 5P = Qs = -125 + 20P.
What is marginal utility with example?
Marginal utility is the enjoyment a consumer gets from each additional unit of consumption. It calculates the utility beyond the first product consumed. If you buy a bottle of water and then a second one, the utility gained from the second bottle of water is the marginal utility.
How do you calculate MUx and MUy?
You know MUx = Y and MUy = X, so MUx/MUy = Y/X.
What is difference between total utility and marginal utility?
Utility in economic terms is the satisfaction that is derived by a person from the consumption of any goods or services....What is Marginal Utility?Total utilityMarginal utilityResultIt suffers from diminishing returns.Marginal utility reduces with the consumption of each additional unit.4 more rows
What is marginal utility and example?
Marginal utility is the enjoyment a consumer gets from each additional unit of consumption. It calculates the utility beyond the first product consumed. If you buy a bottle of water and then a second one, the utility gained from the second bottle of water is the marginal utility.
What is marginal utility of money with example?
Example: if a rupee can buy 100 g of sugar and 500 g of rice( which represents a standard basket of goods to the consumers) and if the total utility from these goods is 4 utils, then 4 is to be taken as marginal utility of money.
What is total utility in simple words?
Total utility is the overall satisfaction that a consumer derives from the consumption of particular goods and services. Each individual unit of goods or services has a marginal utility of their own. Total utility is the sum of marginal utilities of all such individual items.
How do you do marginal utility?
Marginal Utility = Change In Total Utility / Change In Units The change in total utility can be calculated as the current total utility subtracted by a previous total utility. The change in units can be calculated as the current unit amount subtracted by a previous unit amount.
1. Define consumer equilibrium?
Consumer equilibrium is a point at which a consumer’s derived utility from a commodity is at its maximum, given a fixed level of income and price o...
2. Explain the concept of consumer equilibrium?
Consumers derive utility from each commodity they consume. This utility is dependent on the price of a product. The point at which the marginal uti...
3. Define utility.
The utility is defined as the want satisfying power of goods. The more they need for the particular commodity or the strong desire to have it, the...
4. What does marginal utility mean?
Marginal utility or MU is the change in total utility due to the consumption of one additional unit of a commodity. For example, suppose 5 mangoes...
5. What does total utility mean?
Total utility or TU of a fixed quantity of a commodity is defined as the total satisfaction derived from consuming the given amount of some commodi...
What is Consumer Equilibrium?
A consumer is said to be in an equilibrium state when he feels that he cannot change his situation either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the number of things he buys. A rational consumer will purchase a commodity up to the point where the price of the commodity is equivalent to the marginal utility obtained from the thing.
What is the marginal utility of two or more commodities?
In the case of two or more commodities, the marginal utility derived from one commodity in proportion to its price should be equal to the marginal utility derived from a second commodity in proportion to its price.
What is MU1 in economics?
Here, MU1 is the marginal utility of commodity 1 and P1 is its price. If a consumer derives a higher MU/P from one commodity than the other, he/she will purchase more units of the former commodity from his/her given income than the latter until both MU/P components are equal.
What happens to marginal utility when the price is lower than the price?
Similarly, if the marginal utility of a product is lower than its price, a consumer would reduce his/her consumption until marginal utility climbs back to the fixed price level.
What would a rational consumer continue to purchase more or less of a commodity until such marginal utility derived from it?
A rational consumer would continue to purchase more or less of a commodity until such marginal utility derived from it meets the price of that commodity.
What is equilibrium level in consumer?
A consumer attains equilibrium at such level where marginal utility derived from the consumption of a commodity is equal to its one unit price.
What happens when a MU curve intersects the price level when moving downwards?
If an MU curve intersects the price level when moving downwards, a consumer will derive negative utility from any additional consumption beyond that point.
What Is Marginal Utility?
Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. The concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an item consumers are willing to purchase.
Why do economists use marginal utility?
Economists use the idea of marginal utility to gauge how satisfaction levels affect consumer decisions. Economists have also identified a concept known as the law of diminishing marginal utility. It describes how the first unit of consumption of a good or service carries more utility than later units. Although marginal utility tends ...
Why is marginal utility important?
Marginal utility is useful in explaining how consumers make choices to get the most benefit from their limited budgets. In general, people will continue consuming more of a good as long as the marginal utility is greater than the marginal cost. In an efficient market, the price equals the marginal cost. That is why people keep buying more until the ...
What is diminishing marginal utility?
The law of diminishing marginal utility is often used to justify progressive taxes. The idea is that higher taxes cause less loss of utility for someone with a higher income. In this case, everyone gets diminishing marginal utility from money. Suppose that the government must raise $20,000 from each person to pay for its expenses.
What happens to marginal utility of the next unit?
At that point, the marginal utility of the next unit equals zero and consumption ends.
How many gallons of milk does David have?
David has four gallons of milk, then decides to purchase a fifth gallon. Meanwhile, Kevin has six gallons of milk and likewise chooses to buy an additional gallon. David benefits from not having to go to the store again for a few days, so his marginal utility is still positive.
Why are poll taxes so unpopular?
That is why poll taxes, which require everyone to pay an equal amount, tend to be unpopular. Also, a flat tax without individual exemptions that required everyone to pay the same percentage would impact those with less income more because of marginal utility.
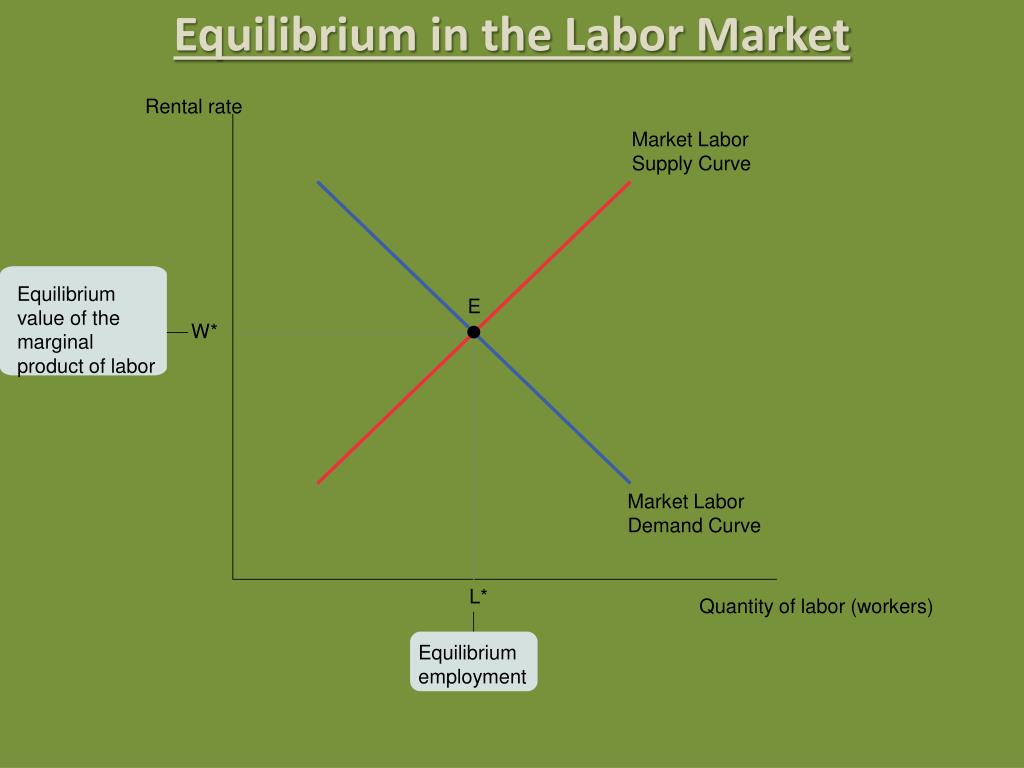
What is Economic Equilibrium?
Economic equilibrium is a condition or state in which economic forces are balanced. In effect, economic variables remain unchanged from their equilibrium values in the absence of external influences. Economic equilibrium is also referred to as market equilibrium.
Why do buyers have to offer higher prices?
So something has to give; buyers will have to offer higher prices to induce sellers to part with their goods. As they do, the market price will rise toward the level where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, just as a balloon will expand until the pressures equalize.
What happens when the price of a market is too low?
If the price in a given market is too low, then the quantity that buyers demand will be more than the quantity that sellers are willing to offer. Like the air pressures in and around the balloon, supply and demand will not be in balance. consequently a condition of oversupply in the market, a state of market disequilibrium .
How do entrepreneurs compete in the economy?
Entrepreneurs compete throughout the economy, using their judgement to make educated guesses as to the best combinations of goods, prices, and quantities to buy and sell. Because a market economy rewards those who guess better, through the mechanism of profits, entrepreneurs are in effect rewarded for moving the economy toward equilibrium. The business and financial media, price circulars and advertising, consumer and market researchers, and the advancement of information technology all make information about the relevant economic conditions of supply and demand more available to entrepreneurs over time. This combination of market incentives that select for better guesses about economic conditions and the increasing availability of better economic information to educate those guesses accelerates the economy toward the “correct” equilibrium values of prices and quantities for all the various goods and services that are produced, bought, and sold.
Why is equilibrium a fundamentally theoretical construct that may never actually occur in an economy?
Equilibrium is a fundamentally theoretical construct that may never actually occur in an economy, because the conditions underlying supply and demand are often dynamic and uncertain. The state of all relevant economic variables changes constantly.
What is equilibrium in economics?
Equilibrium is a concept borrowed from the physical sciences, by economists who conceive of economic processes as analogous to physical phenomena such as velocity, friction, heat, or fluid pressure. When physical forces are balanced in a system, no further change occurs. For example, consider a balloon.
What happens when a balloon expands?
Once the balloon expands enough so that the air pressure inside and out have are in balance it stops expanding; it has reached equilibrium.
What Is Marginal Benefit?
A marginal benefit is a maximum amount a consumer is willing to pay for an additional good or service. It is also the additional satisfaction or utility that a consumer receives when the additional good or service is purchased. The marginal benefit for a consumer tends to decrease as consumption of the good or service increases.
What happens when units are consumed?
As units are consumed, the consumer often receives less utility or satisfaction from consumption. To demonstrate this, consider the example above. Assume there is a consumer who wants to purchase an additional burger. If this consumer is willing to pay $10 for that additional burger, the marginal benefit of consuming that burger is equal to ...
What is it called when a consumer is willing to pay higher than the market price for a good or service?
When a consumer is willing to pay higher than the market price for a good or service, it is known as consumer surplus. The marginal benefit of some products that are necessities, such as medication, does not decrease over time.
What is the marginal benefit of eating a second burger?
However, if the consumer decides they are only willing to spend $9 on the second burger, the marginal benefit is $9. The more burgers the consumer has, the less they want to pay for the next one.
What is the difference between market price and price the consumer is willing to pay?
The difference between the market price and the price the consumer is willing to pay—when the perceived value is higher than the market price —is called consumer surplus. This is not to be confused with economic surplus .
What is utility in a consumer?
The term utility is used to describe the level of satisfaction a consumer has assigned to the unit being consumed. Often expressed by the number of dollars a consumer is willing to spend for a unit, utility assumes a consumer finds a minimum amount of intrinsic value equal to the dollar amount paid for the item.
Why do companies conduct research?
Companies can use the research they conduct into marginal benefits for the best possible price point for any deal. Companies can also use this research to find out what the additional expenses are for selling a second item relative to the first.
What Is Marginal Utility?
- Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a g…
Positive marginal utility occurs when the consumption of an additional item increases the total utility. On the other hand, negative marginal utility occurs when the consumption of one more unit decreases the overall utility. - Marginal utility is the added satisfaction a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good o…
The concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an item consumers are willing to purchase.
Understanding Marginal Utility
- Economists use the idea of marginal utility to gauge how satisfaction levels affect consumer de…
Although marginal utility tends to decrease with consumption, it may or may not ever reach zero depending on the good consumed. - Marginal utility is useful in explaining how consumers make choices to get the most benefit fro…
The law of diminishing marginal utility is often used to justify progressive taxes. The idea is that higher taxes cause less loss of utility for someone with a higher income. In this case, everyone gets diminishing marginal utility from money. Suppose that the government must raise $20,000 …
Types of Marginal Utility
- There are multiple kinds of marginal utility. Three of the most common ones are as follows:
Positive marginal utility occurs when having more of an item brings additional happiness. Suppose you like eating a slice of cake, but a second slice would bring you some extra joy. Then, your marginal utility from consuming cake is positive. - Zero marginal utility is what happens when consuming more of an item brings no extra measur…
Negative marginal utility is where you have too much of an item, so consuming more is actually harmful. For instance, the fourth slice of cake might even make you sick after eating three pieces of cake.
History of Marginal Utility
- The concept of marginal utility was developed by economists who were attempting to explain th…
This disparity intrigued economists and philosophers around the world. In the 1870s, three economists—William Stanley Jevons, Carl Menger, and Leon Walras —each independently came to the conclusion that marginal utility was the answer to the water and diamonds paradox. In hi…
Example of Marginal Utility
- David has four gallons of milk, then decides to purchase a fifth gallon. Meanwhile, Kevin has six …
The chief takeaway from this scenario is that the marginal utility of a buyer who acquires more and more of a product steadily declines. Eventually, there is no additional consumer need for the product in many cases. At that point, the marginal utility of the next unit equals zero and consu…