What does ECG stand for?
ECG Stands for Electro-Cardio-Gram. ECG is a medical test that records heart-beat on a paper-graph or on the computer screen in the form of electrical impulses. ECG test Diagnoses different types of heart problems and heart functioning through the electric wave.
Is ECG and EKG the same thing?
There are no considerable differences between the two. ECG and EKG, both are acronyms that carry the same meaning. ECG stands for Electrocardiogram, while EKG is an acronym for the German-translated word Elektro-kardiographie.
What are the uses of an ECG?
Uses and Functions of ECG Machine An ECG machine is used for graphically recording and monitoring the electrical activity of various phases of heart beat. This is done with the help of electrodes externally attached to the outer surface of skin, on the chest and limbs of patients with heart diseases.
What is the purpose of an EKG?
Your doctor uses the EKG to:
- assess your heart rhythm
- diagnose poor blood flow to the heart muscle (ischemia)
- diagnose a heart attack
- diagnose abnormalities of your heart, such as heart chamber enlargement and abnormal electrical conduction
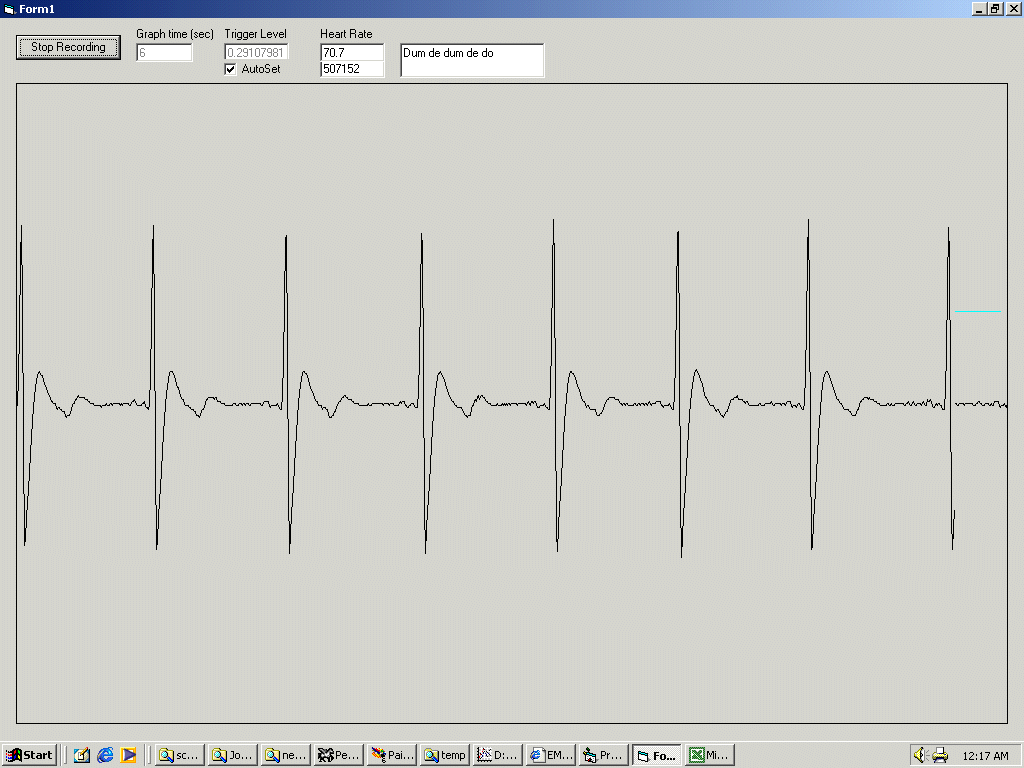
Whats the meaning of ECG?
ElectrocardiogramAn electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple test that can be used to check your heart's rhythm and electrical activity. Sensors attached to the skin are used to detect the electrical signals produced by your heart each time it beats.
What are the 3 types of ECG?
3 Types Of Electrocardiogram MonitoringHolter Monitor. A Holter Monitor is a portable EKG device. ... Cardiac Event Monitor. Like the Holter Monitor, the Cardiac Event Monitor is a portable EKG device. ... Stress Test.
What ECG used for?
An electrocardiogram records the electrical signals in the heart. It's a common and painless test used to quickly detect heart problems and monitor the heart's health. An electrocardiogram — also called ECG or EKG — is often done in a health care provider's office, a clinic or a hospital room.
Which ECG is normal?
If the test is normal, it should show that your heart is beating at an even rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. Many different heart conditions can show up on an ECG, including a fast, slow, or abnormal heart rhythm, a heart defect, coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, or an enlarged heart.
What is ECG normal range?
Normal ECG values for waves and intervals are as follows: RR interval: 0.6-1.2 seconds. P wave: 80 milliseconds. PR interval: 120-200 milliseconds.
Who needs ECG?
When are ECGs needed? In some cases, it can be important to get this test. You should probably have an ECG if you have risk factors for an enlarged heart such as high blood pressure or symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, an irregular heartbeat or heavy heartbeats.
What is abnormal ECG?
An abnormal ECG can mean many things. Sometimes an ECG abnormality is a normal variation of a heart's rhythm, which does not affect your health. Other times, an abnormal ECG can signal a medical emergency, such as a myocardial infarction /heart attack or a dangerous arrhythmia.
How do you read an ECG?
How to read ECG paperEach small square represents 0.04 seconds.Each large square represents 0.2 seconds.5 large squares = 1 second.300 large squares = 1 minute.
What is a 3 lead ECG called?
Information gathered between these leads is known as "bipolar". It is represented on the ECG as 3 "bipolar" leads.
What type of ECG is most commonly used?
The standard 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the most commonly used medical studies in the assessment of cardiovascular disease.
What does 3 channel ECG mean?
3 Channel ECG Machine : As the name suggest, 3 Channel ECG Machine print 3 waveforms/channels at a time. In 3 channels machines, the ECG signals selected by the microprocessor are amplified , filtered and sent to a 3 channel multiplexer.
Where are 3 ECG leads placed?
Position the 3 leads on your patient's chest as follows, taking care to avoid areas where muscle movement could interfere with transmission:WHITE.RA (right arm), just below the right clavicle.BLACK.LA (left arm), just below the left clavicle.RED.LL (left leg), on the lower chest, just above and left of the umbilicus.
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is defined as a recording of the heart’s electrical activity. It is a graphic record produced by an electrocardiograph that...
What are the three components of ECG?
An ECG has three main components – the P wave denotes the depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex denotes depolarization of the ventricles, an...
What does an abnormal ECG mean?
An abnormal ECG mainly denotes a variation in the heart rate or heart rhythm. For example, an irregular QRS complex without a P wave denotes atrial...
What does the broken line on the ECG mean?
Fig. 140 ECG . A tracing of the electric currents that initiate the heartbeat. The broken line indicates diastole, the solid line systole.
What is the purpose of ECG?
The electrocardiogram (ECG), a noninvasive study, measures the electrical currents or impulses that the heart generates during a cardiac cycle (see figure of a normal ECG at end of monograph).
What are the three waves of the cardiac cycle?
Each cardiac cycle produces three distinct ECG waves, designated as P , QRS and T . These waves represent changes in electrical potential between two regions on the surface of the heart. The spread of atrial depolarization creates the P wave; spread of ventricular depolarization is represented by the QRS wave; repolarization of the ventricles produces the T wave. To obtain an ECG, electrodes are attached to various parts of the body surface, usually both arms and the left leg.
What is the spread of ventricular depolarization?
The spread of atrial depolarization creates the P wave; spread of ventricular depolarization is represented by the QRS wave; repolarization of the ventricles produces the T wave. To obtain an ECG, electrodes are attached to various parts of the body surface, usually both arms and the left leg.
How does exercise stress test work?
The patient exercises on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle to increase the heart rate to 80% to 90% of maximal heart rate determined by age and gender, known as the target heart rate. Every 2 to 3 min, the speed and/or grade of the treadmill is increased to yield an increment of stress. The patient’s electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood pressure are monitored during the test. The test proceeds until the patient reaches the target heart rate or experiences chest pain or fatigue. The risks involved in the procedure are possible myocardial infarction (1 in 500) and death (1 in 10,000) in patients experiencing frequent angina episodes before the test. Although useful, this procedure is not as accurate as cardiac nuclear scans for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD).
Where are the ECG bundles located?
These bundles are located within the right and left ventricles. The impulses continue to the cardiac muscle cells by terminal fibers called Purkinje fibers. The ECG is a graphic display of the electrical activity of the heart, which is analyzed by time intervals and segments.
What to monitor during recovery phase after MI?
Monitor rhythm changes during the recovery phase after an MI
How to measure electrical activity of the heart?
The electrical activity of the heart can be measured on the surface of the skin – even as far from the heart as on your arms or legs. The standard “12-lead ECG” uses a total of ten electrodes: six on your chest, and then one each on your lower arms and calves. If there is too much body hair, these areas are shaved first; other than that, no preparation is needed. These electrodes are connected by cables to an ECG machine. The machine converts the signals it receives into an ECG graph and saves it. Some machines can also print the graphs out.
How does a Holter monitor work?
Holter monitor: The electrical activity of the heart is typically recorded over a period of 24 hours. Three or four electrodes are attached to your chest, and a small recording device is worn on a belt or hung around your neck. The ECG data are then transferred to a computer later on at the doctor's office for analysis. To do this, the doctor also needs information about your daily schedule (like unusual events, physical activity and sleep). A Holter monitor may be used if, for instance, you only have an irregular heartbeat some of the time and it doesn't show up in a “normal” ECG.
How do nerves communicate with each other?
Our nerve and muscle cells communicate with each other using electrical and chemical signals. Regular electrical signals also control our heartbeat. These signals are sent by a group of cells in the right atrium of the heart known as the sinoatrial node (SA node), and they spread through the heart muscle tissue as tiny electrical impulses. This causes first the atria and then the ventricles of the heart to contract. The way that these signals spread through the heart can also be measured on the surface of our skin. An ECG measures these changes in electrical signals (or, in fact, voltage) on different areas of skin and plots them as a graph. The resulting ECG graph is called an electrocardiogram.
What is the first peak of the ECG?
If the heart is beating steadily, it will produce the typical ECG pattern: The first peak (P wave ) shows how the electrical impulse (excitation) spreads across the two atria of the heart. The atria contract (squeeze), pumping blood into the ventricles, and then immediately relax. The electrical impulse then reaches the ventricles. This can be seen in the Q, R and S waves of the ECG, which is called the QRS complex. The ventricles contract. Then the T wave shows that the electrical impulse has stopped spreading, and the ventricles relax once again.
What is IQWiG health information?
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services. Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system.
What is the ECG of a heart?
Exercise ECG: Here the electrical activity of your heart is measured while you are physically active. This usually involves riding an exercise bike. The amount of exertion is steadily increased to a high level by making it increasingly difficult to turn the pedals.
What is it?
An electrocardiogram — abbreviated as EKG or ECG — is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers.
Does it hurt?
No. There’s no pain or risk associated with having an electrocardiogram. When the ECG stickers are removed, there may be some minor discomfort.
How to tell if an ECG is normal?
First, by measuring time intervals on the ECG, a doctor can determine how long the electrical wave takes to pass through the heart. Finding out how long a wave takes to travel from one part of the heart to the next shows if the electrical activity is normal or slow, fast or irregular. Second, by measuring the amount of electrical activity passing ...
What is the first wave of the heart?
A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers. The right and left atria or upper chambers make the first wave called a “P wave" — following a flat line when the electrical impulse goes to the bottom chambers.
How Is An ECG Carried Out?
An ECG is a safe and painless test that usually takes only a few minutes.
How does the heart depolarize?
During each pulse, a healthy heart has an ordered process of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, extends throughout the atrium, and moves through the atrioventricular node into its bundle and into the fibres of Purkinje, spreading throughout the ventricles and to the left. The electrical activity occurs in a small patch of pacemaker cells called the sinus node during a regular heartbeat. This produces a small blip called the P wave when the impulse stimulates the atria (see the diagram below). It then activates the main pumping chambers, the ventricles, and produces the large up-and-down in the middle, the QRS complex. The last T wave is a time of regeneration as the impulse reverses over the ventricles and travels back. If the heart is beating normally, it takes about a second (approximately 60 heartbeats per minute) for the entire cycle.
What is the state of the atria and ventricles that shows a lack of coordination of movement?
Atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation is the state when the atria and the ventricles show a lack of coordination of movement. It results in rapid heartbeat, weakness and shortness of breath. On ECG, it is represented by jumpy baseline and the P wave disappears.
Why is ECG not used?
Evidence does not support the use of ECGs as an attempt for prevention among those without symptoms or at low risk of cardiovascular disease. This is because an ECG may incorrectly suggest a concern, leading to misdiagnosis, initiation for invasive procedures, and overtreatment. Individuals working in certain sensitive professions, such as aeroplane pilots, may need to have an ECG as part of their routine safety evaluations.
What is an ECG?
Electrocardiogram (ECG) An electrocardiogram is a graphic record produced by an electrocardiograph that provides details about one’s heart rate and rhythm and depicts if the heart has enlarged due to hypertension (high blood pressure) or evidence of a myocardial infarction previously (heart attack if any). Electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the most ...
What is the normal pattern of ECG?
In the normal ECG pattern, there is a regular pattern of The P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. They occur in a sequence.
What is ECG test?
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the most common and effective tests in all drugs. It is easy to perform, non-invasive, yields outcomes instantly, and is useful to identify hundreds of heart conditions. A sample of an electrocardiogram is as given below.
Are there any risks or side effects?
An ECG is a quick, safe and painless test. No electricity is put into your body while it's carried out.
How does an ECG work?
Generally, the test involves attaching a number of small, sticky sensors called electrodes to your arms, legs and chest. These are connected by wires to an ECG recording machine. You don't need to do anything special to prepare for the test.
What is an ambulatory ECG?
For an ambulatory ECG, the ECG machine will store the information about your heart electronically, which can be accessed by a doctor when the test is complete.
How to close a modal window?
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
What are the symptoms of a heart problem?
It can be used to investigate symptoms of a possible heart problem, such as chest pain, palpitations (suddenly noticeable heartbeats), dizziness and shortness of breath.
When is an ambulatory ECG more appropriate?
For example, an exercise ECG may be recommended if your symptoms are triggered by physical activity, whereas an ambulatory ECG may be more suitable if your symptoms are unpredictable and occur in random, short episodes.
How many types of ECG are there?
There are 3 main types of ECG:
What is Q wave?
A q-wave is an initial downward deflection in the QRS complex. These are normal in left-sided chest leads (V5, 6, lead I, aVL) as they represent septal depolarization from left to right. This is as long as they are <0.04secs long (1 small square) and <2mm deep.
How many ECGs are recorded 10 minutes apart?
If you are concerned that there are dynamic changes in an ECG it is helpful to ask for serial ECGs (usually three ECGs recorded 10 minutes apart) so they can be compared. These should always be labelled 1, 2 and 3.
What is EKG interpretation?
ECG (EKG) Interpretation. As with all investigations the most important things are your findings on history, examination and basic observations. Having a good system will avoid making errors. To start with we will cover the basics of the ECG, how it is recorded and the basic physiology. The 12-lead ECG misleadingly only has 10 electrodes (sometimes ...
What does it mean when a P wave is not associated with a QRS complex?
At this point you can also assess whether each p wave is associated with a QRS complex. P-waves not in association with QRS complexes indicate complete heart block.
How many electrodes are in the heart?
The leads can be thought of as taking a picture of the heart’s electrical activity from 12 different positions using information picked up by the 10 electrodes. These comprise 4 limb electrodes and 6 chest electrodes.
What is the axis of the heart?
Axis is the sum of all the electrical activity in the heart. The contraction travels from the atria to the right and left ventricles. As the left ventricle is larger and more muscular normal axis lies to the left (at -30 degrees to 90 degrees – see Figure 5).
Why is QTc important?
A long QTc interval (known as “long QT”) is especially important to identify in patients with a history of collapse or transient loss of consciousness.
When is an ECG needed?
An ECG is required if you have risk factors for an enlarged heart or symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or an irregular heartbeat . You may need the test for screening or occupational requirements, or if you have a personal or family history of heart disease, diabetes, or other risks and you want to start exercising.
What does it mean when your ECG is abnormal?
An abnormal ECG can mean many things. Sometimes an ECG abnormality is a normal variation of a heart’s rhythm, which does not affect your health.
What to do if your electrocardiogram is abnormal?
This person may require a pacemaker, which helps restore the heart to a more normal rhythm.
What does the heart rate monitor show?
It provides information about your heart rate and rhythm and shows if there is an enlargement of the heart due to high blood pressure or evidence of a previous heart attack.
Can electrolytes be corrected?
People with electrolyte imbalances may require correction with medications or fluids. For example, a person with dehydration may have imbalanced electrolytes that are causing an abnormal ECG.
