
How do you calculate enzyme activity?
Total enzyme activity is obtained by calculating the dilution ratio of your assay. For instance, if you measure the OD of your catechol-1,2-dioxygenase with say 10 microliter of your enzyme preparation and that your enzyme preparation is 25 ml, your dilution ratio would be 2,500.
What does enzyme activity mean?
The enzyme activity refers to the number of moles of product formed per unit time. Once we know the enzyme activity and the concentration of the enzyme, we can then determine the specific activity of the enzyme. The specific activity is the ratio of the enzyme activity to enzyme concentration.
What is the rate of enzyme activity?
The specific activity of an enzyme is expressed as the number of units per milligram of protein. The rate of a biochemical reaction at a given temperature and pH depends on the enzyme concentration and the substrate concentration.
What is the equation for enzyme activity?
enzyme activity= change in OD/time taken (min) x 1/extinction coefficient of enzyme x total reaction volume/ volume of enzyme extrct taken x total volume of enzyme extract/ Fresh wt of tissue (g ...
What is enzyme activity and specific activity?
The enzyme activity refers to the number of moles of product formed per unit time. Once we know the enzyme activity and the concentration of the enzyme, we can then determine the specific activity of the enzyme. The specific activity is the ratio of the enzyme activity to enzyme concentration.
Where is enzyme activity?
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the active site (since that's where the catalytic “action” happens). A substrate enters the active site of the enzyme. This forms the enzyme-substrate complex.
What is an example of enzyme activity?
For example, the enzyme sucrase breaks down a sugar called sucrose. Lactase breaks down lactose, a kind of sugar found in milk products. Some of the most common digestive enzymes are: Carbohydrase breaks down carbohydrates into sugars.
What is enzyme activity and how is it measured?
Enzymatic activities are measured by breakdown of the substrates and generation of products. The methods used for measuring enzymatic activities include spectrophotometry, fluorescence, and radiolabeling.
What affects enzyme activity?
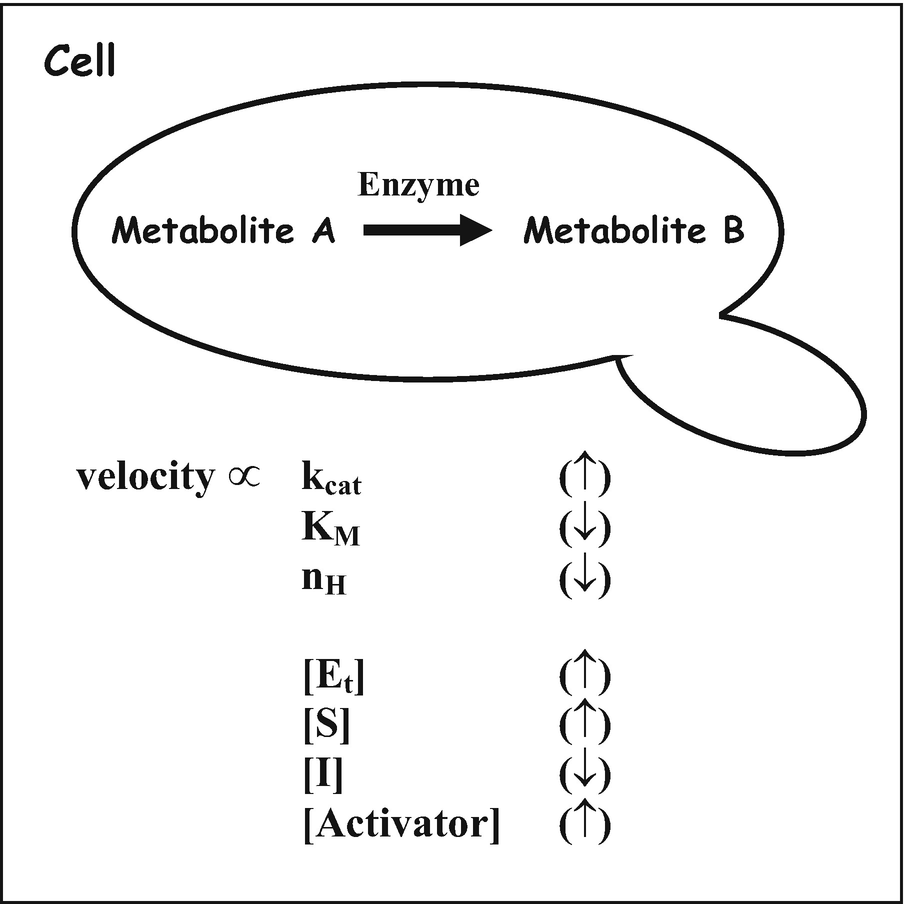
Enzyme activity can be affected by a variety of factors, such as temperature, pH, and concentration. Enzymes work best within specific temperature and pH ranges, and sub-optimal conditions can cause an enzyme to lose its ability to bind to a substrate.
What are the steps of enzyme activity?
Four Steps of Enzyme ActionThe enzyme and the substrate are in the same area. Some situations have more than one substrate molecule that the enzyme will change.The enzyme grabs on to the substrate at a special area called the active site. ... A process called catalysis happens. ... The enzyme releases the product.
What is a simple definition of enzyme?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost always a protein. It speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction and is used over and over.
What are the 4 functions of enzymes?
Enzymes include detoxification, muscle building, and breaking down food particles during digestion. Enzymes actually accelerate the rate of a chemical reaction to support life. Enzymes are very helpful in performing important functions of our body.
What is unit of enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity The SI unit is the katal, 1 katal = 1 mol s−1 (mole per second), but this is an excessively large unit. A more practical and commonly used value is enzyme unit (U) = 1 μmol min−1 (micromole per minute). 1 U corresponds to 16.67 nanokatals.
Is enzyme activity the same as rate of reaction?
Enzyme activity is a measure of how many active enzymes are present in a system. Meanwhile, the rate of an enzyme reaction is a measure of how many reactants are consumed during a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme or how many products are produced during that catalyzed reaction.
What instrument measures enzyme activity?
The NanoDrop 3300 was shown to be a very practical tool for the measurement of enzymatic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Where is enzyme located in the cell?
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes.
What is an enzyme and where is it found?
An enzyme is a type of protein found within a cell. Enzymes create chemical reactions in the body, and can actually speed up the rate of a chemical reaction to help support life. Enzymes are produced naturally in the body and help with important tasks, including: building muscle.
Where are enzymes stored in the body?
These proteins speed up chemical reactions that turn nutrients into substances that your digestive tract can absorb. Your saliva has digestive enzymes in it. Some of your organs, including your pancreas, gallbladder, and liver, also release them. Cells on the surface of your intestines store them, too.
Where is each enzyme found?
ProteasesRegion of digestive systemEnzymeWhere producedStomachProtease - pepsinGastric glands in stomachSmall intestine - DuodenumProtease - trypsinPancreasSmall intestine - IleumProtease - peptidaseWall of ileum
What is an enzyme?
An enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being...
What are enzymes composed of?
A large protein enzyme molecule is composed of one or more amino acid chains called polypeptide chains. The amino acid sequence determines the char...
What are examples of enzymes?
Practically all of the numerous and complex biochemical reactions that take place in animals, plants, and microorganisms are regulated by enzymes,...
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity is affected by various factors, including substrate concentration and the presence of inhibiting molecules. The rate of an enzymati...
What is enzyme activity?
enzyme activity the catalytic effect exerted by an enzyme, expressed as units per milligram of enzyme ( specific activity) or molecules of substrate transformed per minute per molecule of enzyme ( molecular activity ).
What are some interventions for diversional activity deficit?
These activities could include music, games, reading, handwork, or any other pastimes enjoyed by the patient . Patients may need assistance in identifying available resources and motivation to take advantage of the activities they provide.
What is a deficient diversional activity?
deficient diversional activity a nursing diagnosis approved by the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association, defined as the experiencing by an individual of decreased stimulation from, interest in, or engagement in recreational or leisure activities. Formerly called diversional activity deficit.
What is the optimal concentration of MgS[O.sub.4]x7[H.sub.2?
These data were similar with the results reported by Chen et al., in which they observed that the optimal concentration of MgS[O.sub.4]x7[H.sub.2]O for glucose isomerase production of Streptomyces flavogriseust was 0.1% with the highest enzyme activity(1.93 U/mg protein); either the lower concentration (0.03%) or the higher concentration (0.5%) resulted in a decline of enzyme activity[12].
What is the catalytic effect of enzymes?
enzyme activitythe catalytic effect exerted by an enzyme, expressed as units per milligram of enzyme (specific activity) or molecules of substrate transformed per minute per molecule of enzyme (molecular activity).
What is sustained rhythmic activity?
sustained rhythmic activitythe continuous generation of action potentialswithin the heart in the absence of artificial or external stimulation.
What is pulseless electrical activity?
pulseless electrical activity (PEA) continued electrical rhythmicity of the heart in the absence of effective mechanical function; it may be due to uncoupling of ventricular muscle contraction from electrical activity or may be secondary to cardiac damage with respiratory failure and cessation of cardiac venous return.
How is the rate of an enzymatic reaction determined?
Thus, enzymatic reaction rate is determined by the speed at which the active sites convert substrate to product.
How does competitive inhibition occur?
Competitive inhibition occurs when molecules similar to the substrate molecules bind to the active site and prevent binding of the actual substrate.
How are enzymes named?
Because of this specificity, enzymes often have been named by adding the suffix “-ase” to the substrate’s name (as in urease, which catalyzes the breakdown of urea ). Not all enzymes have been named in this manner, however, and to ease the confusion surrounding enzyme nomenclature, a classification system has been developed based on the type of reaction the enzyme catalyzes. There are six principal categories and their reactions: (1) oxidoreductases, which are involved in electron transfer; (2) transferases, which transfer a chemical group from one substance to another; (3) hydrolases, which cleave the substrate by uptake of a water molecule (hydrolysis); (4) lyases, which form double bonds by adding or removing a chemical group; (5) isomerases, which transfer a group within a molecule to form an isomer; and (6) ligases, or synthetases, which couple the formation of various chemical bonds to the breakdown of a pyrophosphate bond in adenosine triphosphate or a similar nucleotide.
What are the two things that enzymes do?
Enzymes catalyze all aspects of cell metabolism. This includes the digestion of food, in which large nutrient molecules (such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) are broken down into smaller molecules; the conservation and transformation of chemical energy; and the construction of cellular macromolecules from smaller precursors.
Why is an energy barrier necessary in chemical reactions?
This barrier prevents complex molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids from spontaneously degrading, and so is necessary for the preservation of life.
What is the role of enzymes in a chemical reaction?
Enzyme, a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. In the induced-fit theory of enzyme-substrate binding, a substrate approaches the surface of an enzyme (step 1 in box A, B, C) and causes a change in the enzyme shape ...
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The active site of an enzyme is a groove or pocket that binds a specific substrate. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Enzyme synthesis and activity also are influenced by genetic control and distribution in a cell. Some enzymes are not produced by certain cells, and others are formed only when required.
What is enzyme in biology?
Enzymes are catalysts that are capable of catalysing reactions of biological origin. They are protein in nature and are highly specific. Enzymes have an active site into which the substrate gets fit to proceed with the chemical reaction. Enzymes combine with the substrate molecule to form an enzyme-substrate complex. Enzymes act by lowering the activation energy of the reaction and then combine with the substrate molecule to form an enzyme-substrate complex. This, in turn, results in the formation of products. Various factors affect the activity of enzymes like temperature, pH, the concentration of substrates, etc.
What is enzyme inhibitor?
Enzyme inhibitors are substances that decrease the activity of enzymes when they bind to the active site present on the enzyme.
What chemicals increase enzyme activity?
6. Activators and Poisons: Some chemical substances or molecules increase the activity of enzymes such as co-factors, for example, potassium ion (K⁺), manganese ion (Mn²⁺), etc. These chemicals which increase the activity of enzymes are known as activators. On the other hand, salts of heavy metals and compounds such as cyanides, azides, and iodoacetate destroy the tertiary structure of enzymes, thus affecting the activity of enzymes. These chemicals are known as poisons.
What is irreversible or permanent inhibition?
Irreversible or permanent Inhibition: This type of inhibition occurs due to change or destruction in the conformation of enzymes. It occurs due to the covalent binding of heavy metals or other inhibitors with the enzymes, resulting in their in activation.
What is the Km constant?
In the graph, Km is a constant known as the Michaelis-Menten constant. It is defined as the concentration of substrate ( expressed in moles/lit) to produce half-maximum velocity in a reaction that is catalysed by an enzyme. It indicates that half of the enzymes molecules are bound with the substrate molecules when the substrate concentration is the same as the Km value.
What is the effect of light on enzymes?
8. Light: Enzymes are sensitive to light. The presence of light increases the reaction rate in some enzymes whereas the presence of harmful radiation such as UV rays and X-rays decreases enzymes ’ catalytic activity.
What temperature is the enzyme activity?
The temperature at which an enzyme shows its maximum activity is called optimum temperature. The optimum temperature for most of the enzymes is between 25-35°C. Temperature above and below this range affects the enzyme activity. High temperature above 50°C results in the destruction of enzymes by causing their denaturation, and very low temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive state.
What Substrate Concentration Should I Use?
Since the rate of an enzyme reaction is likely to fall when more than about 15% of the substrate has been hydrolysed, the initial concentration of substrate should generally be at least 10x the concentration of product that is known to give an acceptable assay signal.
Do I Plot Concentration or Absolute Amount on the X Axis?
However, laboratory reagents are usually prepared at known concentrations, and it is often easier to plot these values on the x axis. However, when you calculate the activity (or specific activity) of your enzyme you must remember to convert the concentration on the x-axis into the number of nmoles of product formed, which means you must take account of the assay volume. The reason is easy to understand: 50ul and 100ul volumes of a standard solution will be at the same concentration, but the larger volume will contain twice the amount of product. Generally, it is best to pick one approach (i.e. either plot absolute amount of product or concentration) so that the same method calculating activity is always used.
What is unit/ml in enzyme assay?
The reported units/ml may give you a rough idea of how much enzyme to add, but as the activity value may not have been determined in a test identical to yours, it is usual to prepare serial dilutions of the enzyme (e.g. log dilutions initially) and to test a fixed volume of each dilution. Depending on the assay signal (which will be related to the amount of substrate converted) a second experiment may be required to home in on a suitable dilution.
How is the volume of an enzyme assay determined?
From a practical perspective the assay volume is determined/limited by the consumable item that you use for your assays (e.g. cuvettes, tubes, or microplates). The signal for most enzyme assays is proportional to the assay volume and attempts to miniaturise the assay (e.g. to conserve reagents) will usually lead to lower signals. However, absorbance assays are often an exception, and a switch from a 3ml cuvette to 1ml micro-cuvette, for example, will not change the absorbance reading if the width (path length) of the cuvette is still 1 cm (i.e. the light still passes through the same ‘length’ of liquid). This is because absorbance is proportional to path length, not to the volume of sample.
What is the unit of enzymes that catalyzes the reaction of 1 umol of substrate per minute?
1 unit (U) is the amount of enzyme that catalyses the reaction of 1 umol of substrate per minute (definition A).
What is the most important parameter in enzyme assay?
This is because the volume (i.e. number of units) that you add will determine the amount of substrate that is converted into product. Remember, 1 unit catalyses the conversion of 1 nmol of substrate per min (definition B).
How is a continuous assay performed?
acid). However, in continuous assays the appearance of product (less commonly the consumption of substrate) is recorded continuously (e.g. by means of a chart recorder). The same basic rules apply; a plot of signal versus time for a fixed amount of enzyme should be linear and the rate should double if the amount of enzyme is doubled. As long as the assay is being operated in the linear range, the activity of appropriately diluted ‘unknowns’ can be accurately determined from the initial rates of reaction measured with a set of standards.
What are the Similarities Between Enzyme Activity and Specific Activity?
Enzyme Activity and Specific Activity are two measurements that assess the ability of the enzyme to convert substrates to products per unit time.
Why is it important to maintain optimal conditions for the enzyme activity to be at its optimal?
In general conditions, the increased concentrations of substrates and enzyme may increase the activity of the enzyme. Furthermore, the presence of inhibitors can retard the enzyme activity.
What is specific activity?
The specific activity of an enzyme defines the purity of an enzyme in a protein mixture. It measures the activity of an enzyme in one milligram of total protein. Hence, this unit is especially important in the purification of enzymes from proteins, in order to assess the purity of the enzyme. Furthermore, the specific activity is measured by ...
What are the two main measurements of enzyme kinetics?
Also, in enzyme kinetics, the behaviour of the enzyme can be expressed in two main measurements. They are the Enzyme Activity and the Specific Activity of the enzyme.
What is enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity defines as the number of moles of substrate converted to products per unit time. Therefore, the enzyme activity measures the number of active enzyme moles present in the reaction. However, this measurement depends on many factors such as the temperate, pH, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, ...
How do enzymes help the body?
Most enzymes are protein molecules. They are biocatalysts and aid biological functions. Enzymes act by increasing the rate of reaction of biochemical reactions. Furthermore, they have specific 3D shapes that facilitate their function.
What is Dr. Samanthi Udayangani's degree?
Dr.Samanthi Udayangani holds a B.Sc. Degree in Plant Science, M.Sc. in Molecular and Applied Microbiology, and PhD in Applied Microbiology. Her research interests include Bio-fertilizers, Plant-Microbe Interactions, Molecular Microbiology, Soil Fungi, and Fungal Ecology.

Features of Enzymes
Mechanism of Action of Enzymes
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Inhibition of Enzyme Activity
Summary
- Enzymes are catalysts that are capable of catalysing reactions of biological origin. They are protein in nature and are highly specific. Enzymes have an active site into which the substrate gets fit to proceed with the chemical reaction. Enzymes combine with the substrate molecule to form an enzyme-substrate complex. Enzymes act by lowering the act...
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs) on Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity