What is meant by hydrogen bonding?
Hydrogen bonding refers to the formation of Hydrogen bonds, which are a special class of attractive intermolecular forces that arise due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another highly electronegative atom which lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom.
What do you need to know about hydrogen bonding?
hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons; such a bond is weaker than an ionic bond or covalent bond but stronger than van der Waals forces. Hydrogen bonds can exist between atoms in different molecules or in parts of the same molecule.
What elements are in hydrogen bonding?
chloroform (CHCl 3 ): Hydrogen bonding occurs between hydrogen of one molecule and carbon of another molecule. ammonia (NH 3 ): Hydrogen bonds form between hydrogen of one molecule and nitrogen of another.
What are some examples of hydrogen bonds?
hydrogen bond. noun. The definition of hydrogen bond is a chemical bond between the hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom. An example of hydrogen bond is water molecules bonding together in the form of ice. One may also ask, what are the different types of hydrogen bond?

What is meant by hydrogen bonding class 11?
Hydrogen bond is a electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom which is bond to a more electronegative atom such as Nitrogen, Oxygen, fluorine. These are two types of hydrogen bonds :- 1) Intermolecular Hydrogen bonding :- It occurs between two separate molecules.
What is hydrogen bonding example?
water (H2O): Water is an excellent example of hydrogen bonding. The bond is between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen atoms of another water molecule, not between the two hydrogen atoms (a common misconception).
What is a hydrogen bond simplified?
Definition of hydrogen bond : an electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom in one polar molecule (as of water) and a small electronegative atom (as of oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) in usually another molecule of the same or a different polar substance.
Why is it called a hydrogen bond?
The positively charged hydrogen side of one water molecule is attracted to the negatively charged oxygen side of a nearby water molecule. This force of attraction is called a hydrogen bond.
What are the 3 types of hydrogen bonds?
Usually three classes are distinguished: weak, moderate, and strong bonds, with energetic boundaries at about 2 and 15 kcal/mol. The weak hydrogen bonds involve less polar X-H groups in proton donors, like C-H or P-H groups, or less polar acceptors, like the N2 molecule in the N2⋯HF complex discussed above.
Where are hydrogen bonds formed?
Hydrogen bonds occur in inorganic molecules, such as water, and organic molecules, such as DNA and proteins. The two complementary strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides (A&T, C&G).
Is hydrogen bond polar or nonpolar?
Covalent molecules made of only one type of atom, like hydrogen gas (H2), are nonpolar because the hydrogen atoms share their electrons equally.
How do you know hydrogen bonding?
To recognize the possibility of hydrogen bonding, examine the Lewis structure of the molecule. The electronegative atom must have one or more unshared electron pairs as in the case of oxygen and nitrogen, and has a negative partial charge.
Is water a hydrogen bond?
In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. The attraction between individual water molecules creates a bond known as a hydrogen bond.
How is hydrogen bond formed?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
What is hydrogen bonding and why is it important?
Hydrogen bonding is important in many chemical processes. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for water's unique solvent capabilities. Hydrogen bonds hold complementary strands of DNA together, and they are responsible for determining the three-dimensional structure of folded proteins including enzymes and antibodies.
Why is hydrogen bonding so important?
Hydrogen bonds provide many of the critical, life-sustaining properties of water and also stabilize the structures of proteins and DNA, the building block of cells. Hydrogen bonds occur in inorganic molecules, such as water, and organic molecules, such as DNA and proteins.
What are some examples of hydrogen?
Examples of biologically important inorganic compounds containing hydrogen are water (H2O) and hydrochloric acid (HCl, which is produced by the stomach). Organic compounds are fundamentally defined as those substances containing carbon atoms and Carbon-Carbon (C-C) and Carbon-Hydrogen (C-H) bonds.
How is hydrogen bonding used in real life?
Human DNA is an interesting example of a hydrogen bond. In fact, the hydrogen bonding that occurs between base pairs in a strand of DNA results in DNA's familiar double helix shape. This hydrogen bond actually enables the replication of DNA strands.
Is CH4 hydrogen bonding?
Methane (CH4 C H 4 ) is not capable of hydrogen bonding because it does not contain an N-H, O-H, or F-H bond. Hydrogen bonding is only possible in molecules with those bonds because the N, O and F atoms are highly electronegative and small, resulting in a very polar bond that leaves the hydrogen nucleus unshielded.
Is NH3 hydrogen bonding?
Although NH3 vigorously accepts hydrogen bonds in the gas phase, there is yet no example in which NH3 acts as a hydrogen-bond donor. The stereochemistry of the weak interactions of ammonia is dominated by its lone-pair orbital, which leads to the characterization of NH3 as a strong Lewis base.
How many hydrogen bonds can be formed by water?
Water can form four hydrogen bonds. The two lone pairs of oxygen atoms and the two hydrogen atoms of water are involved in intermolecular hydrogen...
How does hydrogen bonding affect acidity?
Hydrogen bonding decreases the acidity of the molecule. This is because the hydrogen atom is involved in bonding and cannot be deprotonated. It is...
Why do polar compounds dissolve in hydrogen bonding?
Polar compounds dissolve in water due to hydrogen bonding. The polar molecules are attracted by water molecules through hydrogen bonding and thus t...
What are the consequences of hydrogen bonding?
The density of ice is less in water due to stronger hydrogen bonds in solid ice than in liquid water. This is an important consequence of hydrogen...
How many hydrogen bonds are present between the base pairs Adenine(A) – Thymine (T) and Guanine (G) – Cytosine (C)?
There are two hydrogen bonds between A-T and three hydrogen bonds between G-C.
Q.1. Which compounds will not form hydrogen bonding?
Ans: Non-polar covalent compounds are not miscible with each other and do not form hydrogen bonds, whereas the others are polar and form H-bonds
Q.2. What are the applications of hydrogen bonding?
Ans: Hydrogen bond has a wide range of applications. It occurs in inorganic molecules, such as water, and organic molecules, such as DNA and protei...
Q.3. Why does hydrogen bonding increase boiling point?
Ans: The greater the attractions, the more energy is needed, and hence higher will be the boiling point. In water, because of the hydrogen bonding...
Q.4. Which attractive force is the weakest?
Ans: The London dispersion force is the weakest among all intermolecular forces of attraction. The London dispersion force is a temporary attractiv...
What is Hydrogen Bonding?
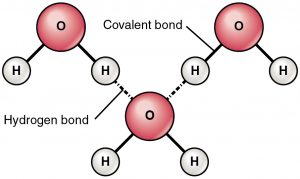
Hydrogen bonding refers to the formation of Hydrogen bonds, which are a special class of attractive intermolecular forces that arise due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another highly electronegative atom which lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom . For example, in water molecules (H2O), hydrogen is covalently bonded to the more electronegative oxygen atom. Therefore, hydrogen bonding arises in water molecules due to the dipole-dipole interactions between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another H2O molecule.
Why does hydrogen bonding occur in water molecules?
Therefore, hydrogen bonding arises in water molecules due to the dipole-dipole interactions between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another H2O molecule. Here, the location of the bond pair of electrons in the O-H bond is very close to the oxygen nucleus (due to the large difference in the electronegativities ...
Why do compounds with hydrogen bonding have high melting and boiling points?
The high melting and boiling point of the compound containing hydrogen bonds is due to the fact that some extra energy is needed to break these bonds.
What happens when a hydrogen atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom?
In a molecule, when a hydrogen atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom, it attracts the shared pair of electrons more and so this end of the molecules becomes slightly negative while the other end becomes slightly positive. The negative end of one molecule attracts the positive end of the other and as a result, a weak bond is formed between them. This bond is called the hydrogen bond.
What is the charge of the hydrogen atom?
Therefore, the oxygen atom develops a partial negative charge (-δ) and the hydrogen atom develops a partial positive charge (+δ). Now, hydrogen bonding can occur due to the electrostatic attraction between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule (with +δ charge) and the oxygen atom of another water molecule (with -δ charge).
Which atom must be electronegative?
The molecule must contain a highly electronegative atom linked to the hydrogen atom. The higher the electronegativity more is the polarization of the molecule.
How do mobile electrons conduct electricity?
On applying an electron field, these mobile electrons conduct electricity throughout the metals from one end to another. Similarly, if one part of the metal is heated, the mobile electrons in the part of the metals acquire a large amount of kinetic energy. Being free and mobile, these electrons move rapidly throughout the metal and conduct heat to the other part of the metal.
What You Need to Know about Hydrogen Bonding
Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
Hydrogen Bond Definition
A hydrogen bond is a type of attractive (dipole-dipole) interaction between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom bonded to another electronegative atom. This bond always involves a hydrogen atom. Hydrogen bonds can occur between molecules or within parts of a single molecule.
But the Atoms Are Already Bonded
How can hydrogen be attracted to another atom when it is already bonded? In a polar bond, one side of the bond still exerts a slight positive charge, while the other side has a slight negative electrical charge. Forming a bond doesn't neutralize the electrical nature of the participant atoms.
Examples of Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are found in nucleic acids between base pairs and between water molecules.
Hydrogen Bonding in Water
Although hydrogen bonds form between hydrogen and any other electronegative atom, the bonds within water are the most ubiquitous (and some would argue, the most important). Hydrogen bonds form between neighboring water molecules when the hydrogen of one atom comes between the oxygen atoms of its own molecule and that of its neighbor.
What are the properties of hydrogen bonding?
Properties of Hydrogen Bonding 1 Solubility: Due to the hydrogen bonding, which the alcohols form with water molecules, the lower alcohols are soluble in water. 2 Volatility: The compounds having hydrogen bonding have high boiling points. As they have high boiling points, the compounds are less volatile in nature. 3 Viscosity and surface tension: The compounds which contain hydrogen bonding exists as an associated molecule and not as a discrete molecule. So their flow becomes comparatively difficult. They have higher viscosity and high surface tension. 4 The lower density of ice than water: The presence of hydrogen bonding in water accounts for the lower density of ice compared to that of water. The hydrogen bonding in solid ice gives rise to a cage-like structure of water molecules. Each water molecule in ice is linked to four other water molecules in a tetrahedral structure. In the solid state of ice, the molecules are not as closely packed as they are in a liquid state. The cage-like structure of ice collapses, when it melts and the molecules come closer to each other. Thus for the same mass of water, the volume decreases and density increases. Therefore, ice has a lower density than water at 273 k. That is why ice floats.
What is the force of attraction of hydrogen bonds?
Hydrogen bonding is primarily the electrostatic force of attraction due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom or group and another highly electronegative bearing a lone pair of electrons that lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom.
Why Do Compounds Having Hydrogen Bonding Have High Melting and Boiling Points?
We know that to boil alcohol, the intermolecular forces of attraction responsible for keeping the alcohols in a liquid state must be overcome by supplying a considerable amount of heat. This explains why alcohol boils at high temperatures.
Why do hydrogen and oxygen form dipoles?
It is due to the dipole dipole interactions that gives rise to hydrogen bonding in water molecule.
What is the charge of the hydrogen atom in a water molecule?
It is due to the electrostatic attraction between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule (with + δ charge) and the oxygen atom of another water molecule (with – δ charge) that leads to the formation of a hydrogen bond.
How many electrons are in a hydrogen sulfide atom?
This helps in the formation of hydrogen bonding between the water molecules. The sulfur atoms in hydrogen sulfide are bigger, with 16 outermost electrons arranged in three orbits around its positive nucleus. The bonding pairs between sulfur and hydrogen are away from the nucleus of the sulfur atom.
What holds the basic structure of the body?
You may be surprised to learn that hydrogen bonds hold our body’s basic structure, which contains the genetic information-DNA. The availability of ice in the solid form is also explained by the hydrogen bond. Have you ever wondered why water exists as a liquid? Why does boiling require a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius? Why is ethyl alcohol water soluble yet ethane isn’t? Let’s find out everything about this in detail in this article.
What is Hydrogen Bonding?
When a special type of dipole-dipole attraction to a strongly electronegative atom exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons, it forms hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonds are generally stronger than ordinary dipole-dipole and dispersion forces, but weaker than true covalent and ionic bonds.
When a hydrogen bonding is present within a molecule itself, then it is called?
When a hydrogen bonding is present within a molecule itself, then it is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
What is it called when there is hydrogen bonding between different types of molecules of the same compounds?
When there is hydrogen bonding between different types of molecules of the different or the same compounds, then it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Taking an example – hydrogen bonding in water, alcohol, etc.
What is the dotted line in a hydrogen bond?
Generally, such an interacting system is denoted as Dn-H..Ac. where the solid lines denote a polar covalent bond and the dash or the dotted lines indicate the hydrogen bond. IUPAC recommends especially these three centered dots. While hydrogen bonds have both electrostatic and covalent contribution, the degree to which they contribute is currently debatable. The present evidence implies that the contribution which is primary is covalent.
What is X-H in chemistry?
It is said to be an interaction which is between an atom from a molecule or it’s a fragment of the molecule which is denoted as X-H in which X is a lot more electronegative than H, and a group or an atom in the different or same molecule in which there is evidence of bond development. [Image will be uploaded soon]
How to determine the strength of hydrogen bonds?
The strength of intermolecular bonds of hydrogen is most often evaluated by measurements of equilibria between molecules containing donor or acceptor units most often in the solution . The intermolecular strength of bonds can be studied with equilibria between conformers and with and without hydrogen bonds. The method of most important identification of hydrogen bonds also in complicated molecules is known as crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, sometimes. In a particular distance, acceptor and donor which are smaller than the sum of the Van der Waals radii can be taken as the strength of the hydrogen bond.
Which type of bonding occurs in two groups of compounds?
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding takes place in the two such groups of compounds where one group has a hydrogen atom linked to an electronegative atom and the other contains a highly electronegative atom which is linked to a lesser electronegative atom of the other group.
What is hydrogen bond?
: an electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom in one polar molecule (as of water) and a small electronegative atom (as of oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) in usually another molecule of the same or a different polar substance. Other Words from hydrogen bond Example Sentences Learn More About hydrogen bond.
What are some examples of hydrogen bonds?
Recent Examples on the Web Perhaps the most basic—and astonishing— of these concepts is the hydrogen bond, which holds together the literal stuff of life: water. — Meghan Herbst, Wired, 11 May 2021 The two main components of this body fluid are water and urea, a molecule that allows the hydrogen bonds to be broken and therefore reduces the viscosities of many aqueous mixtures. — Jennifer Ouellette, Ars Technica, 31 Mar. 2020
Why do hydrogen bonds form?
Reason of hydrogen bonding. Because of the presence of very electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen, the shared electron pair between oxygen and hydrogen are pulled towards the more electronegative atom. This unequal distribution of electron pair leads to the formation of two partial dipole.
When hydrogen bonding occurs between to atoms of different molecule then it is called?
When hydrogen bonding occurs between to atoms of different molecule then it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
What is the term for the bonding between two partially charged atoms of the same molecule?
2. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding. When hydrogen bonding occurs between two partially charged atoms of same molecule that is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding . This occurs when two functional groups are present in same molecule and they are in such way that can attract each other to form hydrogen bond. For example salicylic acid has two ...
What is intermolecular hydrogen bonding?
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding. When hydrogen bonding occurs between to atoms of different molecule then it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding. For such bonding one molecule should have a partially positive hydrogen as acceptor atom and another should have a partially negative or donor atom. As for example, hydrogen bonding between aldehyde ...
Why is the boiling point of polar compounds higher than no polar compounds?
Because of intermolecular hydrogen bonding the boiling point of polar compounds are higher than no polar compounds with same a.
What is the bond between hydrogen and nitrogen?
Hydrogen bond is an attractive force between a partially positive charged hydrogen and a partially negative charged atom (oxygen and nitrogen). This is a very weak bond and strength of hydrogen bond (5-10 Kcal per bond) is much less than the strength of covalent bond. Hydrogen bonds are usually showed as dotted lines between two atoms.
How many types of hydrogen bonds are there?
Hydrogen bonding can occur between two atoms of same molecule or between two atoms of different molecule. Depending on that hydrogen bonding are of two types: