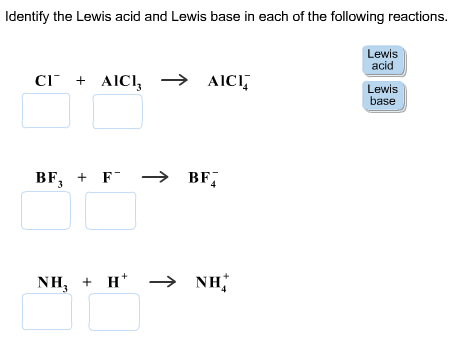
What is the difference between Lewis acid and base?
In general terms, Lewis acid is considered to be an acceptor of electron-pairs, whereas the Lewis base is considered to be donor of electron-pairs. Lewis acid is an acid substance which accepts a lone or single pair of electrons from some other molecule to complete its own stable group atom.
How do you identify Lewis acids and bases?
You can identify Lewis Acids and Bases by looking at the configuration of the molecules and counting the electrons. If the molecule has space to accept an electron pair it is an acid, if it has 2 ...
Which best describes the definition of Lewis acids and bases?
In other words, a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor. A Lewis base is any substance, such as the OH - ion, that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis base is therefore an electron-pair donor. One advantage of the Lewis theory is the way it complements the model of oxidation-reduction reactions.
Is (CO3) 2 a Lewis acid or a base?
[CO3] (2-) is carbonate ion. It can accept a proton (H+) to form bicarbonate ion, [HCO3] (-), making carbonate ion a Bronsted-Lowry base. Since the proton binds by accepting an electron pair from carbonate ion to form a bond, carbonate ion is also a Lewis base.

What is called Lewis base?
A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons.
What is Lewis acid with example?
H+ ions can be considered as Lewis acids. An atom or ion or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as a Lewis acid. For example, AlF3 (Aluminum fluoride). Molecules whose central atom can have more than 8 electrons in a valence shell and can accept electrons, can be called Lewis acid.
What is Lewis acid formula?
pair, which is called a Lewis acid. In complexes of the formula [M(H2O)6]n+, the central metal ion acts as the Lewis acid and the ligand molecules act as the Lewis bases by virtue of a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom (only one of the lone pairs is…
Is NaOH a Lewis base?
NaOH is a Lewis base because the lone pairs on the hydroxide ion can be donated to other compounds.
What is Lewis acid class 10?
Lewis acid is any acid which is an electron pair acceptor. Lewis Base: Lewis base is any base which is an electron pair donor.
What is Lewis base class 11?
Lewis concept of acids and base In the Lewis theory of acid-base reactions, bases donate pairs of electrons and acids accept pairs of electrons. A Lewis acid is therefore any substance, such as the H+ ion, that can accept a pair of non-bonding electrons. In other words, a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor.
Why is HCl a Lewis acid?
Explanation: A Lewis acid is an acid which accepts an electron pair from a compound donor. In the above image cited, H of hydrochloric acid accepts a pair of electrons from H2O .
Is h2so4 a Lewis acid?
Sulphuric acid is a Lewis acid and is a dense oily liquid which acts as a strong dehydrating agent due to its high affinity towards water.
Lewis Acid
Lewis acid is a substance that is always an electron pair acceptor. Classically, It is described by trigonal planar structure and an empty p or d-orbital.
Lewis Base
Lewis bases are electron-rich species that also act as nucleophiles. These are the chemical species that have the most localized highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO. These species can donate their electron pairs to Lewis acids for the formation of coordinate covalent bonds or complexes.
Lewis adduct
When a Lewis base donates its electrons from the highest occupied molecular orbital, HOMO (high energy) to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, LUMO (low energy) of Lewis acid, a coordinate covalent bond or complex is formed called Lewis adduct. It is represented with dots in the center of the complex as a gesture of showing electrons.
Common reactions between Lewis acids and Lewis bases
In this reaction, fluoride anion is an electron donor, and boron from boron trifluoride is an electron acceptor. This means that the fluoride ions act as a Lewis base and boron trifluoride as a Lewis acid. An adduct is formed when Lewis base (F –) attacks the Lewis acid (BF 3 ).
Applications of Lewis acids and Lewis base
They are used in the Friedel-Crafts reactions (acylation and alkylation).
Concepts Berg
Metal ions such as sodium (Na 1+ ), magnesium (Mg 2+ ), and cerium (Ce 3+ ), etc act as Lewis acids because they have empty orbitals. They can coordinate with bases to form adducts. This means all metal ions that have one or more empty orbital can be Lewis acid.
What is a Lewis Base?
Lewis base definition: A Lewis Base is any molecule or compound that has a filled orbital which donates a pair of non-bonding electrons; it can also be known as an electron pair donor or nucleophile.
Is a Lewis Acid a proton donor?
Not exactly. A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A Lewis acid is defined as an electron acceptor, and a Lewis base is defined as a electron donor. All Bronsted-Lowry bases (proton acceptors) are Lewis bases, but not all Lewis bases are proton acceptors. The Lewis definition of an acid and base is the broadest of the three definitions.
Is Lewis theory the same as oxidation reduction?
The Lewis theory is extremely similar in concept to oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. This is because in redox reactions, there is movement of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in changes in oxidation numbers, which is essentially the same thing!
Who was the first person to propose the Lewis acid-base theory?
Gilbert N. Lewis, a physical chemist, from the University of California, proposed the Lewis acid-base theory in 1916. G.N. Lewis never won the Nobel Prize, and some people speculate he was blocked by someone on the prize committee for personal reasons. He was found dead in his lab after working with hydrogen cyanide, probably of natural causes, not from the cyanide.
How many electrons are in a boron trifluoride?
For example in Boron trifluoride there are only 6 electrons in Borons Valence shell hence it accepts a lone pair of electron to form bond hence a Lewis acid
What is the difference between acid and base?
according to Lewis concept a base is defined as a substance which can donate electron , whereas an acid is a substance which can accept electron. in other words while base is an electron donor and acid is an electron acceptor.
What is Lewis base?
Lewis Base: A Base is a substance that have a tendency to donate an electron pair to form a coordinate bond. It is a nucleophile or electron rich species.
What is it called when an atom donates to another atom?
Species in which an atom (usually central atom) is having one or more lone pair donate to other species are known as Lewis base .
Which substance accepts a pair of electrons?
lewis acid is substance which accepts a pair of electrons and lewis base is substance which donates a pair of electrons.
Which ions have an incomplete D orbital?
Generally the positive ions generally known as the cations and compounds which have incomplete d orbital(non metalic oxide) are lewis acid.
Which cation is a weak Lewis acid?
all cation are regarded as Lewis acid because they can accept electron while largest cation and such as sodium ,potassium and barium etc behaviour as a weak Lewis acid. Small cation such as hydrogen ,silver ,ferrous etc. behave as a strong Lewis acid.
CORE Concepts
- So what is a Lewis acid and a Lewis base? In this tutorial, you will learn how to identify Lewis acids and bases, as well as some examples of each of them. In addition, you will put the information together to form the Lewis theory for acid-base chemical reactions!
Topics Covered in Other Articles
Lewis Theory of Acid- Base Reactions
- History of the Lewis acid-base theory
Gilbert N. Lewis, a physical chemist, from the University of California, proposed the Lewis acid-base theory in 1916. G.N. Lewis never won the Nobel Prize, and some people speculate he was blocked by someone on the prize committee for personal reasons. He was found dead in his lab… - What is a Lewis Acid?
Lewis acid definition: A Lewis acid is any molecule or compound that contains an empty orbital that can accept a pair of non-bonding electrons; it can also be known as an electron pair acceptor or electrophile. This broadens the definition so that more molecules can be considered an acid. …
Further Reading
Lewis Acid and Base
- N. Lewis, in 1923, identified acids and bases based on their ability to donate or accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. For this, he gave a generalized definition of acid-base behaviour. When a Lewis acid and base bond together to form a molecule, it is known as a Lewis adduct. According to Lewis concept of acid and base, we have the ...
How to Identify Lewis Acid and Lewis Base
- To identify whether a chemical species is a Lewis acid or base, we can consider the following two conditions: 1. If the valence shell of the chemical compounds’ central atom is filled, it will accept the electron pair and will act as a Lewis acid. 2. If the central atom of the chemical compound has any pair of electrons not bonded, it will donate that pair and will act as a Lewis base. For exampl…
Chemical Reactions Between Lewis Acid and Base
- Various chemical reactions involve Lewis acid and base. These are as follows: 1)Reaction between Ammonia and Silver cation: NH3+Ag+⟶Ag(NH3)2+ In this reaction, silver cation acts as a Lewis acid while ammonia acts as a Lewis base. 2)Reaction between H+ and H2O: H++H2O⟶H3O+ In this reaction, H+ acts as a Lewis acid while H2O acts as a Lewis base. 3)Rea…
Application of Lewis Acid and Base
- Following are the applications of Lewis acid and base: 1. Lewis acids act as a catalyst in many reactions like in the Friedel-Crafts reaction – AlCl3 accepts a lone pair of electrons which belongs to the chloride ion leading to AlCl4−formation. The chemical reaction for this can be written as follows: AlCl3+RCl⟶AlCl4−+R+ 1. Lewis acids are also widely used to encourage many cationic …