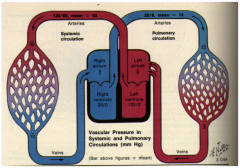
What is meant by pulmonary circulation?
Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re-saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation.
What is meant by systemic circulation?
The systemic circulation provides the functional blood supply to all body tissue. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells and picks up carbon dioxide and waste products. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body.
What is pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation class 10?
Pulmonary circulation only occurs between the heart and the lungs. Systemic circulation refers to the circulation of blood in which oxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the body and deoxygenated blood is returned back to the heart. Systemic circulation occurs between the heart and the entire body.
What is the difference between pulmonary and systemic vessels?
The main difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation is that pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and oxygenated blood back to the heart whereas systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart throughout the body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
What are the 3 types of circulation?
3 Kinds of Circulation: Systemic circulation. Coronary circulation. Pulmonary circulation.
What is systemic circulation class 11?
Systemic circulation is the portion of the cardiovascular system which transports oxygenated blood away from the heart through the aorta from the left ventricle where the blood has been previously deposited from pulmonary circulation, to the rest of the body, and returns de-oxygenated blood back to the heart.
What is systemic circulation of blood Class 10?
Systemic circulation starts with the heart pumping oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the aorta, then through the arteries and capillaries, it is transported to different tissues in the body. Deoxygenated blood from tissues is carried back to the right atrium through venules, veins and vena cava.
What is systemic circulation Byjus?
A. flow of oxygenated blood from the ascending aorta to the heart muscle and the return of deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle to the right atrium.
What is the difference between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation quizlet?
pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
What are the two types of blood circulation?
Two pathways come from the heart: The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again. The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
What are the steps of systemic circulation?
Systemic circulation flows through arteries, then arterioles, then capillaries where gas exchange occurs to tissues. Blood is then returned to the heart through venules and veins, which merge into the superior and inferior vena cavae and empty into the right atrium to complete the circuit.
What is systemic circulation class 8?
The systemic circulation is the portion of the cardiovascular system that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
How do you say systemic circulation?
0:010:35Systemic circulation Meaning - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSystemic circulation the part of blood circulation.MoreSystemic circulation the part of blood circulation.
What is systemic circulation Wikipedia?
Systemic circulation is the portion of the cardiovascular system which transports oxygenated blood away from the heart through the aorta from the left ventricle where the blood has been previously deposited from pulmonary circulation, to the rest of the body, and returns oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart.
What are the steps of systemic circulation?
Systemic circulation flows through arteries, then arterioles, then capillaries where gas exchange occurs to tissues. Blood is then returned to the heart through venules and veins, which merge into the superior and inferior vena cavae and empty into the right atrium to complete the circuit.
What is the difference between pulmonary and systemic circulation?
The main difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation is that pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and oxygenated blood back to the heart whereas systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart throughout the body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
What is the pulmonary circulation system?
Pulmonary circulation is the circulation system that carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart. The two blood vessels involved in the pulmonary circulation are pulmonary artery and the pulmonary vein. The deoxygenated blood flows into ...
What is the systemic circulation?
Systemic Circulation: Systemic circulation is composed of inferior and superior vena cava, aorta, and other small blood vessels.
What is the function of the pulmonary circulation?
The main function of the pulmonary circulation is to oxygenate the blood while the main function of the systemic circulation is to distribute oxygen and nutrients throughout the body while removing the metabolic wastes. This is the difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation.
Which type of circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body?
Conclusion. Pulmonary and systemic circulation are two types of circulations that maintain the homeostasis in the body of many mammals. The pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and returns to the heart. The systemic circulation carries that oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest ...
Which circulation helps to release carbon dioxide from the blood while dissolving oxygen in the blood?
Pulmonary Circulation: Pulmonary circulation helps to release carbon dioxide from the blood while dissolving oxygen in the blood. Systemic Circulation: Systemic circulation helps to provide nutrients and oxygen to the metabolizing cells in the body.
Which vein carries oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart?
Pulmonary Circulation: Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart by the pulmonary vein. Systemic Circulation: Systemic circulation carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart by the superior and inferior vena cava.
Where does systemic circulation start?
Systemic circulation starts in the left atrium when the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs arrives via the pulmonary veins. The blood passes to the left ventricle where it is pumped out through the aorta, the major artery of the body, taking oxygenated blood to the organs and muscles of the body.
Which system circulates oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
The pulmonary circulatory system circulates deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary artery and returns it to the heart via the pulmonary vein. The systemic circulatory system circulates oxygenated blood from the heart around the body into the tissues before returning deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Which system of arteries and veins delivers deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
Pulmonary circulation: the system of arteries and veins that delivers deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Systemic circulation: the system of arteries and veins that carry oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
Which vein carries deoxygenated blood to the heart?
Vena cava: a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart. Deoxygenated: Contains a lesser amount of oxygen than the amount of carbon dioxide. Pulmonary circulation: the system of arteries and veins that delivers deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Systemic circulation: the system ...
Which system of the body circulates blood through the body?
The systemic circulation takes place from the heart to the body parts and then back to the heart. The circulatory system is the continuous system of tubes through which the blood is pumped around the body. It supplies the tissues with their nutritional requirements and removes waste products. The pulmonary circulatory system circulates deoxygenated ...
Which part of the body receives deoxygenated blood?
In pulmonary circulation, the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava, which drains blood from the veins of the upper organs and arms. This deoxygenated blood then passes to the right ventricle, which pumps the blood through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs for re-oxygenation. Systemic circulation starts in the left ...
What is the circulatory system?
Regina Bailey. Updated August 19, 2019. The circulatory system is a major organ system of the body. This system transports oxygen and nutrients in the blood to all of the cells in the body. In addition to transporting nutrients, the circulatory system also picks up waste products generated by metabolic processes and delivers them ...
What is the systemic circuit of the circulatory system?
Wetcake/DigitalVision Vectors/Getty Images. The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body (excluding the lungs). After moving through the pulmonary circuit, oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta.
What is the pulmonary circuit?
Credit: DEA PICTURE LIBRARY/Getty Images. The pulmonary circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the lungs. Blood is pumped to the various places of the body by a process known as the cardiac cycle.
How does the lymphatic system work?
The lymphatic system plays an important role in the proper functioning of the circulatory system by returning fluid to the blood. During circulation, fluid gets lost from blood vessels at capillary beds and seeps into the surrounding tissues. Lymphatic vessels collect this fluid and direct it toward lymph nodes.
Which organ system is responsible for pumping blood?
The heart provides the "muscle" needed to pump blood throughout the body. Blood vessels are the conduits through which blood is transported and blood contains the valuable nutrients and oxygen that are needed to sustain tissues and organs. The circulatory system circulates blood in two circuits: the pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit.
What is the function of lymphatic vessels?
This function of the lymphatic system helps to maintain blood pressure and blood volume.
Where does oxygen rich blood go in the heart?
The now oxygen-rich blood is transported back to the heart by the pulmonary veins. The pulmonary circuit is completed when pulmonary veins return blood to the left atrium of the heart. When the heart contracts again, this blood is pumped from the left atrium to the left ventricle and later to systemic circulation.
How does the circulatory system work?
Circulatory Pathways. Pulmonary circulation works by forming a closed circuit of blood-carrying vessels between the heart and the lungs. To supply the blood with the oxygen it needs, deoxygenated blood exits the heart via the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk.
Which part of the circulatory system is responsible for transporting blood between the heart and the lungs?
Pulmonary circulation is a part of the circulatory system responsible for forming a circuit of vessels that transport blood between the heart and the lungs. Systemic circulation, on the other hand, forms a closed circuit between the heart and the rest of the body.
What are the two major parts of the circulatory system?
The body is made up of circulatory systems that serve as pathways for blood-carrying vessels. These systems are subdivided into two major parts: pulmonary and systemic circulation . Although they are both powered by the heart, they assume different roles in the body.
What is the main function of the pulmonary trunk?
Mainly responsible for supplying oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide to and from the heart. Mainly responsible for moving blood from the heart to the cells of the body, and vice versa. Composed of the pulmonary trunk (also called pulmonary artery) and the pulmonary veins.
Which organ transports oxygenated blood to the cells of the body?
Carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the cells of the body via the aorta. Transports oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins. Transports deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium via the superior and inferior vena cava. Uses the right ventricle and the left atrium as pathways ...
Which artery is used for systemic circulation?
As the system begins, the heart pumps oxygenated blood, which uses the left ventricle and the aorta (the main artery of the body) as a pathway. The movement of oxygen-rich blood towards arterioles and capillary beds facilitates cellular nutrient absorption and waste excretion. Then, the deoxygenated blood, which now carries cellular waste materials, drains into veins and is transported back to the right atrium via the superior and inferior vena cava.
Which vessels carry blood?
Pulmonary circulation involves blood-carrying vessels such as the pulmonary trunk (also called pulmonary artery) and the pulmonary veins. Systemic circulation, on the other hand, is facilitated by the aorta and the superior and inferior vena cava. The superior vena cava carries blood from the upper parts of the body, while the inferior vena cava is responsible for blood transport from the lower parts of the body.
What is the pulmonary blood stream?
Pulmonary circulation, system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs, as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues. On the evolutionary cycle, pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians, ...
What is the blood that takes up oxygen from the air breathed into the air sacs and releases carbon dioxide?
In the capillaries the blood takes up oxygen from the air breathed into the air sacs and releases carbon dioxide. It then flows into larger and larger vessels until the pulmonary veins (usually four in number, each serving a whole lobe of the lung) are reached.
Which veins open into the left atrium of the heart?
The pulmonary veins open into the left atrium of the heart. Compare systemic circulation. The pulmonary veins and arteries in the human. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Read More on This Topic. exercise: Pulmonary effects. The basic function of the lungs is to facilitate the transfer (1) of oxygen from the atmosphere into the blood and (2) ...
