What is a pulverized coal-fired boiler?
Pulverized coal-fired boiler. A pulverized coal-fired boiler is an industrial or utility boiler that generates thermal energy by burning pulverized coal (also known as powdered coal or coal dust since it is as fine as face powder in cosmetic makeup) that is blown into the firebox. The basic idea of a firing system using pulverised fuel...
Why is coal pulverizing important for power plants?
For efficient combustion of the coal in a coal fired power plant, pulverizing to a fine powder for burning is an important requirement. Read on to know why coal pulverizing is important. Coal for Power Plants The coal fired power plant converts energy in coal to electricity. The basic input into the system is the fuel that is coal.
How is coal pulverized to make coal fuel?
The raw coal is then fed into the pulverizer along with air heated to about 650°F / 340°C from the boiler. As the coal gets crushed by the rolling action, the hot air dries it and blows the usable fine coal powder out to be used as fuel. The powdered coal from the pulverizer is directly blown to a burner in the boiler.
What are the different types of pulverized coal power plants?
Pulverized coal power plants are broken down into four categories, with operating temperatures and pressures as a function of the steam temperature and pressure: Subcritical pulverized coal (SubCPC) plants, below the critical point of water (540°C and 170–220 bar), have an operating efficiency <38%.
What is meant by pulverization of coal?
When coal is grounded or broken into fine particles using a device called powdered coal mill, the resultant coal obtained is called powdered coal or pulverized coal. It is used in cosmetics, for the generation of electricity etc.
What is the meaning of pulverized fuel?
Finely ground coal or other combustible material, that can be burned as it issues from a suitable nozzle, through which it is blown by compressed air. Ref: Pryor, 3.
Why is coal need to be pulverized?
Pulverization of coal is currently the favored method of preparing coal for burning. Mechanically pulverizing coal into a fine powder enables it to be burned like a gas, thus allowing more efficient combustion.
What is pulverized coal Mcq?
ANSWER: Coal broken into fine particles.
What is the size of pulverized coal?
The particle sizes of the low rank coal were varied among 45–75, 75–90, and 150–180 μm. The particle sizes of high rank coal were constant at 75–90 μm. The residence time of EDTR was about 4.5 s, which was calculated based on the gas flow rate and the reactor volume for all experiments.
Which equipment is used for pulverizing the coal?
Pulverizers (coal pulverizer) are used to pulverize pieces of coal into fine particles (100μm) before placing into a boiler, to ensure efficient combustion. Pulverizers have three functions, pulverization, drying and classification.
What is pulverized system?
In the pulverized fuel firing system, we make the coal in fine particles with the help of grinding mills. We refer the process of making the fuel powder as pulverization. This pulverized coal gets sprayed in the combustion chamber with a blow of hot air.
How is coal pulverized in the ball mill?
1. How is coal pulverized in the ball mill? Explanation: The pulverization in ball mill takes place as a result of action between the balls and coal, as the cylinder they are put in is made to rotate. The cylinder is partly filled with various sized steel balls.
How is PCI coal made?
Pulverized Coal Injection (PCI) is a process that involves blowing large volumes of fine coal granules into the BF. This provides a supplemental carbon source to speed up the production of metallic iron, reducing the need for coke production. As a result energy use and emissions can be reduced.
What do you mean by pulverization Mcq?
Definition of pulverization “Pulverization” (comminution, crushing, grinding) is the process of applying an external force to a (solid) material of a certain size to destroy it and reduce it into pieces that are smaller than the original size.
What is a need of use for pulverized coal Mcq?
By using pulverized coal the surface area can be increased for burning. This type of coal can increase the combustion rate.
What state does the pulverized coal burn?
gaseous stateExplanation: The combustion of pulverised coal occurs in gaseous state due to which its rate of combustion can be controlled easily.
What is pulverized system?
In the pulverized fuel firing system, we make the coal in fine particles with the help of grinding mills. We refer the process of making the fuel powder as pulverization. This pulverized coal gets sprayed in the combustion chamber with a blow of hot air.
Why pulverized fuel is preferred?
Pulverized coal firing ensures complete combustion of coal, thus ensuring higher efficiency of steam generators. It is predominantly adopted in large coal-fired utility boilers. The finer the grinding of coal, the more efficient its combustion.
Which is an advantage of using pulverized fuel?
Due to the use of pulverized fuel, the combustion rate is faster due to greater surface area of coal per unit mass of coal. It means more coal surface is exposed to heat and oxygen. This decreases excess air required for complete combustion and also decreases fan power.
What are the methods used for pulverized fuel burning?
Pulverized Fuel Firing For obtaining the most calorific value of coal, the coal is pulverised in fine powder and then mixed with sufficient air. The mixture of coal powder and the air is fired in the steam boiler furnace to achieve most efficient combustion process.
What data is needed for pulverized coal combustion?
Data measured in the combustion chamber typically include (1) locally measured values of the gaseous flow field velocity, temperature, and species composition, (2) coal particle burnout, number density, velocity, temperature, and composition, and (3) wall temperatures and heat fluxes. Evaluation should include comparisons with measurements from a wide variety of combustors and furnaces that range in scale from very small laboratory combustors (0.01–0.5 MW) and industrial furnaces (1–10 MW) to large utility boilers (up to 1000 MW).
How is powdered coal injected into the combustion chamber?
The powdered coal is pneumatically transported to burners and injected via particle-laden jets into the combustion chamber. The transport air that carries the coal from the mill to the burners is a small fraction of the total combustion air.
What are the burners in a PC boiler?
Although there are a great variety of burners in PC combustion boilers, the most widespread types are the circular burners and the vertical nozzle arrays. Circular burn ers are usually positioned perpendicularly to the combustion chamber walls, whereas vertical nozzle arrays are in the corners, firing tangentially onto the circumference of an imaginary cylinder in the middle of the combustion chamber. Designs utilizing circular burners are more concerned with the tailoring of the individual burner flame, whereas vertical nozzle arrays in tangentially fired furnaces are designed to rely more on the furnace volume for the mixing of the fuel and air streams. Complete combustion with a minimum (typically less than 15%) of excess air is a challenging task for a coal combustion system. The excess air, usually expressed as the percentage of the theoretically required combustion air, is the additional air needed for complete burnout of the fuel. The significance of the excess air is that the heat carried by the stack gases into the atmosphere, the largest heat loss (about 10%) of boiler operation, is directly proportional to the volume of the flue gas and, hence, to the excess air.
What is a burner?
The burner is a key component in the design of the combustion system. It also determines the flow and mixing patterns, ignition of volatiles, flame stability, temperature, and generation of pollutants. Burners can be classified into two types—swirl and nonswirl.
Where does coal combustion take place?
Pulverized coal combustion takes place within the vertical vortex system as depicted in sixteen pulverized-coal burners with an opposite-fired shifted arrangement are located at two levels.
What is PC combustion?
Pulverized coal (PC) combustion is presently the system of choice for coal-fired power-generating plants. In PC combustion, the coal is dried and is ground to a specified fineness, with a maximum particle size of 250–300 μm, depending on the reactivity of the coal. Coal preparation, which involves feeding, drying, and grinding of the coal, and the pneumatic transport of the pulverized coal to the burners, is fully integrated with the boiler. For lower reactivity coals, the fineness of grind is increased to create a larger specific surface area so as to improve conditions for ignition and combustion. The powdered coal is pneumatically transported to burners and injected via particle-laden jets into the combustion chamber. The transport air that carries the coal from the mill to the burners is a small fraction of the total combustion air. It is kept at low temperature, limited to about 373 K, for reasons of safety against ignition and explosion in the mill and in the powdered coal transport pipeline between the mill and the burners. The rest of the combustion air, which can be preheated to higher temperatures, is injected separately and admixed with the already ignited coal particle-laden jet in the combustion chamber. A schematic illustration of a PC combustion boiler is shown in Fig. 3. The combustion chamber is typically of parallelepiped shape; the dimensions of a 300-MW coal-fired boiler would be approximately be 15×15 m2 of cross-sectional area and 45–50 m in height. The combustion chamber walls are completely cooled by steam-generating tubes. As the pulverized coal particles burn, the flame transfers heat, mainly by thermal radiation, to the steam-cooled tube walls of the boiler. The design of the combustion chamber has to provide for sufficient residence time of the burning particle to complete combustion, and for the cooling of the residual fly ash particles to below their “softening temperature” before entry to narrow convective heat exchanger passages, to prevent the buildup of sticky ash deposits. At regular intervals, friable deposits are removed by soot blowing using steam.
What is pulverized coal?
A pulverized coal-fired boiler is an industrial or utility boiler that generates thermal energy by burning pulverized coal (also known as powdered coal or coal dust since it is as fine as face powder in cosmetic makeup) that is blown into the firebox.
What is coal ground to?
Coal is ground to the size of a fine grain, mixed with air and burned in the flue gas flow. Biomass and other materials can also be added to the mixture. Coal contains mineral matter which is converted to ash during combustion. The ash is removed as bottom ash and fly ash. The bottom ash is removed at the furnace bottom.
How does coal burner work?
How it works. See also: Coal burner. The concept of burning coal that has been pulverized into a fine powder stems from the belief that if the coal is made fine enough, it will burn almost as easily and efficiently as a gas. The feeding rate of the pulverized coal is controlled by computers, and is varied according to the boiler demand and ...
When did the Mercer use coal?
In 1929 , the United States Shipping Board evaluated a pulverized coal-boiler on the steamship Mercer, a 9,500 ton merchant ship. According to its report, the boiler heated with pulverized coal on the Mercer ran at 95% of the efficiency of its best oil-fuelled journey. Firing pulverized coal was also cheaper to operate and install than ship boilers using oil as fuel. First steps towards using Diesel engines as means of propulsion (on smaller ships) were also undertaken by the end of the 1920s ― see Dieselisation.
What are the different types of coal boilers?
Pulverized coal power plants are divided into three categories: subcritical pulverized coal (SubCPC) plants, supercritical pulverized coal (SCPC) plants, and ultra-supercritical pulverized coal (USCPC) plants . The primary difference between the three types of pulverized coal boilers are the operating temperatures and pressures. Subcritical plants operate below the critical point of water (647.096 K and 22.064 MPa ). Supercritical and ultra-supercritical plants operate above the critical point. As pressures and temperatures increase, so does the operating efficiency. Subcritical plants operate at about 37% efficiency, supercritical plants at about 40%, and ultra-supercritical plants in the 42-45% range.
What is coal fired power?
The coal fired power plant converts energy in coal to electricity. The basic input into the system is the fuel that is coal. All other systems and equipment only aid in this conversion process.
Why is coal burned in combustion?
Burning the coal in the combustion process to release the energy in the fuel.
What is the grindability of coal?
Grindability. There is one important characteristic of coal that decides the type, size, and power required for pulverizing. This is the grindability of coal and is denoted by the Hardgrove Grindability Index (or HGI). Grindability in general is a function of the grade of coal.
Which coal has a lower grindability index?
Anthracitic coals, higher grade coals, have higher hardness and consequentially a lower Grindability Index in the range of forty or less. Lignite, the lower grade of coal, on other hand is very soft and easy to pulverize and can have an index of a hundred and greater. The Grindability Index decides what type of pulveriser to use and ...
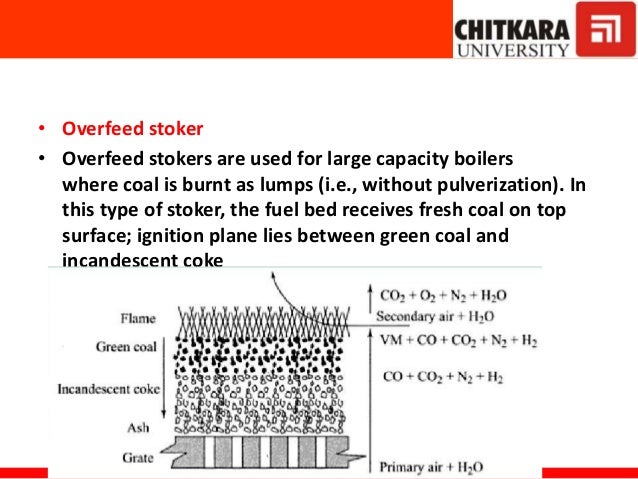
What is the loss of carbon in a boiler?
This means every particle comes into contact with the air. The loss due to unburned carbon is only in the range of 0.5 % or less making the boilers very efficient. The pulverizer does the powdering or the pulverizing. Pulverizers come in different models and are a very important auxiliary of a power plant.
How many phases does coal go through before it is burned?
The coal input to the boiler of the power plant passes through three different phases before combustion in the boiler.
Why do carbon particles go out of coal?
Because of the large size of coal, some of the carbon particles do not come in contact with the air. These unburned carbon particles go out with ash. This is a loss and could be in the range of 5 % or greater in the older grate-fired combustion.
