What is stress definition in mechanical engineering? In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material.
What is the meaning of stress in engineering?
Every component in a mechanical or structural system is loaded in some way due to applied forces or motion. The response and resistance of the component to these loads will be determined by its mechanical qualities. In engineering, stress can be simply explained as the force of resistance offered by a body against deformation per unit area.
What is the difference between mechanical stress and tensile stress?
Stress acting on a body, when two equal and opposite pull forces are applied is known as Tensile Stress. Tensile Stress results in an overall increase in length and decrease in the cross section area of the body. Mechanical Stress acting on a body, when two equal and opposite push forces are applied is known as compressive stress.
What is the unit of mechanical stress in physics?
Mathematically mechanical stress is equal to the internal resisting force acting on a body per unit area. Stress is an area or surface-based property. Its value at any point can be determined by considering A→0 SI unit of mechanical stress is N/m². But in the material datasheet, it is written as MPa.
What is an example of a mechanical stress?
Stress (mechanics) Stress may also be imposed on a material without the application of net forces, for example by changes in temperature or chemical composition, or by external electromagnetic fields (as in piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials).

What is meant by stress and strain?
Stress is the ratio of force over area (S =R/A, where S is the stress, R is the internal resisting force and A is the cross-sectional area). Strain is the ratio of change in length to the original length, when a given body is subjected to some external force (Strain= change in length÷the original length).
What is stress and its types in mechanics?
There are six types of stress: compression, tension, shear, bending, torsion, and fatigue. Each of these stresses affects an object in different ways and is caused by the internal forces acting on the object. The internal forces are the result of how forces are applied to an object.
What is stress and its unit?
Stress is defined as the total force applied per unit area. In units, stress is exactly the same as pressure (Newtons per meter).
What is mechanical stress simple?
Mechanical Stress is a measure of internal resistance exhibited by a body or material when an external force is applied to it. it is denoted by sigma (σ). The elastic limit of the material is the limit where resisting force becomes equal to the applied forces.
What is stress?
Stress is how we react when we feel under pressure or threatened. It usually happens when we are in a situation that we don't feel we can manage or control. When we experience stress, it can be as: An individual, for example when you have lots of responsibilities that you are struggling to manage.
What does it mean by stress?
Stress can be defined as any type of change that causes physical, emotional or psychological strain. Stress is your body's response to anything that requires attention or action. Everyone experiences stress to some degree.
What is stress formula?
Stress is denoted by σ. It is represented as N/m2. Stress formula is articulated as. Where, =Stress(N/m2)
What is stress and examples?
Stress means physical or mental tension. An example of stress is the pressure to finish three large projects by the end of the day. An example of stress is discomfort and pain in your arms from carrying too heavy of an item.
What is the symbol of stress?
σThe conventional symbols for stress are the Greek letters σ and τ and the symbols used for strain are ε and γ.
What is stress in metal?
Stress & Strain in Metals Under Loads. Stress occurs when forces pull (tension), push (compression) or act in combination on a material. When a force is applied the material reacts by distorting to counterbalance the force. A greater force will cause a correspondingly greater distortion until the item breaks.
What is the difference between stress and pressure?
Stress can be defined as the internal resistive force to the deformation per unit area. Pressure can be defined as the amount of force applied per unit area.
What are the 5 types of stress?
5 types of stress: Environmental, postural, emotional, dental and nutritional.
What types of stress are there?
The 3 types of stressAcute stress.Episodic acute stress.Chronic stress.
How many types of stress are there?
Stress is a normal feeling. There are two main types of stress: Acute stress. This is short-term stress that goes away quickly.
What are the three types of stress in physics?
There is various type of stress in physics but mainly it is categorized into three forms: Normal stress. Tangential stress or Shearing stress. Hydraulic stress.
What is stress and examples?
Stress means physical or mental tension. An example of stress is the pressure to finish three large projects by the end of the day. An example of stress is discomfort and pain in your arms from carrying too heavy of an item.
What is it called when the resistive force is perpendicular to the applied load?
So if the resistive force is parellel to the applied load then it is called Shearing stress and if the resistive force is perpendicular to the applied load then it is called Normal stress .
How does stress develop?
Before doing so, we have to understand how stress develops within a body. When some amount of force is applied on a body, the force will try to deform the body. But an equal amount of force will try to resist this deformation due to the cohesive force among the particles of the body . And this “internal resistance force which the body offers to resist the deformation being caused by external force is known as stress.”
How does stress develop within a body?
Before doing so, we have to understand how stress develops within a body. When some amount of force is applied on a body, the force will try to deform the body. But an equal amount of force will try to resist this deformation due to the cohesive force among the particle
What is the resistive force per unit area offered by the body to the external force applied?
Stress is the resistive force per unit area offered by the body to the external force applied.
What happens when an object is bonded to another object?
The atoms of any material are bonded to each other (having a system of balanced forces that keep the atoms in place still allowing them to vibrate). Whenever an external force is applied to an object, the object deforms ( the deformation in most cases is very small and is usually unnoticeable). the deformation causes the atoms to dislocate from their usual bonded positions which in turn leads to development of unbalanced internal forces, which gives the stress.
What are the two types of stresses?
In mechanics, only two types of stresses are defined- direct (or normal) stress and shear stress . direct stress arises when a force normal to the object is applied and shear force arises when a couple (two anti-parallel forces placed a small distance apart) acts on the object.
How is stress measured?
Stress is, generally, measured on unit area basis by dividing the total external force by the cross-sectional area over which it is acting. So, “stress is (internal resistance) force per unit area.”
What is Stress in Engineering?
When designing a structure like a bridge, engineers must make many decisions about which materials to use. One important factor is the stress in the different parts of the structure, but what is stress in engineering? Whenever forces are applied to an object, it creates stress within it.
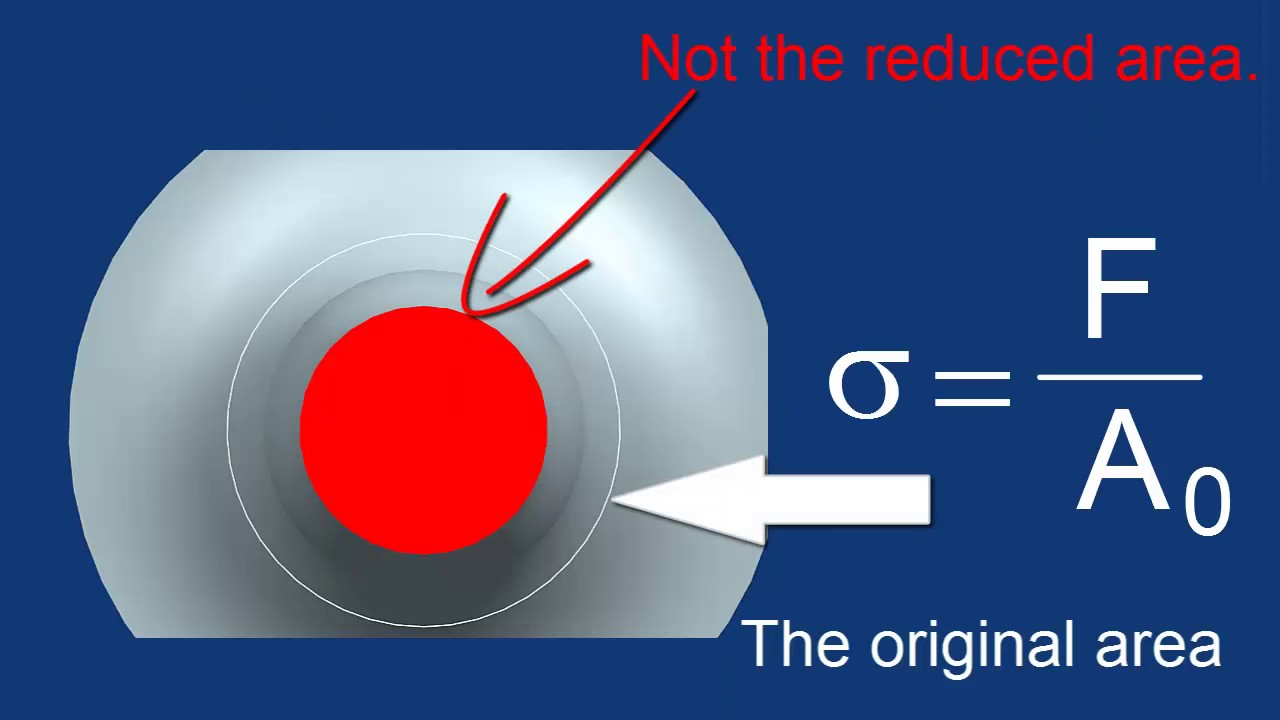
Stress Equation
The stress definition in engineering says that stress is the force applied to an object divided by its cross-section area. Therefore, the applied force must be known to determine the stress within an object. In addition, the cross-sectional area of the object is also important.
Types of Mechanical Stress
Force is typically applied to an object in one of two directions. Axial forces are applied parallel to the major axis of the object and perpendicular to the cross-sectional area. This type of loading can create compressive or tensile stress.
Engineering Stress True or False Activity
In this activity, you will check your knowledge regarding the definition and equation of engineering stress, as presented in the lesson.
How does stress affect material?
Conversely, stress is usually correlated with various effects on the material, possibly including changes in physical properties like birefringence, polarization, and permeability. The imposition of stress by an external agent usually creates some strain (deformation) in the material, even if it is too small to be detected. In a solid material, such strain will in turn generate an internal elastic stress, analogous to the reaction force of a stretched spring, tending to restore the material to its original undeformed state. Fluid materials (liquids, gases and plasmas) by definition can only oppose deformations that would change their volume. However, if the deformation is changing with time, even in fluids there will usually be some viscous stress, opposing that change. Such stresses can be either shear or normal in nature. Molecular origin of shear stresses in fluids is given in the article on viscosity. The same for normal viscous stresses can be found in Sharma (2019).
How is stress analysis done?
Stress analysis may be carried out experimentally, by applying loads to the actual artifact or to scale model, and measuring the resulting stresses, by any of several available methods. This approach is often used for safety certification and monitoring. However, most stress analysis is done by mathematical methods, especially during design. The basic stress analysis problem can be formulated by Euler's equations of motion for continuous bodies (which are consequences of Newton's laws for conservation of linear momentum and angular momentum) and the Euler-Cauchy stress principle, together with the appropriate constitutive equations. Thus one obtains a system of partial differential equations involving the stress tensor field and the strain tensor field, as unknown functions to be determined. The external body forces appear as the independent ("right-hand side") term in the differential equations, while the concentrated forces appear as boundary conditions. The basic stress analysis problem is therefore a boundary-value problem .
What is the stress T that a particle P applies on another particle Q across a surface?
In general, the stress T that a particle P applies on another particle Q across a surface S can have any direction relative to S. The vector T may be regarded as the sum of two components: the normal stress ( compression or tension) perpendicular to the surface, and the shear stress that is parallel to the surface.
What is the difference between strain and stress?
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material.
How many offset blocks are needed to load shear stress?
Shear stress in a horizontal bar loaded by two offset blocks.
Which stress tensor expresses the stress relative to the reference configuration?
In the case of finite deformations, the Piola–Kirchhoff stress tensors express the stress relative to the reference configuration. This is in contrast to the Cauchy stress tensor which expresses the stress relative to the present configuration. For infinitesimal deformations and rotations, the Cauchy and Piola–Kirchhoff tensors are identical.
Which tensor obeys the tensor transformation law?
The Cauchy stress tensor obeys the tensor transformation law under a change in the system of coordinates. A graphical representation of this transformation law is the Mohr's circle of stress distribution.
What is the portion of the graph that shows stress produced in the wire?
The portion OA of the graph is a straight line showing that up to point A, Stress produced in the wire is directly proportional to the strain i.e., stress ∝ strain.
How is shearing strain measured?
It is measured as the ratio of the displacement of the surface that is in direct contact with the applied shear stress from its original position.
What is the stress of a wire?
E.g., If the applied force is 10N and the area of cross section of the wire is 0.1m 2, then stress = F/A = 10/0.1 = 100N/m 2.
What is proportionality of limit?
The proportionality of limit is the maximum stress that a material can hold without the departure from a linear stress-strain relation. If the applied force from any point between O and A is removed, then wire will regains its original length.
What are the two quantities that are used to define the nature of the applied force and resulting deformation?
Stress and strain are two quantities that are used to define the nature of the applied force and resulting deformation.
What happens when you plot a graph between stress and strain?
If we plot the graph between stress and strain, then shape of the curve will be as shown in fig just below:
What is the term for the increase in length of the body due to applied force?
Tensile stress: Tensile stress is defined as the increase in length of the body due to applied force.
What is Stress?
Stress is defined as the resistance force acting per unit cross-section area of the body. It is also defined as the ratio of applied load to the cross section area of the body.
What is the resisting force induced in the body?
The resisting force induced resists the deformation in the body. When this resisting force is taken on unit basis, we get a quantity called stress. Within certain limit the resisting force induced in the body is proportional to the. deformation produced. This certain limit is called elastic limit.
What is the term for the body being subjected to two equal and opposite pushes?
Compressive Stress: When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite pushes, than the stress induced in the body is called compressive stress. Compressive stress results in the increase in the cross section area and decrease in length of the body.
What is the internal force of a body?
Due to this applied load, internal forces induce within the body. This internal force is called as resisting force and the direction of resisting force is opposite to the direction of applied load. The resisting force induced resists the deformation in the body.
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite forces acting tangential to the resisting section,?
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite forces acting tangential to the resisting section, than the stress induced in the body is called shear stress. The shear stress tries to#N#shear off the resisting section. The shear stress acts tangential to the area. It is denoted by symbol ‘τ’ (tau).
What does R mean in physics?
R = Resisting force induced in the body.
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite pulls, than the stress induced in the body?
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite pulls, than the stress induced in the body is called tensile stress. Tensile stress results in the increase in length and decrease in the cross section of the area of the body.

Summary
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity. It results when forces like tension or compression act on a body. The greater this force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. So stress is measured in newton per square meter (N/m ) or pascal (Pa).
Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous …
History
Humans have known about stress inside materials since ancient times. Until the 17th century, this understanding was largely intuitive and empirical, though this did not prevent the development of relatively advanced technologies like the composite bow and glass blowing.
Over several millennia, architects and builders in particular, learned how to put …
Overview
Stress is defined as the force across a "small" boundary per unit area of that boundary, for all orientations of the boundary. Being derived from a fundamental physical quantity (force) and a purely geometrical quantity (area), stress is also a fundamental quantity, like velocity, torque or energy, that can be quantified and analyzed without explicit consideration of the nature of the material or of its p…
Simple stress
In some situations, the stress within a body may adequately be described by a single number, or by a single vector (a number and a direction). Three such simple stress situations, that are often encountered in engineering design, are the uniaxial normal stress, the simple shear stress, and the isotropic normal stress.
General stress
Often, mechanical bodies experience more than one type of stress at the same time; this is called combined stress. In normal and shear stress, the magnitude of the stress is maximum for surfaces that are perpendicular to a certain direction , and zero across any surfaces that are parallel to . When the shear stress is zero only across surfaces that are perpendicular to one particular dir…
Stress analysis
Stress analysis is a branch of applied physics that covers the determination of the internal distribution of internal forces in solid objects. It is an essential tool in engineering for the study and design of structures such as tunnels, dams, mechanical parts, and structural frames, under prescribed or expected loads. It is also important in many other disciplines; for example, in geology, to study p…
Alternative measures of stress
Other useful stress measures include the first and second Piola–Kirchhoff stress tensors, the Biot stress tensor, and the Kirchhoff stress tensor.
In the case of finite deformations, the Piola–Kirchhoff stress tensors express the stress relative to the reference configuration. This is in contrast to the Cauchy stress tensor which expresses the stress relative to the present configuration. For infinitesimal deformations and rotations, the Ca…
Further reading
• Chakrabarty, J. (2006). Theory of plasticity (3 ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 17–32. ISBN 0-7506-6638-2.
• Beer, Ferdinand Pierre; Elwood Russell Johnston; John T. DeWolf (1992). Mechanics of Materials. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 0-07-112939-1.
• Brady, B.H.G.; E.T. Brown (1993). Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining (Third ed.). Kluwer Academic Publisher. pp. 17–29. ISBN 0-412-47550-2.