What is the Med BGP attribute?
What is the MED? The MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator) is an optional BGP attribute, that is used when there are multiple external points for a single AS. For example, you may want traffic coming into your AS destined for network A to take one path but traffic destined for network B to take another.
What is a BGP multi exit discriminator (med)?
The purpose of this document is to provide a better understanding of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Multi Exit Discriminator (MED) Attribute when crossing over an autonomous system (AS) boundary by implementing it in different scenarios.
How does BGP choose the best path for me?
BGP follows a systematic procedure for choosing the best path. There are other important attributes such as weight, local preference, originate route, and AS path that are taken in to account before considering the MED attribute. So, if any of these criteria matches, the MED attribute will not be considered.
Is it possible to use BGP always-compare-med?
However, routers can be configured with bgp always-compare-med and then, well, the MED is always compared if multiple routes to a destination have the same local preference and AS path length.

What is the default Med in BGP?
0If BGP Best Path is selected via MED (metric) attribute, the Lowest MED (metric) value is better and it is selected as BGP path. The default MED value is 0.
What is the difference between AS path and Med?
If so the key difference between MED and path prepending is that MED is only relevant to the neighboring AS ie. it does not go beyond that. Path prepending does. So if you wanted to influence routing beyond your neighboring AS path prepending would be the one to use.
What is the difference between local preference and Med?
Hi JNL, For the first question, the Local_Pref attribute indicates the BGP preference of a device and helps determine the optimal route when traffic leaves an AS. The multi-exit discriminator (MED) attribute helps determine the optimal route when traffic enters an AS.
What is the default MED value?
0By default, the default med-value is 0. The multi-exit discriminator (MED) is an external metric of a route. Different from local preference, MED is exchanged between ASs and will stay in the AS once it enters the AS. The route with a lower MED is preferred.
What does BGP Always compare MED do?
Enables comparison of the Multi Exit Discriminator (MED) for paths from neighbors in different autonomous systems. Any changes in BGP configuration are applied by restarting the current BGP sessions on the VRFs. The no form of this command sets comparison of MED to the default setting (disabled).
What is local preference in BGP?
When an autonomous system (AS) has multiple routes to another AS, the local preference indicates the degree of preference for one BGP route over the other BGP routes. The BGP route with the highest local preference value is preferred.
How do I find my best path in BGP?
BGP Table path selectionPrefer the highest local-preference value.Prefer the shortest AS-path length.Prefer the lowest origin value.Prefer the lowest MED value.Prefer routes learned from an EBGP peer over an IBGP peer.Prefer best exit from AS.For EBGP-received routes, prefer the current active route.More items...
What is the difference between weight and local preference in BGP?
You can use weight instead of local preference to influence the selected path to external BGP peers. The difference is that weight is configured locally and is not exchanged in BGP updates. On the other hand, the local preference attribute is exchanged between iBGP peers and is configured at the gateway router.
Is local preference inbound or outbound?
inbound directionLocal Preference is applied to the inbound direction of the interface. It is the exit point of your AS towards another AS. Different routers have different Local Preference values for that destination and this values is shared within the AS (Autonomous System).
What is BGP weight?
The BGP Weight Attribute Weight is a value that is assigned to our prefixes as a locally significant value. Weight is a simple number in the range of 0 through 65535, and the higher the weight value, the higher the preference for that path. When the prefix is locally generated, it will get a weight of 32768.
What is BGP Multipath?
BGP multipath allows you to install multiple internal BGP paths and multiple external BGP paths to the forwarding table. Selecting multiple paths enables BGP to load-balance traffic across multiple links.
What are different BGP message types?
BGP runs by sending five types of messages: Open, Update, Notification, Keepalive, and Route-refresh. These messages use the same header format.
What is the MED attribute in BGP?
When BGP needs to choose which route to reach a certain destination is best, it first looks at the local preference and AS path attributes, as discussed in previous articles. When the local preference and AS path length are the same for two or more routes towards a certain prefix, the Multi Exit Discriminator (MED) attribute comes into play. Unlike with the local preference and weight, where higher is more preferred, with the MULTI_EXIT_DISC, also known as “metric”, the lowest value is preferred.
What is a BGP identifier?
The BGP identifier is one of the IPv4 addresses of a BGP router, which is used to determine if two BGP sessions are two sessions towards the same router or two sessions towards two different routers.
Why is it problematic to compare the MEDs sent by different ASES?
Also, comparing the MEDs sent by different ASes is problematic because the MED values will not have a consistent meaning: perhaps one AS uses an MED of 10 for “good” and 20 for “bad” while another uses 100 for “good” and 200 for “bad”.
Why is MED only considered when two or more routes are received from the same neighboring AS?
The reason for the MED’s limited propagation is that its original purpose is only to allow directing traffic over the desired link if there are multiple links between two ASes. So normally, the MED is only considered when two or more routes are received from the same neighboring AS.
Can a router use BGP always compare?
However, routers can be configured with bgp always-compare-med and then, well, the MED is always compared if multiple routes to a destination have the same local preference and AS path length. Also, in RFC 1771, the original BGP version 4 RFC, it is left unspecified how a route with no MED attribute compares to a route with ...
What is a BGP multiple exit discriminator?
The BGP multiple exit discriminator (MED, or MULTI_EXIT_DISC) is a non-transitive attribute, meaning that it is not propagated throughout the Internet, but only to adjacent autonomous systems (ASs). The MED attribute is optional, meaning that it is not always sent with the BGP updates.
What is the purpose of MED?
The purpose of MED is to influence how other ASs enter your AS to reach a certain prefix. The MED attribute has a value that is referred to as a metric. If all other factors in determining an exit point are equal, the exit point with the lowest metric is preferred.
What is MED metric?
A MED metric is advertised with a route according to the following general rules: A more specific metric overrides a less specific metric. That is, a group-specific metric overrides a global BGP metric, and a peer-specific metric overrides a global BGP or group-specific metric.
What is the MED?
The MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator) is an optional BGP attribute, that is used when there are multiple external points for a single AS.
Verification
To verify our configured is working correctly, we can look at the BGP table to look at the valid and best BGP paths on R1. As you can see the metric is assigned correctly again each prefix for R2 and R3.
What is BGP MED?
BGP MED (Multi Exit Discriminator) Attribute is the BGP Path attribute which provides information to the external neighbours, about how to come their Autonomous System. This is opposite of Local Preference. BGP Local Preference Atribute says to the internal neighbours, “ How to Exit AS ”. BGP MED Attribute says to the external neighbours, “How to Enter AS ”.
Can BGP MED be sent to neighbours?
BGP MED Attribute can be sent only EGP neighbours . In other words, Local Preference can exchanged in the AS, MED attribute can exchange between ASs. Here, one of the important point is this, MED attribute can be carried into an AS and used inside this AS. But it does not leave that AS.
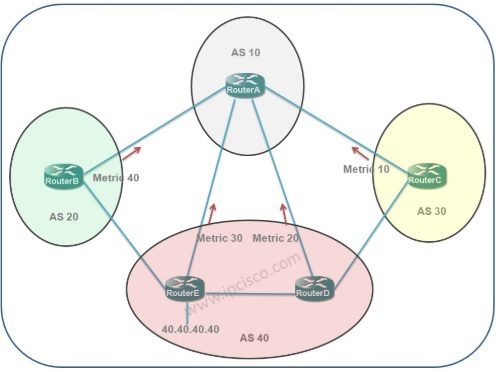
What is MED in routers?
MED is exchanged between autonomous systems. The lowest MED is the preferred path. MED is propagated to all routers within the neighbor AS but not passed along any other autonomous systems. Let’s look at an example:
What is MED in R2?
MED (also called metric) is exchanged between autonomous systems and you can use it to let the other AS know which path they should use to enter your AS. R2 is sending a MED of 200 towards AS 3. R3 is sending a MED of 300 to AS 3.
