Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel was a scientist, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brno, Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a German-speaking family in the Silesian part of the Austrian Empire and gained posthumous recognition as the founder of the modern scienc…
Monohybrid cross
A monohybrid cross is a mating between two individuals with different alleles at one genetic locus of interest. The character(s) being studied in a monohybrid cross are governed by two or multiple alleles for a single locus.
Which law of Mendel is revealed by a dihybrid cross?
Which law of Mendel has been concluded from dihybrid cross? Mendel’s Second Law of Inheritance The outcome that Mendel observed from his dihybrid crosses confirmed that each trait could be described by a pair of factors that segregated to form progeny (his First Law), and further suggested that factors for multiple traits segregated independently, thus forming the basis for Mendel’s Second Law of Inheritance.
Did Mendel report results of genetic crosses?
Mendel was the first scientist to recognize that the principles of probability can be used to predict the results of genetic crosses. What is a Punnett square? A chart that shows all of the possible allele combinations that can result from a genetic cross.
How many genes are involved in monohybrid cross?
How many genes are involved in a monohybrid cross? 1 gene Monohybrid = one gene Example = gene for hair color. How many alleles are involved in a monohybrid cross?
What was Mendels experiments with dihybrid crosses?
Things to Remember
- Crossing between genes that differ in two comparative properties is known as dihybrid crossing.
- Gregor Mendel is recognized as being the first to discover the basic principles of heredity. ...
- The phenotypic ratio of F2 offspring in the dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1.
- The genotypic ratio F2 generation is 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1.
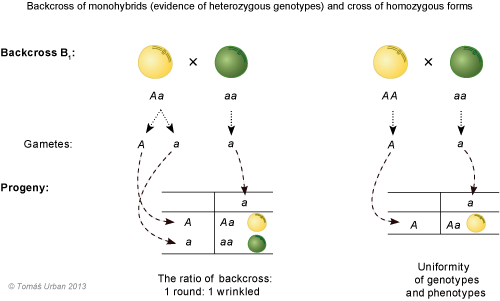
What is Mendel's monohybrid and Dihybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross is defined as the cross happening in the F1 generation offspring of parents differing in one trait only. A dihybrid cross is a cross happens F1 generation offspring of differing in two traits.
What is monohybrid simple words?
monohybrid. / (ˌmɒnəʊˈhaɪbrɪd) / noun. genetics the offspring of two individuals that differ in respect of a single gene.
What does monohybrid mean in biology?
Definition of monohybrid : an individual or strain heterozygous for one specified gene.
What is a monohybrid example?
0:002:46Monohybrid Cross Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn this video we will walk through a monohybrid cross a monohybrid cross is a mating event betweenMoreIn this video we will walk through a monohybrid cross a monohybrid cross is a mating event between two parents that are heterozygous in respect to a single gene. This means that each parent carries
What is monohybrid cross BYJU's?
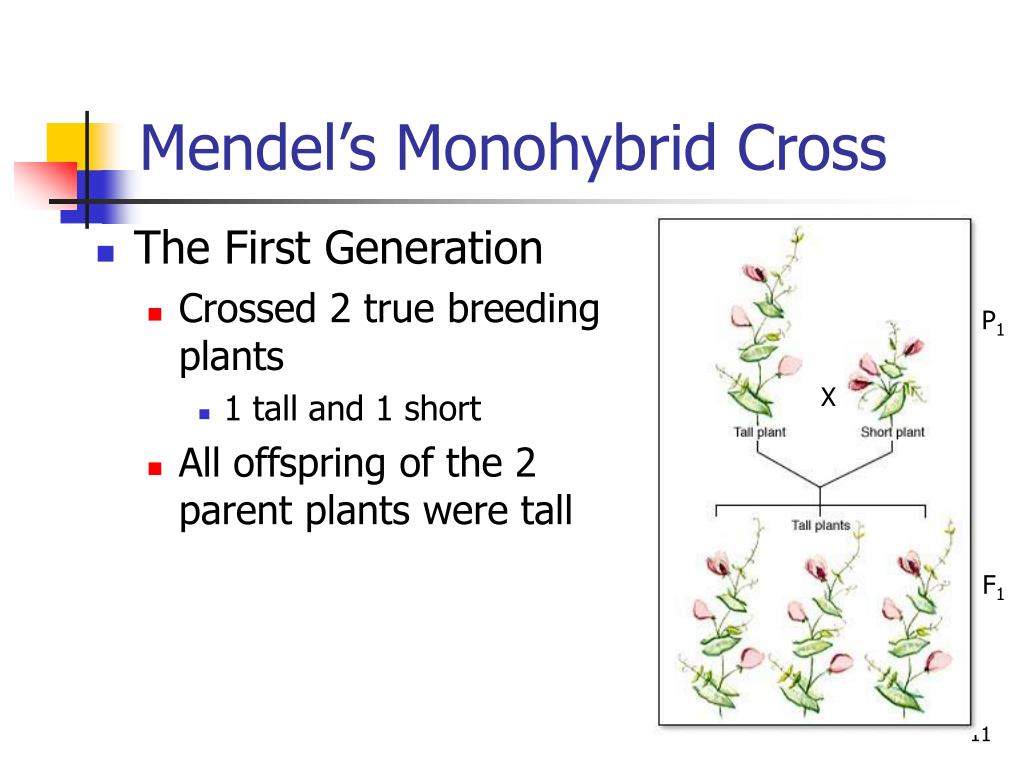
Monohybrid cross is a cross of two individuals with different alleles of a single trait. Eg:-Mendel crossed pure tall plant with pure dwarf plant. He expected plants of intermediate. height, in F1 generation but to his surprise all the plants were tall.
What is a dihybrid cross in biology?
A dihybrid cross describes a mating experiment between two organisms that are identically hybrid for two traits. A hybrid organism is one that is heterozygous, which means that is carries two different alleles at a particular genetic position, or locus.
What is monohybrid law?
In a monohybrid cross, both the alleles are expressed in the F2 generation without any blending. Thus, the law of segregation is based on the fact that each gamete contains only one allele. This law is based on four basic concepts: A gene exists in more than one form of an allele.
What is monohybrid and dihybrid cross give one example of each?
An example of a monohybrid cross is the cross between tall pea plants and dwarf pea plants. An example of a dihybrid cross is the cross between pea plants with yellow round and green wrinkled seeds.
What is the difference between test cross and monohybrid cross?
For a monohybrid cross of two true-breeding parents, each parent contributes one type of allele resulting in all of the offspring with the same genotype. A test cross is a way to determine whether an organism that expressed a dominant trait was a heterozygote or a homozygote.
What is a dihybrid cross example?
An example of a dihybrid cross is the cross between a homozygous pea plant with round yellow seeds and wrinkled green seeds. The round yellow seeds are represented by RRYY alleles, whereas the wrinkled green seeds are represented by rryy. The gametes formed from these alleles are RY and ry.
How many genes are involved in a monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross is one in which both parents are heterozygous (or a hybrid) for a single (mono) trait.
Which of the following is a monohybrid?
A cross between two parents for a single character is called a monohybrid cross and the ratio obtained out of this cross in the F2 generation is called the monohybrid ratio. Monohybrid Cross results in a phenotypic ratio of 3:1.
What is Monohybrid class 10th?
A cross between two types of plants of same species considering only the transmission of one character is called monohybrid cross. For example, a cross between tall pea plants and dwarf pea plant that is considering only the height of the parents is a monohybrid cross.
What is Dihybrid simple?
A dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment between two organisms which are identical hybrids for two traits. In other words, a dihybrid cross is a cross between two organisms, with both being heterozygous for two different traits. The individuals in this type of trait are homozygous for a specific trait.
What is Monohybrid test?
A monohybrid test cross is the process by which you cross two organisms that are heterozygous for a given trait. In such a case, by the law of dominance and by using the Punnett square, you know that the proportion of the offspring produced will be 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous and 25% homozygous recessive.
How do you write a monohybrid cross?
The genotypic ratio of the offsprings in the F2 generation in the case of a monohybrid cross is 1:2:1. The genotypic ratio of the offsprings in the F2 generation in the case of dihybrid cross is 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1. The test cross-ratio of a monohybrid cross is 1:1:1:1.
What are Mendel's conclusions for monohybrid cross?
Mendel’s Conclusions for Monohybrid Cross: Characters such as a height of a stem, a color of seed etc. are inherited separately as discrete particles or unit. He called them a factor or a determiner. Now it is called a gene. Each factor exists in contrasting or alternative forms.
What is a monohybrid cross?
A cross between two pure (homozygous) patterns in which the inheritance pattern of only one of contrasting characters is studied is called monohybrid cross. It is a cross between two pure (obtained by true breeding) parents differing in a single pair of contrasting characters. The procedure is as follows:
Why is Mendel's generation tall?
Mendel thought F 1 Generation is tall because tallness character is given by female parent and dwarfness character is given by a male parent.
What is the meaning of the term "cross pollination"?
The pollens from the selected male flowers are dusted on the stigma of an emasculated female flower. The cross-pollinated flowers were enclosed in separate bags (bagging) to avoid further deposition of pollens from another source. During the pollination, it was assured that the pollen is mature and the stigma is receptive. This is an artificial cross. Mendel crossed many flowers, collected seeds and raised F1 generation. The plants used as parents are said to represent parental generation and are designated as P 1. The progeny obtained as a result of the crossing between parents is called the first filial (offspring) generation and is represented as F 1. All plants of F 1 generation were tall.
How many pairs of characters did Mendel cross?
Mendel performed monohybrid crosses and reciprocal crosses with all the seven pairs of contrasting characters separately and obtained similar results.
What was Mendel's first experiment?
In this article, we shall study Mendel’s monohybrid cross experiment and its conclusions. The first scientific explanation of inheritance was given by Mendel in 1866. He performed a series of experiments on garden pea in a scientific manner and proposed rules. which are called as Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance. His work is known as Mendelism.
What is the name of the generation that Mendel crossed?
Mendel crossed many flowers, collected seeds and raised F1 generation. The plants used as parents are said to represent parental generation and are designated as P 1. The progeny obtained as a result of the crossing between parents is called the first filial (offspring) generation and is represented as F 1.
What is the purpose of a monohybrid cross?
At the simplest level, a monohybrid cross was used to determine the genetic nature of Huntington’s disease. Everyone carries the aptly-named Huntingtin gene, the gene responsible for the complication. With this information, scientists paired the Huntingtin genes of an individual who is homozygous dominant for the condition (HH) ...
What does it mean when a person crosses a monohybrid?
A monohybrid cross can also signify a genetic mix between two individuals who have heterozygous genotypes. These crosses confirm the dominance of an allele.
What is heterozygous genotype?
Heterozygous – A genotype carrying one dominant and one recessive allele.
How do monohybrid crosses determine a genotype?
We have already discussed how scientists use monohybrid crosses to determine the dominant allele of a genotype. However, monohybrid crosses between homozygous individuals is often only the first step. Heterozygous crosses, in which both parents carry a dominant allele and a recessive allele, helps confirm whether a trait is dominant or recessive.
What is the genetic code that one inherits for a specific trait?
Genotype – The genetic code one inherits for a specific trait. Phenotype – The physical manifestation of a specific genetic trait that signals the inheritance of certain genetic codes. Homozygous – A genotype carrying two dominant or two recessive alleles.
Which gene is homozygous dominant for the condition?
With this information, scientists paired the Huntingtin genes of an individual who is homozygous dominant for the condition (HH) with the Huntingtin genes of an individual who is homozygous recessive for the condition (hh).
Is C a monohybrid?
A monohybrid cross breeds a parent that has a homozygous dominant genotype for a specific trait, with a parent that has a homozygous recessive genotype for a specific trait. In this way, it predicts the dominant allele.
What is monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross is a breeding experiment between P generation (parental generation) organisms that differ in a single given trait . The P generation organisms are homozygous for the given trait. However, each parent possesses different alleles for that particular trait. A Punnett square may be used to predict the possible genetic outcomes ...
What Is a Test Cross?
In this type of cross, an individual of unknown genotype is crossed with an individual that is homozygous recessive for a specific trait. The unknown genotype can be identified by analyzing the resulting phenotypes in the offspring. The predicted ratios observed in the offspring can be determined by using a Punnett square. If the unknown genotype is heterozygous, performing a cross with a homozygous recessive individual would result in a 1:1 ratio of the phenotypes in the offspring.
What happens if you cross a genotype with a homozygous recessive individual?
If the unknown genotype is heterozygous, performing a cross with a homozygous recessive individual would result in a 1:1 ratio of the phenotypes in the offspring.
What are traits in DNA?
Traits are characteristics that are determined by discrete segments of DNA called genes. Individuals typically inherit two alleles for each gene. An allele is an alternate version of a gene that is inherited (one from each parent) during sexual reproduction.
Is green pod color homozygous or homozygous?
True-breeding organisms have homozygous alleles for specific traits. In this cross, the allele for green pod color (G) is completely dominant over the recessive allele for yellow pod color (g). The genotype for the green pod plant is (GG), and the genotype for the yellow pod plant is (gg).
What did Mendel study in his study of segregation?
The specific traits that he studied exhibited complete dominance. In complete dominance , one phenotype is dominant, and the other is recessive. Not all types of genetic inheritance, however, show total dominance .
What is the allele for green seed color?
In this example, the allele for yellow seed color is dominant, and the allele for green seed color is recessive. When the alleles of a pair are different ( heterozygous ), the dominant allele trait is expressed, and the recessive allele trait is masked. Seeds with the genotype of (YY) or (Yy) are yellow, while seeds that are (yy) are green.
How many alleles do organisms inherit?
Organisms inherit two alleles for each trait. When sex cells are produced (by meiosis ), allele pairs separate leaving each cell with a single allele for each trait. When the two alleles of a pair are different, one is dominant and the other is recessive.
Monohybrid Cross Definition
Furthermore, in a monohybrid cross, the term "mono" refers to a single creature, while "hybrid" refers to the offspring of two organisms of different species. Finally, the Punnett Square of 2×2 is adequate to establish the monohybrid cross's possibilities.
Things To Remember
Lower case letters can be used to represent recessive alleles. Upper case letters are used to signify dominant alleles.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the difference between monohybrid and dihybrid? (2 Marks)
When did Mendel discover genetics?
By then, three men — working independently — discovered the same principles. So the present remarkable development of genetics dates from only the start of the 20th century.
What did Mendel predict?
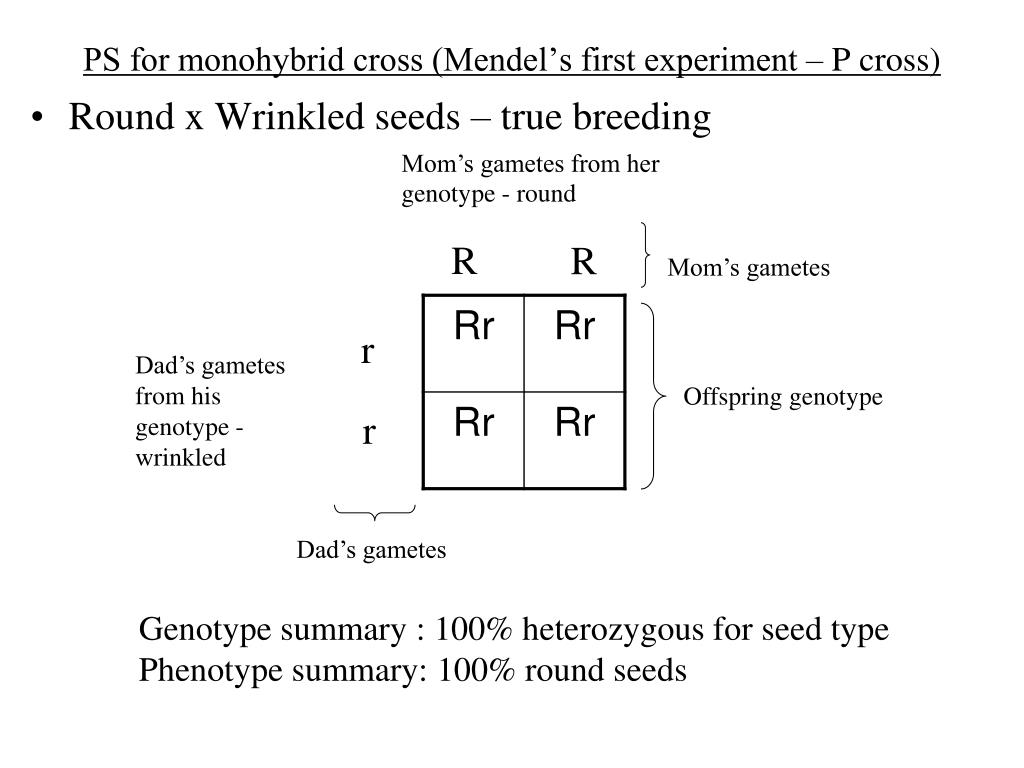
In order to test his hypothesis, Mendel predicted the outcome of a breeding experiment that he had not yet carried out. He crossed heterozygous round peas (Rr) with wrinkled (homozygous, rr) ones. He predicted that in this case one-half of the seeds produced would be round (Rr) and one-half wrinkled (rr)
How many peas did Mendel harvest?
But Mendel predicted that this time he would produce both round and wrinkled seeds and in a 50:50 ratio. He performed the cross and harvested 106 round peas and 101 wrinkled peas.
What is the testcross?
The Testcross: A Test of Mendel's Hypothesis
What was Mendel's second rule?
He found that the inheritance of one trait was independent of that of the other and so framed his second rule: the rule of independent assortment. (But here he was lucky! Link to a discussion of the reason why.) Mendel's rules today. Little attention was paid when Mendel published his findings in 1866.
Which scientist allowed some of each phenotype in the F2generation to self-pollinate?
Mendel then allowed some of each phenotype in the F2generation to self-pollinate. His results:
What is Mendel's rule of segregation?
This statement is often called Mendel's rule of segregation. If an organism has two unlike factors (we call them alleles) for a characteristic, one may be expressed to the total exclusion of the other (dominantvs recessive). The Testcross: A Test of Mendel's Hypothesis. A good hypothesis meets several standards.
Monohybrid Cross Definition
Examples of Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Mendel’s Peas
Although he did not know it at the time, Gregor Mendel used monohybrid crosses to identify dominant and recessive traits in his landmark experiments with peas. Gregor Mendel focused on several different genetic traits, but we will focus on one: stem length. Imagine that two types of … - Huntington’s Disease
Huntington’s Disease is a progressive degenerative condition that occurs in 4 to 15 of every 100,000 people in the United States. Having no cure, it is a certain death sentence for those diagnosed. While little is known about this condition, geneticists are sure that it is inherited via …
Related Biology Terms
- Genotype– The genetic code one inherits for a specific trait.
- Phenotype– The physical manifestation of a specific genetic trait that signals the inheritance of certain genetic codes.
- Homozygous– A genotype carrying two dominant or two recessive alleles. One allele is inherited from the father, and the other, from the mother.
- Genotype– The genetic code one inherits for a specific trait.
- Phenotype– The physical manifestation of a specific genetic trait that signals the inheritance of certain genetic codes.
- Homozygous– A genotype carrying two dominant or two recessive alleles. One allele is inherited from the father, and the other, from the mother.
- Heterozygous– A genotype carrying one dominant and one recessive allele.
Quiz
- 1. A monohybrid cross breeds one parent with a __________ ___________ genotype with another parent with a _________ __________ genotype to determine the ________ ______. A. Homozygous dominant, homozygous retrograde, dominant alley B. Heterozygous dominatrix, homozygous dominant, dominant allele C. Homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, dominant allele D.…