
What is the prognosis for a torn meniscus?
- Pain in the knee joint: usually on the inside (medial), outside (lateral) or back of the knee
- Swelling
- Catching or locking of the knee joint
- Inability to fully extend or bend the knee joint
- Limping
What is the average recovery time for a meniscus tear?
Torn meniscus may take two to three weeks to recover. Recovery time is different in different individuals. It is dependent on the severity of the case, type of treatment, if surgery is done, then it depends on the type of surgery and rehabilitation program. [2] If surgery is performed to treat meniscus tear, then it may take a month to recover.
What tissue makes up the meniscus?
Tissue engineering of the meniscus
- Cell culture experiments in tissue engineering of the meniscus. ...
- Growth factors for tissue engineering of the meniscus. ...
- Biomaterials used in meniscus repair. ...
- Partial reconstruction of meniscus tears. ...
- Production of meniscus prosthesis. ...
- Effects of various procedures on articular cartilage degradation and final considerations. ...
- Conclusions. ...
How long does it take for meniscus surgery to heal?
- Rest - Limit movement to walking. Use crutches to help alleviate pain.
- Ice - Cold helps reduce pain and swelling in the early stages of the injury. ...
- Compress - To control swelling, you can try wrapping the knee with an elastic band or knee brace.
- Elevate - Place a pillow or blanket under your heel or leg when sitting or lying down.
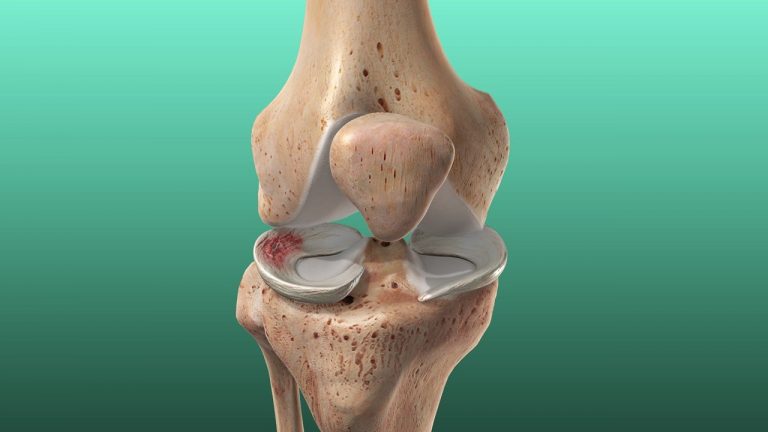
What is the meniscus and what is its function?
The meniscus is often thought of as being shock absorbers between the thighbone and the shinbone. They work to help in the reduction of wear and tear on the knee's cartilage and bones and assist in guiding movement.
What is a meniscus?
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the shinbone and the thighbone. It can be torn if you suddenly twist your knee while bearing weight on it. A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries.
Where is your meniscus?
The menisci sit between the tibia (lower leg bone) and the femur (thigh bone) and protect the lower part of the leg from the shock created by our body weight. The medial meniscus sits on the inside of the knee and the lateral meniscus sits on the outside of the knee.
Is a meniscus a ligament?
Menisci rests between the thigh bone femur and the tibia and there are two knee joint ligaments. They are a type of cartilage in the joint. The rubbery texture of the menisci is due to their fibrocartilagenous structure.
What is the best treatment for a meniscus tear?
TreatmentRest. Avoid activities that aggravate your knee pain, especially any activity that causes you to twist, rotate or pivot your knee. ... Ice. Ice can reduce knee pain and swelling. ... Medication. Over-the-counter pain relievers also can help ease knee pain.
Can you walk on a torn meniscus?
A torn meniscus usually produces well-localized pain in the knee. The pain often is worse during twisting or squatting motions. Unless the torn meniscus has locked the knee, many people with a torn meniscus can walk, stand, sit, and sleep without pain.
Can a meniscus tear heal without surgery?
Meniscus tears are the most frequently treated knee injuries. Recovery will take about 6 to 8 weeks if your meniscus tear is treated conservatively, without surgery.
Can a torn meniscus heal on its own?
In the case of meniscus tears, some people think the injury will heal over time on its own. But the truth is that there are different types of meniscus tears — and some tears won't heal without treatment. If your tear is on the outer one-third of the meniscus, it may heal on its own or be repaired surgically.
What is a meniscus tear?
Meniscus tears are one of the most common knee injuries, affecting approximately 1 million people in the US each year. 1,2 The meniscus can tear from acute injury or trauma to the knee. In addition knees that begin to degenerate over time with age can see changes to both the hyaline cartilage and meniscus, and though changes here are often termed meniscus tears, more accurately they fall more into the category of degeneration, and therefore should be treated differently to acute tears. An acute tear may happen during sports activities or other knee trauma such as twisting injuries. They frequently occur in combination with other knee injuries, particularly cruciate ligament tear (ACL tears). For many of these surgical treatment may be considered.
What is the cartilage on the inside of the knee called?
Each meniscus is smooth, flexible, and rubbery, and acts to provide both stability and shock absorbing protection to the precious knee cartilage lining the joint, also known as the hyaline cartilage. Loss or damage to this hyaline cartilage, for whatever reason, is known as arthritis, so the meniscus is essential to the health of the knee and the prevention of arthritis.
How long do you wear a brace after meniscus surgery?
Generally following meniscus repair surgery, patients typically wear a brace for 2-6 weeks, and usually need crutches for all or part of that time. Heavy lifting, and excessive knee bending may be restricted during this time. Regular rehabilitation exercises are commonly prescribed to restore knee mobility and strength. Generally, patients return to near normal active lifestyles after surgery and rehabilitation.
What is the procedure to repair a meniscus?
Typically your doctor will recommend a minimally invasive procedure called arthroscopy. Arthroscopy allows your doctor to see inside your knee via small incisions to gain access to your knee and meniscus and evaluate it fully before proceeding with definitive surgery. At that point the choice for the doctors is to perform either a meniscus repair where the meniscus is surgically repaired and its shape and function are restored, or a procedure called a meniscectomy, where the damaged section of the meniscus is removed.
How to diagnose a meniscus tear?
These are best diagnosed by a health care professional. A person experiencing any of the common symptoms should consult a sports medicine physician or surgeon for a thorough examination. At the visit, the doctor will do a thorough review the patient’s symptoms and medical history. In addition, the doctor will physically examine and manipulate the injured knee to check for signs of a meniscus tear and other associated pathology. While the diagnosis is often relatively clear from the history and exam, most times an MRI will provide the more definitive picture. X-Rays to look at the overall status of the bones, and in particular to look for arthritis, are frequently done too.
Is meniscectomy a good choice?
While this general trend of less meniscectomies being performed is a welcome development, it must be pointed out that meniscectomy can still be a good choice under the right circumstances, and results from meniscectomy in those cases can be quite satisfying (11)
Can meniscus tears be repaired?
Repairing the meniscus to its original configuration (meniscus repair) rather than removing any part of it (meniscectomy) has obvious advantages, and where possible most surgeons would prefer to repair than resect. However meniscus tissue is somewhat unpredictable in its healing, predominantly due to its variable blood supply and the forces it experiences in the knee. So repair failure rates remain higher than most surgeons like (between 10-30 percent depending on the tear) The post-op rehab for repairs is also considerably more difficult and longer than with meniscectomy. Repair surgery itself also takes longer and is overall more expensive than resection. Lastly, degenerative meniscus has poor structural quality, blood supply and healing ability, so repair is seldom possible or recommendable for tears in this situation.
How does the meniscus work?
They work like shock absorbers, supporting the load by compressing and spreading the weight evenly within the knee. Even while walking, the pressure put on the knee joints can be 2 - 4 times your own body weight; when you run these forces increase up to 6 - 8 times your body weight and are even higher when landing from a jump. By increasing the area of contact inside the joint by nearly 3 times, the menisci reduce the load significantly (dispersing between 30 and 55% of the load).
What Happens When the Meniscus is Injured?
Menisci tend to get injured during movements that forcefully twist your knee while bearing weight. As we age the meniscal tissue degenerates - getting thinner and becoming weaker overall. A degenerated meniscus, as you can probably infer, is more likely to tear as a result of minor injuries or movements.
What ligaments attach the menisci to the knee?
The menisci also attach to leg muscles which help the menisci maintain their position during movement. The semimembranosus and quadriceps attach to both menisci. The lateral meniscus attaches to the popliteus below the knee and the femur via the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). On the inner part of the knee, the ends of the medial meniscus (known as the anterior and posterior horns) are attached to the tibia and joint capsule and along the exterior edge of the meniscus by the coronary ligaments. This means that the medial meniscus is attached at three points compared to the lateral meniscus which is only attached at two points. Coronary ligaments are loose which allow the menisci to pivot freely. However, because the medial meniscus is anchored by a third point, it does not move as freely in the joint as the lateral meniscus and as a result is torn more frequently.
How does the menisci help the knee?
Your menisci act much like a wedge to help naturally prevent over-rotation in the joint, but just as important, the menisci are the true shock absorbers in the knee joint. When walking, jumping or running, there are heavy forces exerted on the knees; your meniscus absorbs and disperses much of the forces instead of the ends of the bones (where the upper leg and lower leg meet in the knee joint) . If the ends of these bones absorb too much force, they will become damaged. It is also worth knowing that the amount of force exerted on the knee joint grows exponentially as speed of movement increases (ie. from walking to running) 1. If you are already suffering from some meniscus damage, it goes without saying that you want to minimize load on the knee joint when you are upright, so take care to avoid running and/or jumping as load forces multiply quite quickly with faster movements.
What is the cartilage in the knee?
As well as providing stability, the tendons, ligaments, articular cartilage and menisci in the joint provide cushioning and protect the upper and lower leg bones where they meet at the knee joint. A type of slick, hard yet flexible tissue known as articular cartilage covers the surface ends of the tibia and femur at your knee joint, allowing them to move easily against one another. The articular cartilage in the knee is generally 1/8 to 1/4 inch thick. A thick, stringy, egg-like fluid, called synovial fluid - found inside the knee capsule - lubricates your knee joint and, along with the meniscus and articular cartilage help reduce friction.
Why does my meniscus tear?
A degenerated meniscus, as you can probably infer, is more likely to tear as a result of minor injuries or movements. Regardless of how the meniscus was damaged, once your meniscus is damaged and/or torn, it starts to move abnormally inside the joint.
Why does a tear on the innermost part of the meniscus heal faster than on the outer peripheral?
The central part of each meniscus has fewer blood vessels and the inner third does not contain any. As a result, a tear on the outer peripheral of the meniscus can heal faster than one on the inner portion. Tears in the innermost part of the meniscus may not heal completely due to the lack of blood supply.
What is the function of meniscus?
A healthy meniscus provides a gliding surface 5 times smoother than that. Menisci also triple joint contact area, decreasing joint pressure by distributing force over a large area. Without menisci, the tibial and femoral condyles would unite in a very small area, causing increased pressure and compression on surrounding articular cartilage.
What is a meniscus tear?
Tears of the meniscus usually occur by two different mechanisms. A traumatic meniscal tear occurs when a patient recalls a specific twisting event during sports or a trauma to the knee. Some meniscal tears can be complicated by also having an MCL Tear. If you want to learn more about torn MCL symptoms, go to: ...
What is the cartilage in the middle of the knee?
The quick answer is the meniscus is a C-shaped piece of soft and fibrous cartilage, also known as fibrocartilage, that provides shock absorption and cushion to your knee.
How are meniscus tears classified?
Meniscal tears are classified and treated based on: Location within the knee. Tear pattern. Complexity of the tear. Quality of the tissue. Depending on the type and location of the tear, you may not need surgical intervention. Tears of the meniscus usually occur by two different mechanisms.
Why do meniscus tears not heal?
Because the blood supply to the meniscus is poor, some tears of the meniscus usually do not heal on their own. Tears are often broken down into three zones based on vascularity: Red Zone – The outer perimeter of the meniscus with adequate blood supply. Red-White Zone – The transitional mid-zone of the meniscus.
How many menisci are there in the knee?
There are two menisci in each knee, one on the inside of the knee and one on the outside of the knee. These are known as your medial and lateral menisci, respectively.
What would happen if you had a complete meniscectomy?
Just to put it into perspective, if you were to have a complete lateral meniscectomy, contact pressure would increase upwards of 200%. That is a lot of pressure that your knees aren’t built to handle independently. To learn more about the knee, please watch this Knee Meniscus Anatomy Video.
What is the shape of the knee meniscus?
Knee Meniscus is a crescent shape structure, triangular in cross section, that cover one half to two thirds of the articular surface of the corresponding tibial plateau. There are two Meniscus in the knee, Medial Meniscus and Lateral Meniscus.
How thick is the medial meniscus?
It’s more mobile than the medial meniscus. The average width is 10 to 12 mm, and the average thickness is 4 to 5 mm. It’s less likely to be injured because: It is firmly attached to the popliteus muscle and to the ligament of Wrisberg or of Humphry, which make it follows the lateral femoral condyle during rotation.
Why is meniscus repair important?
As a vital part of the joint, it acts to prevent the deterioration and degeneration of articular cartilage, and the onset and development of osteoarthritis. For this reason, research into meniscus repair has been the recipient of particular interest from the orthopedic and bioengineering communities
What is the function of menisci?
Reduce the stress on the articular cartilage; they prevent mechanical damage to both the chondrocytes and the extracellular matrix. Shock or energy absorbing functions (from 40% to 60% of the superimposed weight in the standing position are carried by the menisci). See Also: Knee Meniscus Tear.
Which part of the tibia does the menisci follow?
The menisci follow the tibial condyles during flexion and extension, but during rotation they follow the femur and move on the tibia.
What are the three vascular zones of the knee meniscus?
There are three vascular zones of the Knee Meniscus: Red-Red zone: Completely within the vascular zone. Tears within this zone have the highest healing potential. Red-White zone: Intermediate vascularity. Less predictable healing. Red-Red and Red-White comprise the outer 4 mm of the meniscus. White-White zone:
Which artery supplies 10-25 % of the lateral meniscus?
The lateral geniculate artery: Supply 10-25 % from peripheral region of the lateral meniscus.
Where is the medial meniscus located?
They sit on the top surface of the tibia (shin bone) in two crescent shaped parts. 1) Medial Meniscus: is found on the inner side of the knee and is the larger of the two. The meniscus has two distinct areas, the White Zone, which does not have a blood supply, and the Red Zone, which does have a blood supply being vascularised by the joint capsule.
What is the purpose of the meniscus in the knee?
The job of the meniscus is to cushion the knee joint and transfer forces between the tibia and femur, the thigh and shin bones.
How Can I Look After My Knees?
The best way to do this is by doing knee strengthening exercises.
How to tell if a knee is torn?
One of the most common signs of a knee meniscal tear is locking - where the knee gets stuck. This happens which a flap of torn knee meniscus gets stuck in the joint block movement. By wiggling your leg around, you can usually move the torn flap of meniscus out of the way, but the problem will keep occurring. If this is the case, arthroscopic surgery will be advised to trim the damaged flap of knee meniscus.
How to tell if meniscus is broken?
One of the most common signs of a meniscal tear is locking - where the knee gets stuck.
How does a femur help the tibia?
1) Helps the tibia and femur to fit better to each other (increases surface area contact by 40-60%), making the joint more stable. 2) Provides a smooth surface between the femur and tibia, preventing bone rubbing on bone. 3) Helps ensure correct weight distribution between the tibia and femur. 4) Act as shock absorbers/cushions reducing ...
Why do menisci tear?
when playing sports or during a fall. This tends to tear part of the cartilage and can cause bleeding in the joint resulting in swelling. As we age, our cartilage becomes more brittle and can start to wear away. This also makes them more prone to injury.
What is the medial meniscus?
The medial meniscus is the central band of cartilage attached to the tibia, or shinbone.
Why is the medial meniscus less mobile than the lateral meniscus?
It is less mobile than the lateral meniscus because it is firmly attached to the tibial collateral ligament.
What type of surgery is needed for medial meniscus tear?
Common surgery types include arthroscopic repair, partial meniscectomy, and total meniscectomy. Arthroscopic repair is a form of minimally invasive joint surgery.
What is the most common injury to the medial meniscus?
The most common medial meniscus injury is tearing. Intense swelling and pain is expected during the first 24 hours following this injury. Symptoms of a torn medial meniscus include being unable to extend ...
Where is the band on the knee?
The band goes around the knee joint in a crescent-shaped path and is located between the medial condyles of the shin and the femur, or thighbone. The medial condyles are areas of these bones located on the inner sides of the knees.
What is arthroscopic repair?
Arthroscopic repair is a form of minimally invasive joint surgery. Partial meniscectomy involves a partial removal of the meniscus, as opposed to the full removal that occurs during total meniscectomy. Last medically reviewed on January 20, 2018.
What is a torn meniscus?
Torn meniscus. The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between your shinbone and thighbone. It can be torn if you suddenly twist your knee while bearing weight on it. A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries.
How to tell if you tore your meniscus?
If you've torn your meniscus, you might have the following signs and symptoms in your knee: 1 A popping sensation 2 Swelling or stiffness 3 Pain, especially when twisting or rotating your knee 4 Difficulty straightening your knee fully 5 Feeling as though your knee is locked in place when you try to move it 6 Feeling of your knee giving way
What happens if you twist your knee?
A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling and stiffness.
What does it mean when your knee is popping?
A popping sensation. Swelling or stiffness. Pain, especially when twisting or rotating your knee. Difficulty straightening your knee fully. Feeling as though your knee is locked in place when you try to move it. Feeling of your knee giving way.
Can a torn meniscus be caused by a squat?
A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. Even kneeling, deep squatting or lifting something heavy can sometimes lead to a torn meniscus. In older adults, degenerative changes of the knee can contribute to a torn meniscus ...
Can a torn meniscus be a risk?
Performing activities that involve aggressive twisting and pivoting of the knee puts you at risk of a torn meniscus. The risk is particularly high for athletes — especially those who participate in contact sports, such as football, or activities that involve pivoting, such as tennis or basketball.
