
Microanalysis
- Characterization Methods. Microanalysis is one method used to observe pore sizes directly after magnifying the sample. ...
- Nanopowders. ...
- Systems Analysis and Model Synthesis. ...
- Cathodoluminescence microanalysis of ZnO nanowires. ...
- Microanalytical Assays. ...
- Channeling Enhanced Microanalysis
Full Answer
What is Micro Micro Analysis used for?
Micro analysis is a technique of qualitative analysis that analyzes material with less than 10mg mass. It is useful as a chemical identification method and used in qualitative analysis of very small amounts of chemical substances. The mass of the sample can be either 10mg or 1 mL.
What is the meaning of microanalysis?
Definition of microanalysis : chemical analysis on a small or minute scale that usually requires special, very sensitive, or small-scale apparatus Other Words from microanalysis
What is the difference between micro analysis and semi micro analysis?
The key difference between micro analysis and semi micro analysis is that micro analysis is used to analyze material having less than 10mg mass whereas semi micro analysis is used to analyze material having around a 100-500mg mass.
What is Microarray analysis in biology?
Microarray Analysis. Microarray analysis is a method that makes use of gene chips to which thousands of different mRNAs can bind and be quantified. By using such chips to quantify mRNA levels in different tissues or in individuals under different treatments, tens or hundreds of specific genes which vary in relation to the tissue or treatment ...
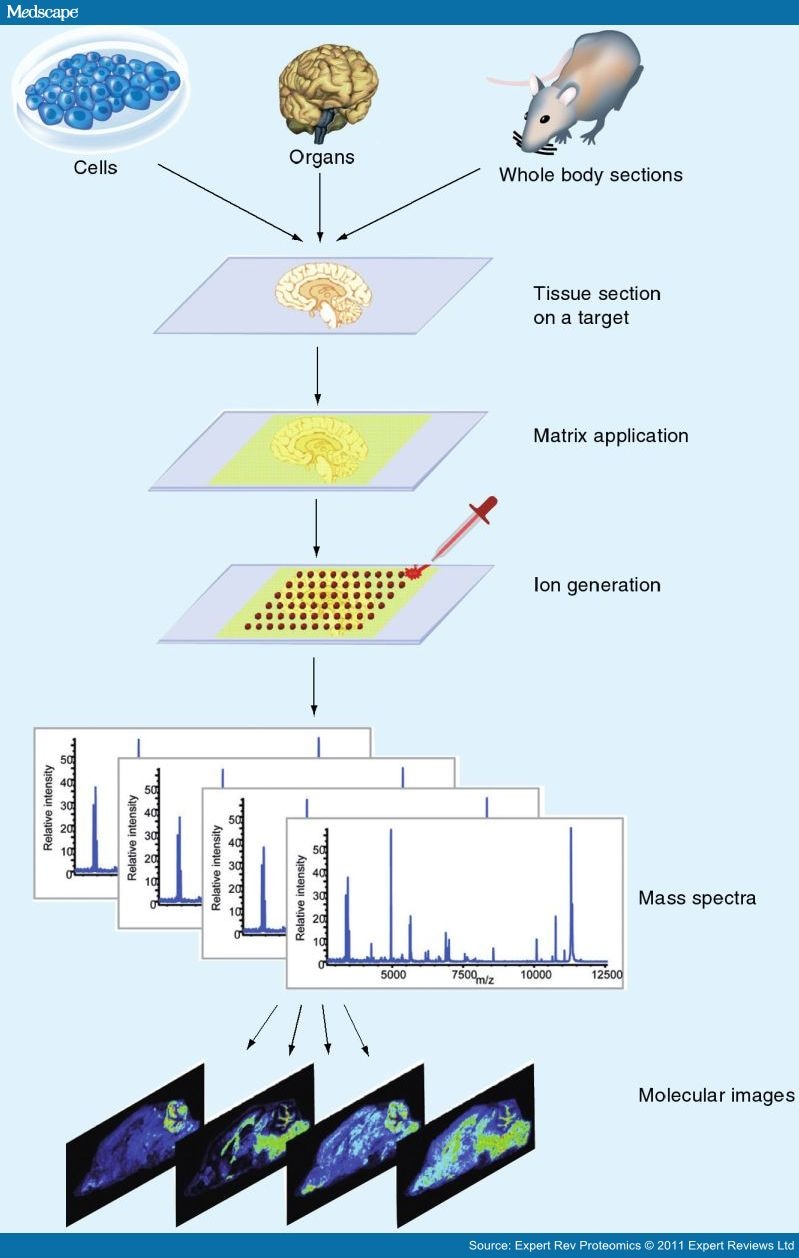
What does micro analyze mean?
Definition of microanalysis : chemical analysis on a small or minute scale that usually requires special, very sensitive, or small-scale apparatus.
What is microanalysis used for?
Compared to normal analyses methods, microanalysis: Can resolve fine-scale variations in chemical elements. Can be used to identify the presence and distribution of different phases in materials. Requires less sample material and therefore can provide information on microscopic objects.
What is meant by micro and Semimicro analysis?
Micro and semi-micro analysis are two types of qualitative analysis. The key difference between micro analysis and semi micro analysis is that micro analysis is used to analyze material having less than 10mg mass whereas semi micro analysis is used to analyze material having around a 100-500mg mass.
What is microanalysis in psychology?
Definition. Microanalysis of face-to-face dialogue: The detailed and reliable examination of observable communication sequences as they proceed, moment by moment, in video-recorded face-to-face dialogue. • The setting is face-to-face dialogue: All participants can interact and contribute spontaneously.
What is sample size for micro analysis?
In the CRP and in this TECDOC the term “microanalytical methods” or “microanalytical techniques” was used for all procedures that extract analytical information from samples weighing 10 mg or less.
What are the two types of semi micro analysis?
(1)Semi-Micro Qualitative Analysis (2)Semimicro-Methods for the Elementary Analysis of Organic Compounds (3) A Textbook of Elementary Quantitative Analysis.
What do you mean by Semimicro analysis?
Semimicroanalysis is the chemical analysis (as of quantities of the order of centigrams) on a scale intermediate between macroanalysis and microanalysis. In order to speed up procedures, all techniques will be on a semimicro scale.
What is macro analysis in analytical chemistry?
Macroanalysis definition (chemistry) Analysis (qualitative or quantitative) in which the size of the sample is of the order of grams. noun.
What is a qualitative analysis?
In business and management, qualitative analysis uses subjective judgment to analyze a company's value or prospects based on non-quantifiable information, such as management expertise, industry cycles, strength of research and development, and labor relations.
How do you write a macro environmental analysis?
Analyzing the Macro EnvironmentIdentify key events and trends within each segment. ... Understand how the various trends relate to each other.Identify the trends likely to have the greatest impact on the organization.Forecast the future direction of these trends, including multiple projections or scenarios.More items...•
How does microanalysis of mother infant communication inform maternal sensitivity and infant attachment?
Microanalysis operates like a “social microscope,” identifying “subterranean,” rapid communications, which are often not quite perceptible in real time. This approach offers the possibility of identifying aspects of maternal sensitivity and the origins of attachment with a more detailed lens.
How does microanalysis apparatus work?
EPMA works by bombarding a micro-volume of a sample with a focused electron beam (typical energy = 5-30 keV) and collecting the X-ray photons thereby emitted by the various elemental species.
What is semi Micro 11 analysis?
: chemical analysis (as of quantities of the order of centigrams) on a scale intermediate between macroanalysis and microanalysis.
Which one of the following apparatus is used for semi microanalysis?
A centrifuge is used to separate a precipitate from a liquid.
What is a microarray analysis?
A microarray is a laboratory tool used to detect the expression of thousands of genes at the same time. DNA microarrays are microscope slides that are printed with thousands of tiny spots in defined positions, with each spot containing a known DNA sequence or gene.
What is the first method of microanalysis?
Microanalysis carried out by electron microprobe (EPMA), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope equipped with suitable analytical devices belong to the first methods.
How does a scanning tunneling microscope work?
In a scanning tunneling microscope [28], during scanning the needle (probe) moves along the sample surface, the tunneling current is kept stable due to the feedback action, and registration of the tracking loop varies depending on the surface topography. These changes are recorded, and on their basis the map of heights is constructed. Another technique is based on the movement of the needle at a fixed height above the sample surface. In this case, the change of the tunneling current is fixed, and on the basis of this information, the topography surface is сonstructed. The resolution is up to 0.01 nm.
How to describe MTM analysis?
In general, Mtm analysis can be likened to opening a series of black boxes. At any given level of detail, the state (or level) of a system can be determined by considering only its inputs and outputs. Thus, the system itself is obscure. The first black box is opened only to discover it contains several black boxes. As each of these black boxes is opened, it is discovered that they also contain additional black boxes. The process is that of differentiating (or articulating) detail. At each level of detail, input and output rates are integrated (or accumulated) over time by a corresponding model to levels that match the system's response over time. Black-box representation of a system is illustrated in Figure 1.13 . Associated with each black box is one state equation and equations for each input and output. Calibration schemes provide values for nonunity coefficients of the equations.
How is quantitative analysis conducted?
Quantitative analysis by EPM is conducted by comparing the x-ray intensity produced from a sample to that produced on a standard of known composition. Therefore, standard quality is of utmost importance in producing acceptable quantitative data. Acquiring good standards is a particular problem in geosciences because of compositional complexity and inhomogeneity of most minerals. Observed x-ray intensities (those “seen” by the spectrometers) differ from the intensities of x rays actually generated by electron bombardment of the specimen because of x-ray absorption, flourescence, and the atomic number effect (discussed further in Section II,D). These effects depend directly on specimen composition, thus the ideal standard is one whose composition is indentical to the unknown. Complete sets of well-analyzed, homogeneous mineral standards, either natural or synthetic, spanning large compositional ranges, are not available. The analyst, therefore, generally must resort to a standard that one hopes is close in composition to the specimen. The very nature of microanalysis places serious restrictions on standards; they must be homogeneous on a micrometer size scale. Most laboratories accumulate a large selection of standards in time, but seldom is a standard available in sufficient abundance for broad distribution among many laboratories. Very little interlaboratory calibration has therefore occurred.
How to measure pore size?
Microanalysis is one method used to observe pore sizes directly after magnifying the sample. The pore structure on the section of sample is observed with a certain magnification, the pore number and size can be measured in the field of view with standard scale, and the pore size and distribution can be calculated, in which the pore size distribution is the percentage of the pore numbers in different pore size ranges.
What is an AFM?
Atomic-force microscopy (AFM) or scanning-force microscopy (SFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM) with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, > 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit
What are the similarities between a system and a model?
Comparison of system and model structures reveal their similarities. As examples, Subsystems correspond to Subsystem Models, Components/Relationships correspond to Variables and Coefficients, and Data Categories correspond to Equation Types of the system model. The system data base identifies two data categories: primary and secondary. Data obtained from historical records are categorized as primary data. Primary data supply values for the exogenous variables of the model. Data initially generated by the model to supplement primary data are categorized as secondary data. Endogenous (solution) variables of the model supply values for these secondary data. The higher the number of primary variables, the lower the initial number of secondary variables to be generated by the model, and vice versa. If there are no primary data, the model is structured to generate a complete data base. Systems modeling is usually attended by a sparsity of primary data. A reverse regression technique is utilized to convert system knowledge items into regression coefficients. Then, given the knowledge-derived coefficients, reverse regression yields the corresponding data.
Why is microanalysis important?
Of particular importance has been the belief in the value of studying social interaction through detailed analysis of film, audiotape, and videotape recordings. Indeed, the effect of the videorecorder has been likened to that of the microscope in the biological sciences. Through the use of recorded data that can repeatedly be examined and dissected in the finest detail, interpersonal communication has become an object of study in its own right.
What can be studied through microanalysis?
Macro issues (such as racism or politics) can be studied through microanalysis. (Bull 2002)
What is the definition of mikroanalysis?
mi·cro·a·nal·y·sis / ˌmīkrōəˈnaləsəs / • n. the quantitative analysis of chemical compounds using a sample of a few milligrams. DERIVATIVES: mi·cro·an·a·lyt·ic / -ˌanlˈitik / adj. mi·cro·an·a·lyt·i·cal / -ˌanlˈitikəl / adj.
What is Micro Analysis?
Micro analysis is a technique of qualitative analysis that analyzes material with less than 10mg mass. It is useful as a chemical identification method and used in qualitative analysis of very small amounts of chemical substances. The mass of the sample can be either 10mg or 1 mL. Also, we can use it for the analysis of substances with a very small surface area (about 1 cm 2 ).
What is the Difference Between Micro Analysis and Semi Micro Analysis?
The key difference between micro analysis and semi micro analysis is that micro analysis is used to analyze material having less than 10mg mass whereas semi micro analysis is used to analyze material having around a 100-500mg mass. Some advantages of micro analysis include its high accuracy, smaller sample size, less waste production, requirement of a short time, and cost-effectiveness. Meanwhile, advantages of semi micro analysis include less waste production and easy handling.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of micro analysis?
The major advantages of micro analysis include the requirement of less time for sample preparation and the requirement of less sample and solvent amounts. It also produces less waste and is cost-effective. The disadvan tages of micro analysis include the difficulty ...
What is qualitative analysis?
Qualitative analysis is the analysis of material based on their properties instead of their quantities. Micro and semi-micro analysis are two types of qualitative analysis. The key difference between micro analysis and semi micro analysis is that micro analysis is used to analyze material having less than 10mg mass whereas semi micro analysis is used to analyze material having around a 100-500mg mass.
Importance, Advantages and Uses
Before Keynesian revolution, the body of economics mainly consisted of micro economics. The classical economics as well as the neo-classical economics belonged to the domain of micro economics.
Limitations and Disadvantages
Microeconomics is not free from limitations (disadvantages). They in brief are:
Definition
The term macro is derived from the Greek word ‘uakpo’ which means large. Macroeconomics, the other half of economics, is the study of the behavior of the economy as a whole. In other words:
Explanation, Advantages and Uses
The main advantages, uses and issues which are addressed in macroeconomics are in brief as under:
Limitations or Disadvantages
The main limitations or disadvantages of macroeconomics are as follows:
What is microarray analysis?
Microarray analysis is a useful, reproducible, and fairly cost-effective tool to assess transcript levels in a wide variety of experimental paradigms. A disadvantage is a requirement for high-quality and abundant input sources of RNA. Whole organism studies can generate significant input amounts of RNA, but do not allow regional or cellular specificity. Regional gene expression analysis is used widely with RNA extracted from cultured cells, animal model tissues, as well as postmortem human brain tissues. However, expression profiles garnered from regional dissections cannot discriminate molecular signatures from admixed neuronal and nonneuronal populations within the region of interest. Ideally, single cells or homogeneous populations of cells could be employed for downstream functional genomic and proteomic based applications.
Why is microarray analysis important?
Microarray analysis not only preserves the practice of query-based biology but has also made biological questioning more important than ever; a recent proposal places ‘the biological question’ as the first step in a microarray experiment. Given the enormous power of microarray assays as data-generating devices, a single set of microarray experiments can generate a large amount of data and may require several months to analyze. Microarray analysis is fundamentally different from the traditional assays that employ gels and nylon membranes. In traditional assays, the ratio of analysis time to experimental time is small but in the microarray, this ratio is enormous. It is therefore suggested that a biological or technical question precede the other four basic steps of every microarray experiment.10
How do microarrays help toxicology?
In this regard, microarray technology offers a near-perfect platform for this type of analysis and possibly serves as a foundation for a fundamentally new approach to toxicology testing. The common methods for assessment of exposure to chemical toxicants are based on quantitation of tissue toxin levels or on surrogate markers of toxicity termed biomarkers. In contrast, gene expression is a sensitive endpoint. A gene expression pattern validated with microarray analysis may be useful as a new biomarker to accurately identify hazards and to assess exposure. Similarly, microarrays can be used in several settings. For example, in environmental toxicology the effect of potential contaminants on the gene-expression profiles of resident organisms can be studied. In an analogous fashion, microarrays could be used to measure gene-expression endpoints in subjects in clinical trials. Another important application of microarray technology, within the context of toxicology studies, is its use as a screening tool for the identification of molecular mechanisms of toxicity. These approaches along with appropriate data comparison with established biomarkers allow researchers to precisely identify those genes and their products (proteins) that are involved in toxic reactions. There are numerous issues that need to be addressed before the full potential of this technology in toxicology research can be realized. For example, selection of model system and the dose, temporal nature of gene expression, and the variability in the global gene expression between organisms before and after toxicant exposure are some examples.
What is CMA coverage?
CMA coverage can be whole genome or targeted, meaning that the array can be created to cover the entire genome at specific intervals or only specific regions associated with disease. The majority of microarrays utilized in the prenatal setting are designed to identify copy number gains or losses of any size in areas associated with known genetic conditions. They often also include broader coverage across the rest of the genome, called the backbone, at equally spaced intervals, which allows the detection of CNVs above a predetermined size, generally 1 Mb in prenatal studies [16].
What is a chromosomal microarray analysis?
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) detects small gains and losses of genetic material at a higher resolution of genetic information (10–100 kb) than traditional karyotype. CMA is recommended as the first-line diagnostic test in fetuses with a structural abnormality and should be offered to any patient (regardless of the presence of a fetal anomaly) who is undergoing diagnostic testing. 137,138
What is the purpose of microarrays?
In an analogous fashion, microarrays could be used to measure gene-expression endpoints in subjects in clinical trials. Another important application of microarray technology, within the context of toxicology studies, is its use as a screening tool for the identification of molecular mechanisms of toxicity.
How are microarrays used?
In an analogous fashion, microarrays could be used to measure gene-expression endpoints in subjects in clinical trials.
