
What is moderate periodontitis?
Moderate Periodontitis. Moderate periodontitis is one of the most critical stages of periodontal disease, because some ‘damage control’ is yet possible before the condition reaches a phase when teeth can not be saved. Surgical treatments of gum disease can stop the progress of the disease but the damage is not reversible.
What is slight periodontal disease?
Slight Periodontal Disease: Slight periodontal disease is the second stage of gum disease. It isn’t reversible, but can be managed. Once you reach stage two, the infection has spread to the bone and has begun to destroy bones. The bacteria have become more aggressive, which is what leads to bone less.
What are the causes of periodontal diseases?
Periodontal diseases are mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed.
What are the signs and symptoms of periodontal disease?
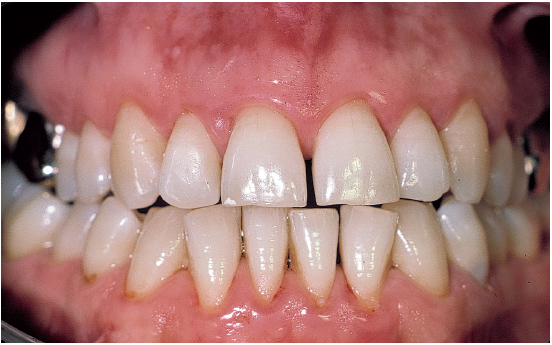
Early periodontal disease may be characterized by swelling and redness of the gums and early horizontal bone loss, but is usually not associated with loss of gum tissues, or gum recession. Early horizontal bone loss around the teeth can be seen on the x-rays below. Typical gum pocket depths would be 4-5mm.

How is moderate periodontitis treated?
Moderate gum disease (mild periodontitis) It is treated with a deep cleaning, a process of cleaning (scaling) below the gum and smoothing the surface of the tooth root (planing) to prevent bacteria from sticking to those surfaces and to allow the gums to reattach.
Can moderate periodontal disease be stopped?
Periodontitis can be stopped if caught and treated early enough. Treatment is typically very successful. If you have periodontitis, regular follow-ups with a dentist are essential to ensure that the disease doesn't continue.
What stage is moderate periodontal disease?
Periodontitis is broken down into four stages: Periodontitis Stage 1: Initial. Periodontitis Stage 2: Moderate. Periodontitis Stage 3: Severe with potential for tooth loss.
What is meant by moderate periodontitis?
Moderate periodontitis is defined as 2 or more interproximal sites with CAL 4 mm or greater (not on the same tooth) or 2 or more interproximal sites with PPD 5 mm or greater (also not on the same tooth); mild periodontitis is defined as 2 or more interproximal sites with CAL 3 mm or greater and 2 or more interproximal ...
Will I lose my teeth if I have periodontal disease?
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications. Periodontitis (per-e-o-don-TIE-tis), also called gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone that supports your teeth.
What toothpaste is good for periodontal disease?
Use Corsodyl Complete Protection Toothpaste, which physically removes the build of plaque bacteria along the gum line, helping to keep the seal between your gums and teeth tight. When used to brush twice daily it is 4x more effective* than a regular toothpaste at removing the main cause of bleeding gums.
Can moderate periodontitis be reversed?
Periodontitis can't be reversed, only slowed down, while gingivitis can be reversed. This is why it's important to catch it in its early stages and prevent it from moving on to periodontitis.
How fast does periodontal disease progress?
Slight Periodontal Disease During the early gingivitis stages, gum inflammation can occur in as little as five days. Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease.
Do I need periodontal maintenance forever?
Instead, you will require special ongoing gum and bone care procedures, known as Periodontal Maintenance Therapy, to keep the disease under control and keep your mouth healthy. In most cases, Periodontal Disease is a lifelong disease that never goes away.
What age do most people get periodontitis?
47.2% of adults aged 30 years and older have some form of periodontal disease. Periodontal disease increases with age, 70.1% of adults 65 years and older have periodontal disease.
Can you stop periodontal disease from getting worse?
How Can Gum Disease Be Prevented? Gingivitis can be reversed and gum disease can be kept from getting worse in nearly all cases when proper plaque control is practiced. Proper plaque control consists of professional cleanings at least twice a year and daily brushing and flossing. Brush your teeth twice a day.
Can gums grow back after periodontal disease?
Can Gums Grow Back? If you were to ask any periodontist if gums can grow back after receding, they would tell you no, they cannot. As nice as it would be to have these soft tissues move back into their original position after treatment, the harsh reality is that they will not.
Can moderate gum disease be reversed?
Though gingivitis, the earliest signs of gum disease, can be reversed with dental treatment and proper at-home dental hygiene, once gum disease gets to the level of periodontal disease, it cannot be reversed.
How fast does periodontal disease progress?
Slight Periodontal Disease During the early gingivitis stages, gum inflammation can occur in as little as five days. Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease.
How do you slow down periodontal disease?
Try these measures to reduce or prevent periodontitis:Brush your teeth twice a day or, better yet, after every meal or snack.Use a soft toothbrush and replace it at least every three months.Consider using an electric toothbrush, which may be more effective at removing plaque and tartar.Floss daily.More items...•
Can you live with periodontal disease?
Living with periodontal disease can cause aesthetic complications and bone loss of a serious nature. Unlike other injuries, periodontal disease does not cause any pain. It is a silent disease when the teeth gum becomes inflamed and bleeds.
What are periodontal diseases?
The word periodontal means "around the tooth." Periodontal diseases, also called gum diseases, are serious bacterial infections that attack the gums and the surrounding tissues. If it's left untreated, the disease will continue and the underlying bone around the teeth will dissolve and will no longer be able to hold the teeth in place. Generally, periodontal disease isn't painful, so it is possible to have it and not be aware of it.
What are the different types of periodontal disease?
The different types of periodontal disease are often classified by the stage the disease including:
What is the term for gums pulling away from the teeth?
Mild periodontitis. Untreated gingivitis leads to mild periodontitis. This stage of gum disease shows evidence of periodontal pockets. This is when gums pull away from the teeth, causing the crevice between the teeth and gums to deepen. It also causes early loss of bone around the teeth.
Why is prompt dental care important?
Prompt dental care is needed to prevent further erosion of bone and gum damage. Moderate to advanced periodontitis. This most advanced stage of gum disease shows significant bone loss, deepening of periodontal pockets, and possibly receding gums surrounding the teeth. Teeth may loosen and need to be extracted.
What does it mean when you have a pus between your teeth?
Pus between the teeth and gums. A change in bite and jaw alignment. The signs and symptoms of gum disease may look like other conditions or medical problems. See a dentist or other oral health specialist for a diagnosis.
What is the term for a person who clenches their teeth?
Bruxism (habitual, involuntary clenching or grinding of the teeth)
What are the causes of gum disease?
As with many other oral health diseases, bacteria and plaque buildup is often the cause. In fact, plaque buildup (which contains many kinds of bacteria) is the leading cause of gum disease. Other factors that contribute to gum disease include: Genetics. Lifestyle choices.
What is mild periodontitis?
Mild periodontitis is the early onset of slight periodontal disease. What makes periodontal disease different from gingivitis is that at this point, bacteria have invaded the gum line and triggered detachment of the tissues. Although the periodontal pockets may be up to 4mm deep, the prognosis is still relatively good.
What is periodontal pocket?
A periodontal pocket is a space that’s created around the root of the tooth when the gums detach, and bone resorbs (due to infection.) Left untreated, pockets will continue to deepen and compromise the stability of the tooth. The depth of each pocket is a major determining factor when diagnosing the stages of periodontal disease.
What is stage IV gum disease?
Stage IV advanced periodontal disease involves extremely deep periodontal pockets as well as significant bone loss around the roots of the teeth. People with stage IV gum disease usually have several missing teeth and are at risk of losing several more. Usually, this stage requires periodontal surgery and/or augmentation of soft tissues or bone to facilitate smile reconstruction.
What causes tooth loss in Los Angeles?
Periodontal disease (gum disease) is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in Los Angeles. Fortunately, recognizing the signs of and treating periodo ntal disease quickly can help prevent bone loss and permanent damage to your smile.
How many teeth do you lose with periodontitis?
Severe periodontitis involves pockets 6mm or greater and the loss of up to four teeth. Vertical bone loss may also be visible on your X-rays. At this point in the disease process, seeing a periodontal specialist is essential. Deep cleanings and periodontal surgery are usually recommended. The prognosis is fair, assuming the infection is caught quickly enough.
Is periodontal disease more aggressive than stage 1?
Moderate periodontal disease is more aggressive than Stage I infections. Pockets are usually up to 5mm deep with slightly visible bone loss on your dental X-rays. At this point, issues such as bad breath or gum recession may also be noticeable. Stage II periodontal disease treatment typically involves scaling and root planing, followed by routine periodontal maintenance.
Can dental implants cause gum disease?
Although dental implants do not develop cavities, the bone and gum tissue around them can still develop advanced periodontitis, especially if home care is not as effective as it should be. Any gum disease around an implant could cause the restoration to fail. Scheduling regular checkups and healthy gum screenings—along with daily brushing and flossing—can help your dental implants last for life. The goal is to prevent any plaque buildup or gingivitis from developing around each of your implant restorations. If you have had poor oral hygiene habits in the past, now is the best time to change them.
Is gum disease a disease?
Periodontal disease is commonly known as gum disease and it’s no fun. Periodontitis is the clinical term and it’s the leading cause of adult tooth loss in the United States. Once established, you’ll need ongoing treatment to keep it from getting worse. And by worse, we mean not only tooth loss, but jawbone deterioration and the possible link to other diseases such as heart disease and stroke.
Does home hygiene prevent periodontal disease?
And it’s all so preventable. Home hygiene prevents periodontal disease in most people. And even in those who haven’t done a great job at home, periodontal disease doesn’t have to rear its head. The downward trend shows itself first in gingivitis, which is a fancy term for gum inflammation. When your gums begin to show areas of red color, instead of the former healthy pink hue, you know you’re not doing a good job with your hygiene. When your gums bleed easily, that’s also gingivitis showing itself. At this point, Dr. Egger can do things such as root planing and simple professional cleaning to bring your teeth back to good health.
What is periodontal disease?
03/04/2020. Periodontal disease is an infection of the tissues that hold the teeth in place. It is caused by poor oral hygiene habits, which allow plaque to build up on the teeth and to harden. When left untreated, it can result in severe damage to the jaw that supports your teeth. It also is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults.
What is the most common treatment for periodontal disease?
Some of the most common periodontal treatments that we use include: Dental cleaning: During a routine dental cleaning, plaque and tartar are removed from above and below the gumline of the teeth. If any signs of gum disease are suspected, we may recommend more frequent dental cleanings.
Why do you need to scale teeth to clean them?
The bacteria have become more aggressive, which is what leads to bone less. Scaling and root planing can be used to deep clean the teeth gums. It removes deposits of bacteria that are deeply rooted in your gums. Moderate Periodontal Disease: The third stage of periodontal disease has more probing depths, which allows for even more bacteria ...
How many stages of periodontal disease are there?
Four stages of periodontal disease. Periodontal disease is broken up into four different stages, which include: Gingivitis: This is the only stage of the disease that is reversible as it hasn’t attacked the bones yet. This is a result of plaque buildup around the teeth. Bleeding gums is one of the first symptoms you may experience.
Why are gums placed around teeth?
The gums are then placed so that the tissue will fit snugly around the tooth. This reduces the space between the gum and tooth, which reduces the chance of bacteria from growing.
What is the procedure to replace bone damaged by gum disease?
Bone grafts: This procedure uses fragments of your own bone, donated bone, or synthetic bone to replace bone destroyed by gum disease. This promotes regrowth of bone, which makes the teeth more stable. Soft tissue grafts can also be used to reinforce thin gums or to fill in places where the gums may have receded.
Can you reverse gingivitis?
Slight Periodontal Disease: Slight periodontal disease is the second stage of gum disease. It isn’t reversible, but can be managed.
What is advanced periodontal disease?
Advanced Periodontal Disease is characterized by more advanced bone loss around the teeth. There is 50% bone loss or more. Pockets typically measure 7-9mm or more, and there may or may not be tissue loss (recession of the gums) and mobility. this is advanced periodontitis with severe inflammation and mobility – this patient is diabetic -note ...
What is the depth of a periodontal pocket?
Early horizontal bone loss around the teeth can be seen on the x-rays below. Typical gum pocket depths would be 4-5mm. Bleeding when measuring (probing) may be ...
How big is a 5mm pocket tooth?
Pockets can measure between 5-7mm, and there may also be associated tissue loss, or gum recession.
Can periodontitis cause bleeding?
All stages of periodontitis – even the advanced stage – may not always be associated with pain, bleeding, or other obvious symptoms and signs. See more pics. There may be no symptoms at all. This is why a thorough examination and x-rays by a periodontist (gum disease specialist) or dentist is highly recommended.
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, otherwise known as gum disease, are inflammatory conditions marked by red, swollen, painful gums, tooth loss, bad breath, and occasionally oral bleeding. Often, these symptoms are first discovered while brushing one’s teeth or using dental floss. We encourage readers to always be mindful of these early symptoms while brushing.
What is gum disease?
Periodontal disease often referred to simply as “gum disease”, encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions that affect the soft tissues surrounding the teeth. Fortunately, good oral hygiene and regular cleaning can help treat and reduce the risk of developing gum disease. Did you know that there are several key stages to the development ...
What does it mean when your gums are bleeding after flossing?
If the plaque does not begin to recede after regular cleaning, it may be advancing into more advanced stages. This early stage of gum disease involves plaque entering the small spaces between your teeth. Gingivitis is commonly identified by bad breath, swollen gums, and bleeding while flossing.
Why do my teeth get so bad?
When it comes to your oral health, there are few things more important than the tissue that holds your teeth in place: your gums. When your gums contract a disease, it is usually due to infections that take hold in the absence of proper brushing and flossing. Foregoing brushing and flossing can lead to excess plaque buildup, which is a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
What to ask your dentist about if you have gum disease?
If you suspect you may have gum disease, or if you are at risk for gum disease, ask your dentist about having your gums checked for infection or disease. To make a more informed judgment, your doctor or dentist will likely ask you about your medical history and your family history of oral disease.
How do you know if you have gum disease?
If you detect any of the following symptoms, consider speaking with your dentist about whether you might have gum disease. Lingering bad breath, even after brushing. Swollen gums or red gums. Loose or sensitive teeth.
How to treat bad breath and pocket depths?
The only treatment method available at this stage is periodontal surgery or laser therapy, which are needed to clean out the deep pockets of bacteria buried under the gums and teeth.
What is periodontal disease?
Inadequate brushing and flossing allows bacteria to thrive where the teeth meet the gums, and the subsequent build-up of plaque and tartar can result in a serious gum infection. Periodontal disease, also called gum disease, can also be caused by smoking. Certain medical conditions such as diabetes or medications that reduce saliva flow are also significant risk factors. Periodontal disease occurs in four separate stages, and only the first stage is reversible—the rest will require advanced dental treatments.
What happens if you ignore the symptoms of periodontal disease?
If you ignore the symptoms of earlier stages of periodontal disease, you will shift into stage 4, which threatens a 50-90% chance of irreversible bone loss. Symptoms of this final stage include red, swollen gums that ooze pus, painful chewing, extreme cold sensitivity, severe bad breath, and loosened teeth. The only remedy at this point is periodontal surgery or periodontal laser therapy, which will clean out the deep pockets of bacteria beneath the gums and allow the infected tissue to heal.
How to tell if you have gingivitis or periodontal disease?
Symptoms of slight periodontal disease include increased swelling or redness of the gums and bleeding during brushing or flossing. Your dentist can diagnose this stage of the disease by probing the depths between your gums and teeth. If the depth is between four and five millimeters, you likely have slight periodontal disease that will need specialized cleaning procedures to treat.
What is the phone number for periodontics in San Diego?
At San Diego Periodontics & Implant Dentistry, we specialize in gum health and treatments, so if you have questions about periodontal disease, check out our FAQ page or call us at (619) 543-0905 to schedule a consultation.
Why is periodontitis considered a critical stage of periodontal disease?
Moderate periodontitis is one of the most critical stages of periodontal disease, because some ‘damage control’ is yet possible before the condition reaches a phase when teeth can not be saved.
How to treat periodontitis?
Treatment of early periodontitis includes tooth scaling and root planing accompanied by improved oral hygiene. Despite the bone damage, the amount of bone loss in this stage of periodontal disease is minor so that usually no additional treatment is required.
What is the first stage of periodontal disease?
1. Gingivitis. Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease representing the mildest form of periodontal disease. Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums characterized by redness, swelling, and sometimes bleeding during brushing or probing. The gums become irritated by the toxins produced by the bacteria of dental plaque and tartar ...
What is the cause of tooth loss?
Periodontal disease also known as gum disease is a progressive inflammatory disease of the gingival and bone tissues that surround and support teeth. Periodontal disease is the main cause of tooth loss after the age of 30 and it is believed that around 80% of the population above the age of 30 may experience the disease some time in their life.
Why do gums get irritated?
The gums become irritated by the toxins produced by the bacteria of dental plaque and tartar that have accumulated on teeth and gums as a result of poor oral hygiene. Gums get inflamed, loosening their attachment to the tooth and exposing previously covered enamel. The space between the gum and tooth (sulcus) gets deeper, forming a periodontal pocket. The depth of pockets is about 1-4mm when measured during periodontal probing.
What is the treatment for gingival pockets?
Gingival pockets are formed below the gumline. Treatment of early periodontitis includes tooth scaling and root planing accompanied by improved oral hygiene. Despite the bone damage, the amount of bone loss in this stage of periodontal disease is minor so that usually no additional treatment is required. 3.
What is the most dangerous form of gum disease?
In order to determine the exact stage of gum disease, the dentist has to perform a periodontal examination (probing). 2. Early Periodontitis . Periodontitis is the more dangerous form of periodontal disease. Infection and inflammation has spread to the bone supporting the teeth.
Causes
Warning Signs
Risk Factors
Prevention and Treatment
What Is The CDC Doing About Periodontal Disease?
- Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus. Tartar build-up can sprea…
Podcasts About Periodontal Disease and Diabetes
- The following are warning signs of periodontal disease: 1. Bad breath or bad taste that won’t go away 2. Red or swollen gums 3. Tender or bleeding gums 4. Painful chewing 5. Loose teeth 6. Sensitive teeth 7. Gums that have pulled away from your teeth 8. Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite 9. Any change in the fit of partial dentures
Additional Resources
- Certain factors increase the risk for periodontal disease: 1. Smoking 2. Diabetes 3. Poor oral hygiene 4. Stress 5. Heredity 6. Crooked teeth 7. Underlying immuno-deficiencies—e.g., AIDS 8. Fillings that have become defective 9. Taking medications that cause dry mouth 10. Bridges that no longer fit properly 11. Female hormonal changes, such as with pregnancy or the use of oral c…
Reference
- Gingivitis can be controlled and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and som…