
Explore
– Aesthetically they are more beautiful than natural ones and can be given any shape and length, not to mention the possibilities of decoration. – They are very resistant and prevent nail cracking, so they are perfect for people with weaker nails or those with a tendency to break.
What are the advantages of nails?
try soaking your feet in warm salty water for 30 minutes to soften the nail and the skin. Ensure you dry your feet properly afterwards and do not put them back in a shoe for a while. You can soak your feet a few time days. Do not wear restrictive tight ...
What to do with your nails?
- Nails are made up of keratin (protein made of dead cells) but the living base part of nail (nail matrix) present under the skin is responsible for the growth of ...
- The new cells (nail matrix) push older cells upward and become harden due to the keratin.
- Fast growth of nails is a good sign of health. ...
Why do my fingernails grow so fast?
Nails. It is a solid substance that coats the fingers, consisting mainly of keratin, and its importance lies in maintaining the hardness and strength of the fingers, and helps in controlling the control of fine things, in addition to raising the internal temperature of the fingers, and also supports the pressure of the fingers on the objects, and helps in the process of tightening and grasping ...
What is the importance of nails on our fingers?
See more
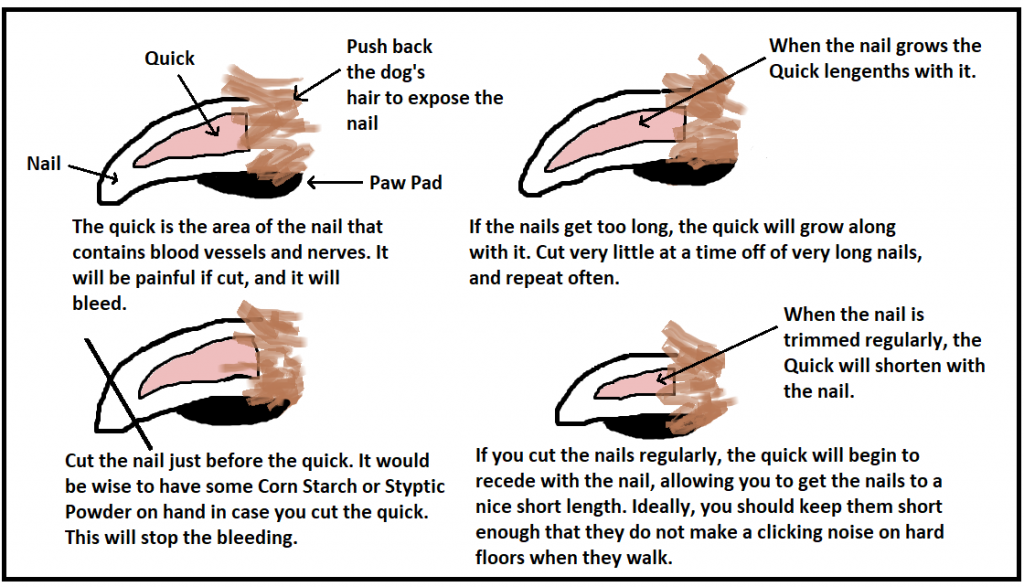
What are the nails 2 functions?
Functions of Nails Both fingernails and toenails protect the soft tissues of the fingers and toes from injury. Fingernails also serve to enhance sensation and precise movements of the fingertips through the counter-pressure exerted on the pulp of the fingers by the nails.
What is a nail?
The nail is a platelike, keratinous, translucent structure that consists of highly specialized epithelial cells. The nail grows from a deep groove in the dermis of the skin.
What is the function of nails where are they located?
0:142:08Anatomy Of Nails - Why Do We Have Nails - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe top view of a nail the outermost whitish part is called the free edge. The next pinkish sectionMoreThe top view of a nail the outermost whitish part is called the free edge. The next pinkish section is the nail body and it has this pinkish color because of blood flowing in the capillaries. Below it
What is the function of the nail cuticle?
The cuticle plays an important role in nail health. They provide protection for the tissue that grows new cells to build nails. As you know, your nails are constantly growing, that's why you have to keep them manicured.
Why is a nail called a nail?
nail (v.) Old English næglian "to fix or fasten (something) onto (something else) with nails," from Proto-Germanic *ganaglijan (source also of Old Saxon neglian, Old Norse negla, Old High German negilen, German nageln, Gothic ganagljan "to nail"), from the root of nail (n.).
What is are the properties of a nail?
The nails and claws of mammals contain α-type fibrous protein filaments. In the human nail the filaments are aligned perpendicular to the growth axis, while nails from other animals show different types of orientation depending on their shape.
What is the nail structure?
Fingernails and toenails are made from skin cells. Structures that are made from skin cells are called skin appendages. Hairs are also skin appendages. The part that we call the nail is technically known as the “nail plate.” The nail plate is mostly made of a hard substance called keratin.
What is the body of nail?
The nail plate is made up of tightly packed, hard, keratinized epidermal cells. It has a nail body, a free edge, and extends deep into the dermis at the proximal end to form the nail root (or nail groove).
Is nail a bone?
Are nails bones? No. Bones are made up of collagen and calcium phosphate, whereas nails are made from keratin.
What are the 7 part of nail?
The parts of the fingernail include nail plate, nail bed, nail matrix, nail sinus, nail root, nail fold, nail cuticle (eponychium), and nail lunula.
Why do we have nails?
The short answer is we have evolved to have nails because they help us pick things up (like food), pick things off (like bugs), and hold tightly onto things. Early humans who had these type of nails (instead of claws) tended to live long enough to have babies and pass on the fingernails gene to their kids.
Where is nail formed?
Nails start in the nail root, hidden under the cuticle. When cells at the root of the nail grow, the new nail cells push out the old nail cells. These old cells flatten and harden, thanks to keratin, a protein made by these cells. The newly formed nail then slides along the nail bed, the flat surface under your nails.
Are nails bones or hair?
Are nails bones? No. Bones are made up of collagen and calcium phosphate, whereas nails are made from keratin.
What does nail mean in slang?
to catch someone[ T ] slang. to catch someone, especially when they are doing something wrong, or to make it clear that they are guilty: The police had been trying to nail those guys for months. Thesaurus: synonyms, antonyms, and examples.
What is a nail made of?
Fingernails and toenails are made from skin cells. Structures that are made from skin cells are called skin appendages. Hairs are also skin appendages. The part that we call the nail is technically known as the “nail plate.” The nail plate is mostly made of a hard substance called keratin.
What kind of machine is a nail?
wedgeAnswer and Explanation: A nail is actually a type of wedge, which is a simple machine. A wedge is often shaped like a triangle. One point is used to cut or push something apart.
What is the structure of fingernails?
Nail Structure and Function. Fingernails and toenails are derived from the stratum corneum. They serve a protective function and can be used as tools. The stratum corneum, or horny layer, of the epidermis gives rise to fingernails and toenails. Like this outer layer, nails are composed primarily of the tough protein keratin.
What is the nail bed?
Like skin elsewhere in the body, the nail bed is skin with a layer of epidermis and a layer of dermis. The epidermis of the nail bed is attached to the nail plate via grooves called matrix crests. This epidermis of the nail bed moves toward the end of the nail as the nail grows.
What is the nail plate?
The nail plate is the actual fingernail that is composed of dead cells. The nail bed is below the nail plate and has both dermis and epidermis tissue. The nail matrix, sometimes called the matrix unguis, is the part of the nail bed that sits at the base of the nail plate. < Hair Structure and Function > Skin Glands.
What are the parts of the nail?
Nails have three main parts: the nail plate, the nail bed, and the nail matrix. The nail plate is the hard part of the nail, composed of layers of dead cells. The nail bed sits beneath the nail plate. Like skin elsewhere in the body, the nail bed is skin with a layer of epidermis and a layer of dermis. The epidermis of the nail bed is attached ...
Why do we need nails?
Nails serve several functions. They help protect the delicate tips of fingers and toes from injury. They exert a counterpressure on the fingertip , which can help with precise movements and touch sensitivity. Finally, nails provide a valuable tool for cutting, scraping, or pinching very fine objects.
What is the cuticle of a nail called?
This is called the lunula, or small moon . The cuticle is a protective layer of dead cells that cover and seal the back of the nail plate. Finally, the hyponychium, or quick of the nail, sits between the open edge of the nail and the fingertip and protects the nail bed. Nails serve several functions.
What is the crescent at the base of a nail called?
A small portion of the nail matrix is visible as a white crescent at the base of some nails. This is called the lunula, or small moon.
What are Fingernails Made of?
Fingernails are a plate or piece of hardened keratin found at the ends of fingers. Keratin is a protein that forms skin, hair, and nails. Fingernails grow continuously from the second trimester of pregnancy for a fetus till a few minutes after death. Their growth rate varies throughout life based on age, nutrition, and illness. The official term for what is commonly called a fingernail is the nail plate. There are other parts to the fingernail that are hidden from sight. Toenails are also made from the same protein and have the same function and parts as the fingernail.
What is the nail bed?
Nail Bed - The nail bed is the skin that lies under the nail. It is a bed for the nail plate. It is made of skin and contributes a small amount of keratin to the nail plate. The blood under the skin in this area gives the nail its light pink color.
How to increase finger sensitivity?
Enhance the sensitivity of the fingertip - While fingernails don't have nerve endings, they do increase sensitivity. When pushing on something with the other side of the finger, the pressure is stopped by the nail applying pressure to the opposing side. This increases the overall sensitivity to the fingertips.
What is the part of the nail plate called?
Parts of the Nail Plate - The free end of the nail, the part that often gets trimmed, is known as the distal edge . The sides of the nail are known as the lateral edges of the nail groove. The edge of the nail plate that emanates from the finger is called the proximal edge.
Where is the nail matrix located?
Nail Matrix - This is the main source of cells that become the layers of the nail plate. It is found in the nail sinus and is not visible. As new cells form, the matrix pushes out the nail plate adding new keratin at the proximal part of the plate.
What does it mean when your fingernails are irregular?
Provide a diagnostic tool for health - Irregularities on fingernails can indicate cardiovascular problems, skin conditions, and an unbalanced diet.
What is the fold of skin on the edge of the nail?
Nail Fold - This is the fold of skin over the edge of the nail on three sides. This part is at higher risk of trauma from injury, ingrown nails, and infections.
What is the site of hangnails, ingrown nails, and paronychia?
The paronychium is the site of hangnails, ingrown nails, and paronychia, a skin infection. Hyponychium: The hyponychium is the area between the free edge of the nail plate and the skin of the fingertip. It also provides a waterproof barrier.
What is the cuticle of the finger?
The cuticle is situated between the skin of the finger and the nail plate. It fuses these structures together and provides a waterproof barrier. Perionychium: The paronychium is the skin that overlaps onto the sides of the nail plate, also known as the paronychial edge.
What happens if your nail doesn't grow?
When the nail grows properly, the nail bed is smooth, but if the nail doesn't grow correctly, the nail may split or develop ridges that aren't cosmetically attractive. Nail plate: The nail plate is the actual fingernail, and it's made of translucent keratin.
How fast do fingernails grow?
Fingernails grow faster than toenails, at a rate of 3 millimeters per month. It takes six months for a fingernail to grow from the root to the free edge. Toenails grow much more slowly, at just 1 millimeter per month.
Why do nails look pink?
The pinkish appearance of the nail comes from the blood vessels that are underneath it . The underside of the nail plate has grooves that run along the length of the nail and help anchor it to the nail bed. Eponychium: The eponychium is more commonly known as the cuticle.
What are the parts of the nail?
The nail structure is divided into six parts: root, nail bed, nail plate, eponychium, paronychium, and hyponychium. Each of these six components has a specific function, and if a component of the nail structure is disrupted, the nail can look abnormal. Nail root: The root of the nail is also known as the germinal matrix.
What is the function of the nail?
They enhance the sensation. The fingers and toes contain nerve endings that allow the body to process the volumes of information that it receives every time something is touched—and the nail acts as a counterforce, providing even more sensory input after a person touches something.
What is the term for a cancerous cell that grows in the nail matrix?
Subungual melanoma (or nail matri x melanoma) is a condition where cancerous cells grow in the nail matrix. The cancerous cells can cause changes in pigments in the nail known as melanin. As a result, a distinct striped discoloration can grow from the nail matrix.
What is a melanonychia?
Melanonychia is a broad descriptive term that can indicate a normal variation on nail color or something as serious as subungual melanoma (see below). Several conditions and events can cause melanonychia, including:
What is the germinal matrix of the finger?
Fingertip skin is connected to the sterile matrix. Germinal matrix. This is the area of the nail below the lunula (closest to the knuckle). An estimated 90 percent of nail production comes from the germinal matrix. This gives a natural curvature to the nail.
What causes a nail to turn dark?
Melanonychia is a broad descriptive term that can indicate a normal variation on nail color or something as serious as subungual melanoma (see below). Several conditions and events can cause melanonychia, including: 1 nail biting 2 psoriasis 3 pregnancy 4 Cushing syndrome 5 chemotherapy medications 6 nail infection
Why do doctors remove the nail matrix?
Because the nail matrix is deep at the nail’s base, doctors usually perform this procedure under local anesthesia. A doctor can strategically inject local anesthetic into the finger’s base, numbing the finger. You shouldn’t be able to feel pain, only pressure, when a doctor removes a portion of the nail’s matrix.
What is the nail matrix?
What is nail matrix? The nail matrix is the area where your fingernails and toenails start to grow. The matrix creates new skin cells, which pushes out the old, dead skin cells to make your nails. As a result, injuries to the nail bed or disorders that affect the matrix can affect your nail growth.
Why do nails change color?
The nail typically changes color beyond the germinal matrix (see below) as it extends to the sterile matrix because cells no longer have nuclei after that time, which makes the nail appear more transparent. This area is the next most common place where nail cells are made.
What is the cuticle of the nail?
Cuticle. A thin layer of dead tissue riding on the nail plate to form a seal between the nail plate and eponychium to prevent pathogens from infecting the matrix area. The cuticle pulls away from the underside of the eponychium and attaches tenaciously to the nail plate.
What is the purpose of a soft tissue seal?
A soft tissue seal underneath the extended “free” edge of the nail plate whose purpose is to prevent pathogens from infecting the nail bed.
What is the proximal fold?
The proximal fold is a required guardian seal that prevents germs and bacteria from getting to the nail matrix, where new cells are created . I always know when girls are cutting. Their entire cuticle line is red and inflamed. Basically, their eponychium is infected all the time.
What is the moon in nail polish?
A bluish-white, opaque area that is visible through the nail plate. This area is the front part of the nail matrix. Sometimes, it’s called the “moon.”
Where does the solehorn cuticle attach?
The solehorn cuticle pulls away from the underside of the hyponychium and attaches tenaciously to the nail plate.
How many layers of keratin are in a nail?
The average person has 50 layers of keratin cells that make up the nail plate.
Where is the living skin at the base of the nail plate?
Living skin at the base of the nail plate that covers the matrix area. This should NOT be confused with the “cuticle”.
