Narration is the use of a written or spoken commentary to convey a story to an audience. [1] Narration is conveyed by a narrator: a specific person or unspecified literary voice, developed by the creator of the story, to deliver information to the audience, particularly about the plot (the series of events).
What does a narrator do?
narrator, one who tells a story. In a work of fiction the narrator determines the story’s point of view. If the narrator is a full participant in the story’s action, the narrative is said to be in the first person. A story told by a narrator who is not a character in the story is a third-person narrative.
What is an example of a narrator?
narātər, narətər; narātər, nərātər The definition of a narrator is a person who is telling a story. An example of narrator is a character in a book who writes the story in first person from his own point of view. noun 6 0 (film and television) The person providing the voice-over in a documentary. noun 1 0 A person who relates a story or account.
What is an example of narrative text?
Some examples of narrative text are novels, short stories, news stories, memoirs and biographies. Narrative text encompasses both fiction and non-fiction, and it includes any form of writing that communicates a series of events. It can be used to entertain, inform or persuade a reader to either accept or reject a premise or idea.
What does narrate mean?
Here are all the possible meanings and translations of the word narrate. To relate a story or series of events by speech or writing. Etymology: In English (recorded only since 1656, but initially stigmatized as 'Scottish', until the 19th century) apparently from narration To give an account.

What should be included in a narratio?
The narratio gives a brief account of the situation your paper addresses. Include anything that is necessary to bring the reader up to date on the topic. What is the current situation? What created the situation?
What is Partitio?
Noun. partītiō f (genitive partītiōnis); third declension. The act of sharing or parting; partition, division, distribution. (philosophy and rhetoric) A logical division into parts or heads, classification, partition.
What is an exordium in writing?
exordium, (Latin: “warp laid on a loom before the web is begun” or “starting point,”) plural exordiums or exordia, in literature, the beginning or introduction, especially the introductory part of a discourse or composition.
What is an exordium argument?
Later writers on rhetoric, such as Cicero and Quintilian, refined this organizational scheme, so that there were eventually six parts: the introduction, or exordium. In the exordium, the speaker gives their main argument, and all relevant information. the statement of the case, or narratio.
How many Muslims were killed during the partition?
An estimated 20,000–100,000 Muslims were massacred. Subsequently, many non-Muslims were massacred by Pakistani tribesmen and soldiers, in the Mirpur region of today's Pakistani administered Kashmir....1947 Jammu massacresDeath(s)20,000–100,000 Muslims 30,000 Hindus and Sikhs in Rajouri; a large number in Mirpur.5 more rows
Why did India separate from Pakistan?
That was part of the end of British Raj, British rule in the Indian subcontinent. One reason for partition was the two-nation theory, which was presented by Syed Ahmed Khan and stated that Muslims and Hindus were too different to be in one country.
How do you write a narratio?
"The narratio follows the exordium and gives background information. It relates events that have occurred which provide the occasion for the speech. 'A narrative based on the persons should present a lively style and diverse traits of character' and have three qualities: brevity, clarity, and plausibility."
What is the opposite of exordium?
Near Antonyms for exordium. envoi. (or envoy), postscript.
What language is exordium?
Borrowed from Latin exordium (“beginning, commencement”), from exōrdior (“I begin, commence”), from ex (“out of, from”) + ōrdior (“I begin”).
What are the 5 parts of discourse?
They are: invention (what to say), arrangement (structure of content), style (language choices), memory (learn the presentation) and delivery (use of more than just words).
What is an example of peroration?
the last part of a speech, especially when the speaker repeats the main points of their argument and tries to make the audience enthusiastic: At the peroration of his closing speech, he was handed a note from his assistant.
What are the 5 parts of a classical argument?
Components and StructureExordium – The introduction, opening, or hook.Narratio – The context or background of the topic.Proposito and Partitio – The claim/stance and the argument.Confirmatio and/or Refutatio – positive proofs and negative proofs of support.Peroratio – The conclusion and call to action.
How do you use the word Exordium in a sentence?
He'd explained his dilemma without any exordium of confidentiality.
What is a confirmation paragraph?
In classical rhetoric, the confirmation is the main part of a speech or text in which logical arguments in support of a position (or claim) are elaborated. Also called confirmatio. Etymology: From the Latin verb confirmare, meaning "strengthen" or "establish."
Origin of the narrative (storytelling)
Initially, the stories were loaded with mythical and religious content.
Types of narration
The narratives can be of different types, depending on their content and their intentions. A possible classification is the following:
Narrator (storyteller) types
The choice of a narrator often determines many things about a story. In principle, there are two different considerations to make regarding the narrator:
Dialogues and descriptions
Descriptions are short pauses in narration that provide details and information.
Importance of storytelling
Narration is a fundamentally human act. It is said that together with the discovery of fire , the burial of the dead and the incest taboo , the appearance of the narrative is a fundamental element for the emergence of human civilization . In fact, from ancient times until today we continue to narrate in many areas of our life.
NARRATIO
narratio (n [schwa]-ray-shee-oh), n. [Latin “narrative”] Hist. A declaration, complaint, or petition in which the plaintiff sets out the facts of a case; an oral narrative by the plaintiff of the facts and legal arguments on which the claim is based. ? The term has also been called the “conte” or “tale.” — Abbr. narr.
Relevant Terms
flexible-constitution: A constitution that has few or no special amending procedures. ? The British Constitution is an example. Parliament can alter constitutional principles and define new baselines […]
What is narration in writing?
Richard Nordquist is professor emeritus of rhetoric and English at Georgia Southern University and the author of several university-level grammar and composition textbooks. In writing or speech, narration is the process of recounting a sequence of events, real or imagined.
What is the point of view in a narrative?
The perspective from which a speaker or writer recounts a narrative is called a point of view. Types of point of view include first person, which uses "I" and follows the thoughts of one person or just one at a time, and third person, which can be limited to one person or can show the thoughts of all the characters, ...
What are the three forms of narrative in De Inventione?
Cicero, however, finds three forms in "De Inventione," as explained by Joseph Colavito in "Narratio": "The first type focuses on 'the case and...the reason for dispute' (1.19.27). A second type contains 'a digression ...for the purpose of attacking somebody,...making a comparison,...amusing the audience,...or for amplification' (1.19.27). The last type of narrative serves a different end—'amusement and training'—and it can concern either events or persons (1.19.27) ." (In "Encyclopedia of Rhetoric and Composition: Communication from Ancient Times to the Information Age," ed. by Theresa Enos. Taylor & Francis, 1996)
What is the person who recounts the events called?
The person who recounts the events is called a narrator. Stories can have reliable or unreliable narrators . For example, if a story is being told by someone insane, lying, or deluded, such as in Edgar Allen Poe's "The Tell-Tale Heart," that narrator would be deemed unreliable. The account itself is called a narrative .
Who is Richard Nordquist?
Dr. Richard Nordquist is professor emeritus of rhetoric and English at Georgia Southern University and the author of several university-level grammar and composition textbooks. In writing or speech, narration is the process of recounting a sequence of events, real or imagined. It's also called storytelling.
Is a story a narrative?
Even "jokes, fables, fairy tales, short stories, plays, novels, and other forms of literature are narrative if they tell a story," notes Lynn Z. Bloom in "The Essay Connection."
Is narration a literature?
Narration isn't just in literature, literary nonfiction, or academic studies, though. It also comes into play in writing in the workplace, as Barbara Fine Clouse wrote in "Patterns for a Purpose": "Police officers write crime reports, and insurance investigators write accident reports, both of which narrate sequences of events.

What Is Narration (Storytelling)?
- A narrative is equivalent to a story or a tale. A narrative is a sequential succession of events or actions, carried out by real or imaginary characters, in a certain place and for a certain amount of time, told by someone in a specific way. That is, in a certain way a narrative is equivalent to a story, a story or a tale, although they are not ent...
Origin of The Narrative
- Initially, the stories were loaded with mythical and religious content. The narrative is as old as humanity itself. We suppose that the first stories arose in the heat of the bonfires, when the primitive tribe gathered to eat and listen to the stories of the hunt, or the origin myths told by the old sages. Initially, the stories were loaded with mythical and religious content. They were foundi…
Types of Narration
- The narratives can be of different types, depending on their content and their intentions. A possible classification is the following: 1. Oral narration: That which is carried out through spoken language and which is marked by the individual’s mode of speech, by everyday life, etc. It is necessarily face-to-face (unless it is recorded in recording) and ephemeral, since th…
Narrative (Storytelling) Elements
- The characters are those involved in the story. In any narrative, some or all of the following elements appear: 1. Storyteller: The voice and point of view from which the story is told, and which may or may not be involved in the events it narrates. 2. Characters: Those actors directly or indirectly involved in the story told, occupying different roles in it: protagonist (on whom the stor…
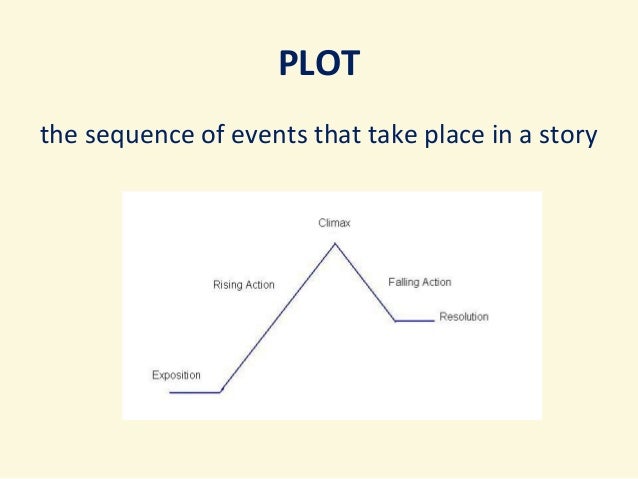
Structure of A Narrative
- The characters are led to one or more complex situations. Narrating means telling a series of events in an orderly, logical and sequential way, that builds a total unity when it nears its end, and that has a sense of causality and plausibility, that is, that is credible and makes sense. In that sense, its structure traditionally involves three parts: 1. Start or presentation: Also called balanc…
Narrator (Storyteller) Types
- The choice of a narrator often determines many things about a story. In principle, there are two different considerations to make regarding the narrator: 1. Narrative person: It refers to the grammatical choice of the voice of the narrator, that is, if he / she will speak in the first person (“I”, “we”) or in the third person (“he / she”, “they / they”). 2. Point of view: It refers to the point of enun…
Dialogues and Descriptions
- Descriptions are short pauses in narration that provide details and information. A dialogue is the moment in which the story reproduces for its readers or viewers a conversation between two or more characters, noting what each person said. Descriptions , on the other hand, are short pauses in narration that provide details and information about what characters, things, or the world arou…
Importance of Storytelling
- Narration is a fundamentally human act. It is said that together with the discovery of fire , the burial of the dead and the incest taboo , the appearance of the narrative is a fundamental element for the emergence of human civilization. In fact, from ancient times until today we continue to narrate in many areas of our life.
The Literary Narrative
- The novels are thick, slow and rambling narratives. Literary narratives, as we have seen, are those that have artistic or aesthetic aspirations, and that are framed in the known narrative genres, which are: 1. Stories: Short to medium length stories, centered on a line of events that is narrated from beginning to end, with the fewest interruptions. 2. Micro-stories: Hyper-short stories, often …
Cinematic Narration
- A film presents characters, a plot, a time, a place, and a narrator. The film , in its complexity, is also an art form that uses narratives. When we watch a film, we are presented with characters, a plot, a time, a place and a narrator (in this case it is the camera itself), to reproduce a story audiovisually. For this reason, films with strategies similar to novels and stories can be studied. I…