
Necrotizing periodontitis is a severe infection of the gums caused by the overgrowth of microorganisms that are normally found in the mouth. There are several other names for this condition including trench mouth, Vincent's stomatitis, necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (NUG), and acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG).
See more
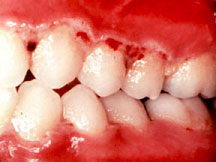
What is necrotising periodontitis?
Necrotizing periodontitis is a disease of tissue destruction of both soft tissue (gums) and hard tissue (alveolar bone). As a result of the disease, both soft and hard tissue defects can make oral hygiene difficult.
What is associated with necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis?
NUP has been associated with HIV-positive and AIDS patients. Obtain a dental history: previous history of NUG and/or periodontal disease, foul metallic taste, pasty saliva, intense excruciating pain.
How is necrotizing periodontitis treated?
Treatment of necrotising periodontal diseasepain relief – paracetamol or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.debridement of necrotic gum tissue.antiseptic mouth rinses – chlorhexidine or hypertonic saline.thorough regular dental cleaning and flossing.oral antibiotics if severe or signs of systemic infection.More items...
What is necrotizing ulcerative?
Introduction. Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (NUG) is a distinct and specific form of periodontal diseases. It has an acute clinical presentation with the distinctive characteristics of rapid onset of gingival pain, interdental gingival necrosis, and bleeding.[1] NUG has been recognized for centuries.
Why do people get ANUG?
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) occurs most frequently in smokers and debilitated patients who are under stress. Other risk factors are poor oral hygiene, nutritional deficiencies, immunodeficiency (eg, HIV/AIDS, use of immunosuppressive drugs), and sleep deprivation.
How long does ANUG take to heal?
Taken together with chlorhexidine, a prescription antibacterial mouthrinse, and saline (mild saltwater) rinses, symptoms should abate within 24 to 48 hours. It is also important to treat the underlying conditions that led to the ANUG in the first place.
What are the symptoms of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis?
Usually, ANUG begins abruptly with painful and bleeding gums, excessive saliva production, and sometimes extremely foul-smelling breath. People may also have a fever and feel ill. The tips of the gums between the teeth appear punched-out and become sores (ulcers) covered with a gray layer of dead tissue.
Does ANUG cause bone loss?
ANUG is characterized by marginal gingival necrosis, gingival bleeding and painful ulceration of the gingival surface (1,2). ANUG is caused by periodontopathic bacteria, mainly spirochetes and oral anaerobes (2,3). As ANUG progresses, extensive bone loss can develop, so this is a serious and notable disease.
Is ANUG transmissible?
Is ANUG Contagious? Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is non-contagious, meaning it is not transmissible and does not spread from one person to another.
Can periodontitis make you sick?
Fever, Chills, Bleeding Gums: Potential Periodontal Disease. As we mentioned when discussing dental abscesses, oral infections can present with flu-like symptoms. This holds true when you experience periodontal disease, also called gum disease.
Is ANUG life threatening?
Treatment of ANUG is by removal of dead gum tissue and antibiotics (usually metronidazole) in the acute phase, and improving oral hygiene to prevent recurrence. Although the condition has a rapid onset and is debilitating, it usually resolves quickly and does no serious harm.
What causes necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis?
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG; 'trench mouth') is a fairly common oral disease of complex cause that occurs in normal individuals. Contributing factors include the fusospirochetal oral flora, reduced host resistance, malnutrition, poor oral hygiene, smoking, and psychologic stress.
What pathogen causes necrotizing stomatitis?
Necrotizing periodontal disease is caused by a mixed bacterial infection that includes anaerobes such as P. intermedia and Fusobacterium as well as spirochetes, such as Treponema.
What is the difference between NUG and NUP?
NUG is an infection limited to the gingiva whereas NUP also involves the attachment apparatus. Predisposing factors may include immune dysfunction, poor oral hygiene, cigarette smoking and emotional stress. NUG and NUP might possibly be different stages of the same infection.
What is periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease?
Periodontology Diagnosis - Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease. Periodontal disease, which is also referred to as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions which affect the tissues that surrounding the teeth.
Clinical Features
Similar to NUG, clinical cases of NUP are defined by necrosis and ulceration of the coronal portion of the interdental papillae and gingival margin, with a painful, bright-red marginal gingiva that bleeds easily.
Microscopic Findings
In a study involving the use of transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy of the microbial plaque overlying the necrotic gingival papillae, Cobb and colleagues 4 demonstrated striking histologic similarities between NUP in HIV-positive patients and previous descriptions of NUG in HIV-negative patients.
What is necrotising periodontal disease?
Necrotising periodontal disease is the term used to describe a group of relatively rare infections affecting the mouth in which ulceration with necrosis is the common feature . Necrosis is the term used to describe death of tissue.
Why does periodontal disease necrotize?
Who gets necrotising periodontal disease and why? Necrotising periodontal disease is triggered by the accumulation of dental plaque associated with poor oral hygiene. However host factors are also important in allowing these necrotising conditions to develop from the dental plaque.
What is the difference between gingivitis and necrotising?
Necrotising ( ulcerative) gingivitis – affects only the gums. Necrotising (ulcerative) periodontitis – involves loss of the specialised tissue that surrounds and attaches the teeth. Necrotising stomatitis – in which more extensive mucosal and bone loss occurs beyond the gums and tissue surrounding and supporting the teeth.
What happens if you have necrotising gingivitis?
An episode of necrotising gingivitis may result in: Spontaneous healing with no residual sign of infection. Persistent ulcers or craters that may quickly flare into another episode of necrotising gingivitis. Progress to necrotising periodontitis with possible involvement of bone and loosening then loss of teeth.
What is the progression of necrotising stomatitis?
Progress to necrotising stomatitis, involving widespread areas of the oral mucosa and bone. 2. Necrotising periodontitis. Infection involves the specialised attachment tissues surrounding one or more teeth and the resulting inflammation is more destructive and deeper than in necrotising gingivitis.
What is the term for a sore mouth?
Necrotising stomatitis – in which more extensive mucosal and bone loss occurs beyond the gums and tissue surrounding and supporting the teeth. Stomatitis means a sore mouth.
What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
Less commonly, the following may be noted: Low grade fever. Halitosis (bad breath) Patients who have had a previous episode, may report prodromal symptoms such as burning gums before a sudden onset of the typical gingivitis.
What is a necrotizing periodontal disease?
Necrotizing periodontal diseases are a type of inflammatory periodontal (gum) disease caused by bacteria (notably fusobacteria and spirochaete species). The diseases appear to represent different severities or stages of the same disease process, although this is not completely certain. These diseases usually have a sudden onset, ...
What is the term for bleeding ulcers that cause pain and loss of interdental papillae?
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis: painful, bleeding, sloughing ulceration and loss of the interdental papillae (usually of the lower front teeth).
What is the term for destruction of orofacial tissues?
Note destruction of orofacial tissues. Main article: Cancrum oris. Cancrum oris (also termed noma) is a necrotizing and destructive infection of the mouth and face, and therefore not strictly speaking a periodontal disease. In modern times, this condition usually occurs in malnourished children in developing countries.
What is the progression of NUP into tissue beyond the mucogingival junction?
Progression of NUP into tissue beyond the mucogingival junction characterizes necrotizing stomatitis, which has many features in similar with cancrum oris.
Is NUP a periodontal disease?
NUP may be an extension of NUG into the periodontal ligaments, although this is not completely proven. In the mean time, NUG and NUP are classified together under the term necrotizing periodontal diseases.
How to treat necrotizing periodontal disease?
The treatment plan for Necrotizing Periodontal Disease may involve oral cleaning, removal of plaque, to medication administration for bacterial infection. Surgery may be necessary in many individuals. The prognosis of the condition depends upon its severity and on the associated condition causing weak immunity (if any)
How is Necrotizing Periodontal Disease Diagnosed?
The diagnostic tests for Necrotizing Periodontal Disease may involve the following:
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Necrotizing Periodontal Disease?
The signs and symptoms associated with Necrotizing Periodontal Disease may include:
What is NPD in dentistry?
Necrotizing Periodontal Disease (NPD) is a rare and very destructive form of periodontitis caused by bacteria. It is characterised by mouth ulceration and tissue death (necrosis), in addition to severe attachment loss and bone destruction.
Why do teeth get necrotized?
The main cause of Necrotizing Periodontal Disease is longstanding infection of the gum, teeth, and surrounding tissue that also involves the jawbones, as a result of poor dental hygiene. Severe gum infection leads to plaque buildup on the affected teeth (or tooth). When this plaque is left on the teeth for extended periods of time, it hardens, ...
What is the most severe form of periodontitis?
Necrotizing (ulcerative) periodontitis: It is a more severe form where involvement of the ‘teeth-attaching’ soft tissue and jawbone is observed. Necrotizing stomatitis: In this severe form, involvement of the entire mouth with extensive tissue and bone destruction may be observed.
Why is periodontitis more likely to develop if you have poor oral habits?
Poor oral habits: This facilitates bacterial growth in the mouth thereby increasing the risk for developing periodontitis
What happens when bone is exposed?
Sometimes bone is exposed, resulting in necrosis and subsequent sequestration
What is the linear erythematous zone?
Linear erythematous zone separating the ulcerated area from the adjacent free gingiva, attached gingiva, and alveolar mucosa with provocation and/or spontaneous bleeding
Can an infection cause rapid destruction of attachment apparatus?
Untreated, the infection may lead to rapid destruction of the attachment apparatus.
What causes trenchmouth?
The mouth normally contains a balance of different bacteria. Trench mouth occurs when there is too much pathologic bacteria. The gums become infected and develop painful ulcers. Viruses may be involved in allowing the bacteria to grow too much.
Why is ANUG called trench mouth?
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) used to be called trench mouth, a term that comes from World War I, when many soldiers in the trenches developed the infection.
What causes peritonitis in gums?
In most cases, the development of periodontitis starts with plaque — a sticky film composed mainly of bacteria. If left untreated, here’s how plaque can eventually advance to periodontitis: Plaque forms on your teeth when starches and sugars in food interact with bacteria normally found in your mouth.
What bacteria causes acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis?
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, otherwise known as Vincent’s angina or trench mouth, is caused by an imbalance in the normal flora of the gingival sulcus with predominant presence of the spirochete Borrelia vincentii and the gram-negative bacillus Fusiformis fusiform.
What is necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis?
Necrotising (ulcerative) periodontitis – involves loss of the specialised tissue that surrounds and attaches the teeth . Necrotising stomatitis – in which more extensive mucosal and bone loss occurs beyond the gums and tissue surrounding and supporting the teeth. Stomatitis means a sore mouth.
What does black spots on your gums mean?
Black spots on your gums are usually harmless, but they can sometimes be a sign of teething problems in children or oral cancer . If you notice a new spot on your gums, make sure to tell your doctor about it. Even if the spot isn’t cancerous, it should be monitored for any changes in shape, size, or color.
What antibiotics treat ANUG?
Treatment. For any signs of systemic involvement, the recommended antibiotics are: Amoxicillin, 250 mg 3 x daily for 7 days and/or . Metronidazole, 250 mg 3 x daily for 7 days .
