
What to expect after thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid or air from around the lungs. A needle is put through the chest wall into the pleural space. The pleural space is the thin gap between the pleura of the lung and of the inner chest wall. The pleura is a double layer of membranes that surrounds the lungs. Inside the space is a small amount of fluid.
What is the best position for thoracentesis?
Nov 15, 2021 · Needle thoracocentesis is a life saving procedure, which involves placing a wide-bore cannula into the second intercostal space midclavicular line (2ICS MCL), just above the third rib, in order to decompress a tension pneumothorax, as per Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) guidelines. What is Needle thoracotomy?
What is the difference between thoracentesis and chest tube?
Needle Thoracentesis. Needle Thoracentesis is the introduction of a needle or catheter into the pleural space to release trapped or accumulated air within the pleural space. Needle Thoracentesis is used to decompress the pleural cavity and allow the collapsed lung to re-inflate and also to reduce the pressure on the heart and unaffected lung
What are the indications of thoracentesis?
What is needle thoracentesis? Needle Thoracentesis is an invasive procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. A cannula, or hollow needle, is carefully introduced into the thorax, generally after administration of …
Why would someone need a thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis may be done to find the cause of pleural effusion. It can also be done to treat symptoms of pleural effusion by removing fluid. The fluid is then examined in a lab.
Is thoracentesis the same as needle decompression?
Thoracentesis /ˌθɔːrəsɪnˈtiːsɪs/, also known as thoracocentesis (from Greek θώραξ thōrax 'chest, thorax'—GEN thōrakos—and κέντησις kentēsis 'pricking, puncture'), pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, or needle decompression (often used term) is an invasive medical procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space ...
What is needle thoracostomy?
Needle thoracostomy is insertion of a needle into the pleural space to decompress a tension pneumothorax. Needle thoracostomy is an emergency, potentially life-saving, procedure that can be done if tube thoracostomy.
Where is the thoracentesis needle?
Thoracentesis involves placing a thin needle or tube into the pleural space to remove some of the fluid. The needle or tube is inserted through the skin, between the ribs and into the chest.
What is needle decompression used for?
Needle thoracostomy, also known as "needle decompression" is a procedure performed to stabilize deteriorating patients in the life-threatening situation of a tension pneumothorax.
When is needle decompression used?
A needle decompression should only be performed if the patient has a tension pneumothorax. When inserting the needle, it should be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the chest wall. This is a critical point as this will position the needle straight into the pleural space.Jan 17, 2011
How do you landmark the site for needle Thoracocentesis?
Needle thoracocentesis is a life saving procedure, which involves placing a wide-bore cannula into the second intercostal space midclavicular line (2ICS MCL), just above the third rib, in order to decompress a tension pneumothorax, as per Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) guidelines.
How do you perform a thoracentesis needle?
0:010:55Needle Thoracentesis ATLS - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd over the needle catheter that is at least 2 inches or 5 centimeters. In length is inserted intoMoreAnd over the needle catheter that is at least 2 inches or 5 centimeters. In length is inserted into the chest over the top of the third rib. Into the second intercostal.
Can nurses do needle decompression?
The Practice and Education (P & E) Committee has carefully considered the issue of registered nurses performing needle decompression for the treatment of tension pneumothorax. Pursuant to 405.01, appropriate training and competency is a requirement for performing nurse care.
Is thoracentesis painful?
You may feel discomfort or pain in your shoulder or the area where the needle was inserted. This might happen toward the end of your procedure. It should go away when the procedure is finished, and you shouldn't need medication for it.Feb 15, 2021
When should thoracentesis be done?
Thoracentesis should be performed diagnostically whenever the excessive fluid is of unknown etiology. It can be performed therapeutically when the volume of fluid is causing significant clinical symptoms. Typically, diagnostic thoracentesis is a small volume (single 20cc to 30cc syringe).Jan 24, 2022
Who performs a thoracentesis?
The following specialists perform thoracentesis: Pulmonologists specialize in the medical care of people with breathing problems and diseases and conditions of the lungs. Pediatric pulmonologists specialize in the medical care of infants, children and adolescents with diseases and conditions of the lungs.
What is Needle thoracotomy?
Needle thoracostomy is insertion of a needle into the pleural space to decompress a tension pneumothorax. Needle thoracostomy is an emergency, potentially life-saving, procedure that can be done if tube thoracostomy.
Is thoracentesis the same as needle decompression?
Thoracentesis /ˌθɔːrəsɪnˈtiːsɪs/, also known as thoracocentesis (from Greek θώραξ thōrax ‘chest, thorax’—GEN thōrakos—and κέντησις kentēsis ‘pricking, puncture’), pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, or needle decompression (often used term) is an invasive medical procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space
What is the purpose of needle decompression?
Needle thoracostomy, also known as “needle decompression” is a procedure performed to stabilize deteriorating patients in the life-threatening situation of a tension pneumothorax.
Where is the needle inserted in thoracentesis?
A needle is inserted between your ribs into the pleural space. You may feel some discomfort or pressure when the needle is inserted. As your doctor draws out excess fluid from around your lungs, you may feel like coughing or have chest pain. The needle will be removed, and a small bandage will be applied to the site.
When is needle decompression needed?
A needle decompression should only be performed if the patient has a tension pneumothorax. When inserting the needle, it should be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the chest wall. This is a critical point as this will position the needle straight into the pleural space.
Who invented needle Thoracostomy?
Dr. Ian McNeil, a past Chairman of the British Association for Immediate Care invented it. ThoraQuik has a large bore 10cm needle to both improve success reaching the pleural space and minimizing the risk of catheter occlusion once it is reached.
Where do you put needle for needle decompression?
The most recent Advanced Trauma Life Support manual recommends “inserting a large-caliber needle into the second intercostal space in the midclavicular line of the affected hemithorax,” but also notes that chest wall thickness can affect the chances of successful needle decompression.
What is tension pneumothorax?
Tension Pneumothoraxis a life threatening condition that can occur due to the progression of a pneumothorax or hemothorax. As air, blood or both build in the pleural cavity, the vital structures and organs in the thoracic cavity can be shifted to the unaffected side. As the condition progresses this shift can cause the colapse of the unaffected lung.
Is needle thoracentesis contraindicated?
In that situation, there are essentially no contraindications since the only alternative is almost certain death.
What is a thoracentesis?
Interpreting Results. Thoracentesis is a medical procedure to remove some fluid between the lungs and the chest wall. The name derives from the Greek words thorax (“chest”) and centesis (“puncture”). It is used to help diagnose and treat medical conditions causing this fluid buildup, called a “pleural effusion.”.
Where is thoracentesis performed?
Depending on the situation, it may be performed in a hospital or at a doctor’s office. 3
How does thoracentesis help with pleural effusion?
Thoracentesis removes some of the excess fluid surrounding the lungs when there is a pleural effusion. Sometimes thoracentesis is used as a treatment to decrease symptoms from a pleural effusion. All that extra fluid may make you feel short of breath. Removing some of it may help you feel more comfortable. 1 .
What are the complications of thoracentesis?
The most common potentially serious complication of thoracentesis is pneumothorax. Some other possible problems include: 1 Re-expansion pulmonary edema (REPE) 2 Damage to the spleen or liver 3 Infection 4 Air embolism 5 Shortness of breath 6 Pain 7 Bleeding 5
Is a thoracentesis diagnostic inconclusive?
Sometimes a diagnostic thoracentesis is inconclusive. That just means that your physician needs more information to determine the cause of your medical problems. Depending on the context, you might need one or more of the following:
Can thoracentesis be done at the bedside?
Someone will surgically drape the area and get it ready for the procedure. In the past, thoracentesis was often performed at the bedside without any kind of imaging. However, now it is frequently done with the help of ultrasound.
Can you have thoracentesis with severe respiratory failure?
For example, thoracentesis is not usually recommended for people with severe respiratory failure or people who don’t have adequate blood pressure. People who are unable to sit still for the procedure are also not able to have it safely.
How to do needle thoracocentesis?
Needle thoracocentesis involves placing a wide-bore cannula into the mid-clavicular line of the second intercostal space, just above the third rib, in order to decompress a tension pneumothorax. 1 Normally, the pleural cavity is a potential space that is free from air and contains only a thin layer of fluid. When air enters the pleural cavity it is termed a pneumothorax. 2 Tension pneumothorax is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the intrapleural pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure. It is created when injury to the chest or respiratory structures allows air to enter but not to leave the pleural space, resulting in a rapid increase in pressure on the affected side. This causes collapse of the affected lung, compression atelactasis of the unaffected lung, mediastinal shift towards the opposite side of the chest, and compression of the vena cava. 2
Where is the needle inserted in the chest?
The recommended point for insertion of a needle is between the 2nd and 3rd intercostal space in the mid-clavicular line. Whilst this is easy to access, it does entail penetration of pectoral muscles and a variable quantity of subcutaneous tissue, which may be increased by oedema and subcutaneous emphysema. It has previously been recommended that the minimum length should be 4.5 cm (standard length 14-gauge cannula); 17 although up to one third of trauma patients have a chest wall thickness greater than 5 cm at the normal insertion point. 18,19
Is needle thoracocentesis effective?
Needle thoraco centesis is often ineffective on its own and requires subsequent tube thoracostomy, 9–14 hence why it should be seen as a temporary measure at best. There are also a number of factors that could cause needle decompression to fail; these include:
Can a pneumothorax be expanded?
However, if surgery and ventilation are required under anaesthesia, this can be expanded to a tension pneumothorax.
Is tension pneumothorax more common in ventilated patients than awake patients?
The actual incidence of tension pneumothorax is not known, but it is more common in ventilated than awake patients and possibly most common in ventilated patients with visceral pleural injury from chest trauma. 4 Emergency needle decompression is widely advocated for use in the emergency management of tension pneumothorax 6,7,8 but there needs to be an appreciation of the potential problems associated with the technique; these will be discussed later.
What is a thoracentesis needle?
Thoracentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space between the lungs and the chest wall. This procedure is done to remove excess fluid, known as a pleural effusion, from the pleural space to help you breathe easier. It may be done to determine the cause of your pleural effusion.
What are the risks of thoracentesis?
The risks of thoracentesis include a pneumothorax or collapsed lung, pain, bleeding, bruising, or infection. Liver or spleen injuries are rare complications. for more information about this topic.
How does a needle work?
A needle is inserted between your ribs into the pleural space. You may feel some discomfort or pressure when the needle is inserted. As your doctor draws out excess fluid from around your lungs, you may feel like coughing or have chest pain. The needle will be removed, and a small bandage will be applied to the site.
What is the procedure to remove fluid from the pleural space?
Thoracentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space between the lungs and the chest wall to remove excess fluid from the pleural space to help you breathe easier.
Where is the needle placed for thoracentesis?
The intercostal neurovascular bundle is located along the lower edge of each rib. Therefore, the needle must be placed over the upper edge of the rib to avoid damage to the neurovascular bundle.
How to use a thoracentesis needle catheter?
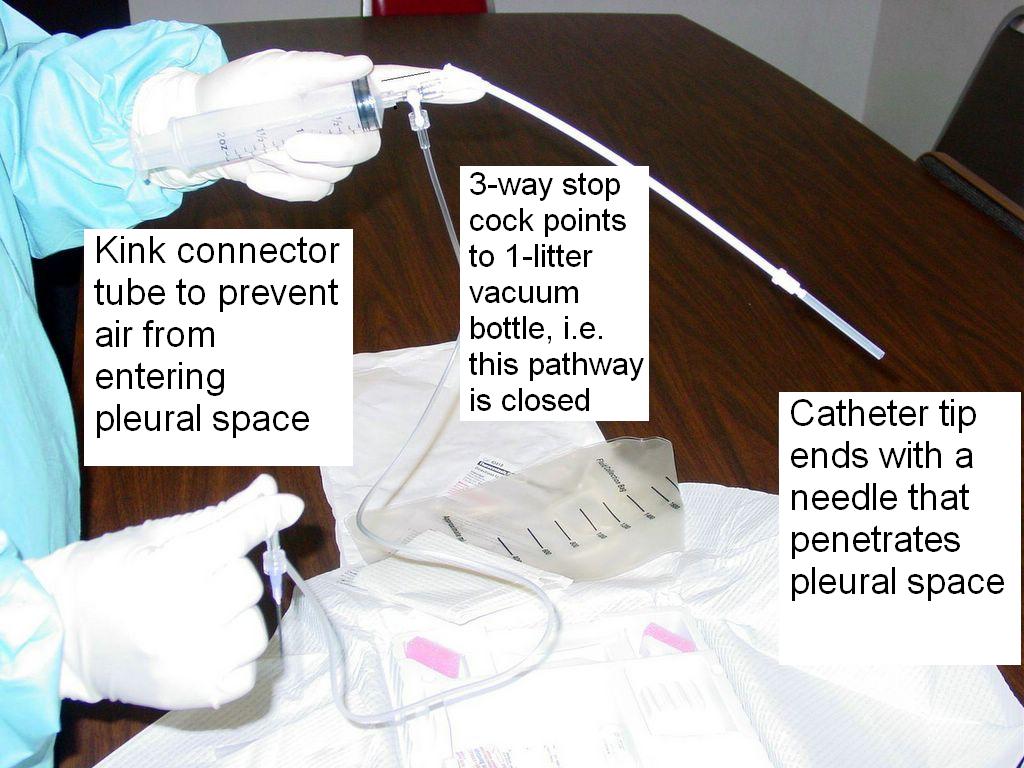
Attach a large-bore (16- to 19-gauge) thoracentesis needle-catheter device to a 3-way stopcock, place a 30- to 50-mL syringe on one port of the stopcock and attach drainage tubing to the other port. Insert the needle along the upper border of the rib while aspirating and advance it into the effusion.
What is therapeutic thoracentesis?
Therapeutic thoracentesis. To relieve symptoms in patients with dyspnea caused by a large pleural effusion. If pleural fluid continues to reaccumulate after several therapeutic thoracenteses, pleurodesis (injection of an irritating substance into the pleural space, which causes obliteration of the space) may help prevent recurrence.
When fluid or blood is aspirated, what is the procedure to insert a catheter?
When fluid or blood is aspirated, insert the catheter over the needle into the pleural space and withdraw the needle, leaving the catheter in the pleural space. While preparing to insert the catheter, cover the needle opening during inspiration to prevent entry of air into the pleural space.
When is thoracentesis not needed?
Diagnostic thoracentesis is usually not needed when the etiology of the pleural fluid is apparent (eg, viral pleurisy, typical heart failure). Selection of laboratory tests typically done on pleural fluid is discussed in pleural effusion.
What is the thickness of pleural fluid?
Indicated for almost all patients who have pleural fluid that is new or of uncertain etiology and is ≥ 10 mm in thickness on computed tomography (CT) scan, ultrasonography, or lateral decubitus x-ray (see figure Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion)
What are the complications of thoracentesis?
Major complications include. Pneumothorax. Bleeding (hemoptysis due to lung puncture) Re-expansion pulmonary edema and/or hypotension ( 1) Hemothorax due to damage to intercostal vessels. Puncture of the spleen or liver. Vasovagal syncope.
How does thoracentesis work?
From there, most cases happen this way: You'll sit up on a bed or chair, with your arms resting on a table. This position spreads out the space between the ribs. The area where the needle will be inserted is cleaned and numbed.
What happens during thoracentesis?
During the thoracentesis, your doctor removes fluid from the pleural space. This eases your shortness of breath, chest pain, and pressure on your lungs. That fluid is then tested to figure out the reason behind the build-up.
How many teaspoons of fluid are in the pleural space?
There are normally 4 teaspoons of fluid in this area, known as the “pleural space.”. A variety of things can cause that amount to go up.
How long does it take for a needle to be removed?
The spot where the needle went in will close without any stitches. This normally is a 15-minute procedure . If there is a lot of fluid to remove, it may take longer.
Is thoracentesis surgery safe?
Every surgical procedure has some potential problems. Though thoracentesis is generally considered safe, these complications can happen: Pulmonary edema, or fluid in the lungs. Pneumothorax, or collapsed lung. Infection at the site where the needle pierced your skin.
How many emergency physicians were included in the ATLS?
Twenty five emergency physicians were included: six senior house officers, five staff grades, six specialist registrars, and eight consultants. Twenty two of the participants had completed ATLS training within the previous 10 years. The other four were senior house officers who had no formal ATLS teaching but were assumed to be aware of the procedure given the speciality they were working in.
Is needle thoracocentesis life saving?
The use of a single human volunteer was an attempt to standardise the testing procedure; however, a range of volunteers may have given more useful results. Needle thoracocentesis for decompression of a tension pneumothorax is life saving, but is associated with potentially serious complications.
Purpose of Thoracentesis
Procedure to remove excess fluid accumulated in pleural space.
Treatment for: Pleurisy · Tuberculosis · Pneumonia · Pleural Empyema
Type of procedure: Minimally invasive
Recovery time: About one day
Duration: Few minutes
Hospital stay: Not typically needed
Risks and Contraindications
Before The Procedure
During The Procedure
After The Procedure
- People with certain medical conditions cannot have thoracentesis safely. For example, thoracentesis is not usually recommended for people with severe respiratory failure or people who don’t have adequate blood pressure. People who are unable to sit still for the procedure are also not able to have it safely. Healthcare providers are also very cautious in giving thoracentesi…
Interpreting Results
- Before the thoracentesis, your healthcare provider will talk to you about all your medical conditions, perform a physical exam, and assess your health. This will help ensure that thoracentesis makes sense for you. You should also review your medications with your clinician. If you take medications that affect your blood (like Coumadin), you might need to not take your …