How does feedback help maintain homeostasis?
Feedback loops help maintain homeostasis by allowing the organism to respond to changes in its environment. Feedback loops are important because organisms are always dealing with changes in environment or internal condition, so the feedback loop prevents those changes from going too far and becoming dangerous.
What are some examples of positive feedback mechanisms?
Positive Feedback Examples
- The Ferguson reflex is the start of contractions during delivery.
- In the case of childbirth, the uterine walls ultimately expand due to the baby’s development, which is represented by the stretch receptors.
- This stretching will promote the release of oxytocin hormones, which will engage the uterine muscles and reduce the uterine gap.
Which are examples of negative feedback regulation?
There are many negative feedback pathways in biological systems, including:
- Temperature regulation
- Blood pressure regulation
- Blood sugar regulation
- Thyroid regulation
- Photosynthesis in response to increased carbon dioxide
- Predator/prey population dynamic
What are examples of positive and negative feedback loops?
negative feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes change in the opposite direction.For example, an increase in the concentration of a substance causes feedback that ultimately causes the concentration of the substance to decrease. Positive feedback loops are inherently unstable systems.
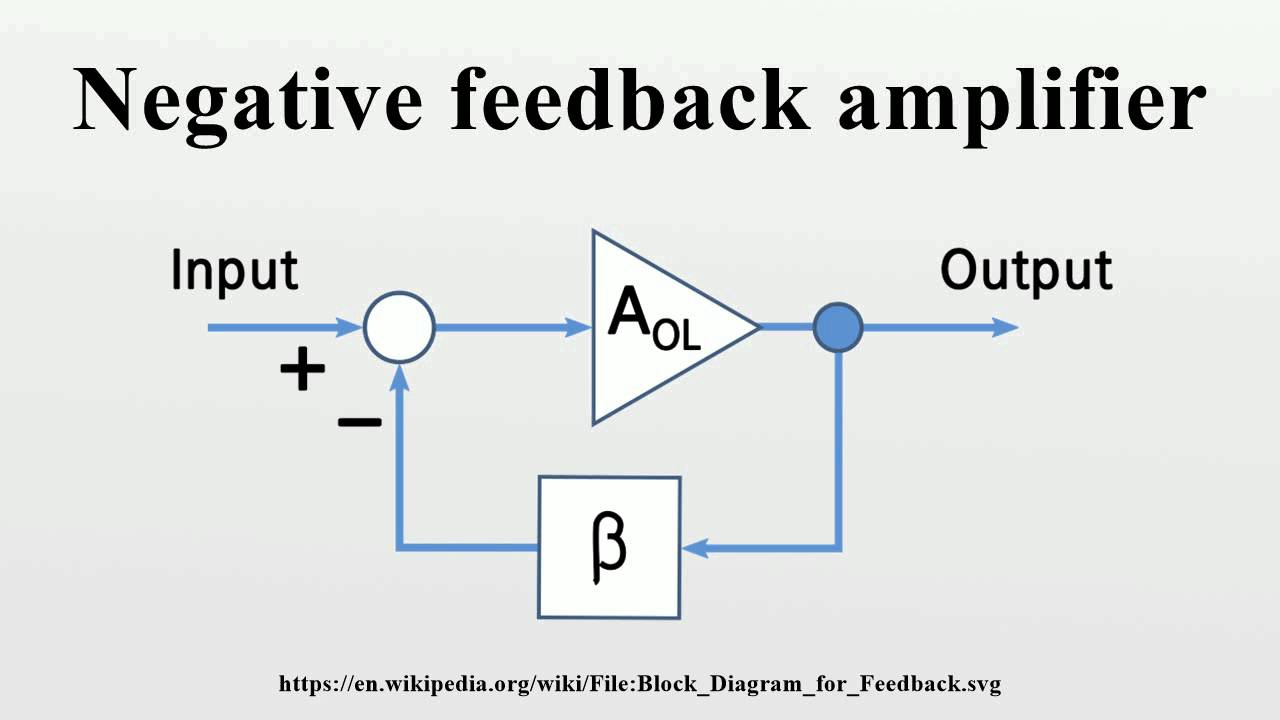
What is the negative feedback of mechanism?
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.
What is a negative feedback mechanism give an example?
A typical example of a negative feedback mechanism in the human body is the regulation of body temperature via endotherms. When the body's temperature rises above normal, the brain sends signals to various organs, including the skin, to release heat in the form of sweat.
What is the difference between positive and negative feedback in homeostasis?
Homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops that counteract changes of various properties from their target values, known as set points. In contrast to negative feedback loops, positive feedback loops amplify their initiating stimuli, in other words, they move the system away from its starting state.
What is the difference between positive and negative feedback mechanisms?
Positive feedback loops enhance or amplify changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable. Negative feedbacks tend to dampen or buffer changes; this tends to hold a system to some equilibrium state making it more stable.
What is negative feedback in simple terms?
: feedback that tends to dampen a process by applying the output against the initial conditions.
Which of these are examples of negative feedback?
When a high level of particular hormone inhibits their further secretion is called as negative feedback. As the level of water in the blood falls, negative feedback ensures that the amount of ADH rises. As the level of water in the blood rises, negative feedback ensures that the amount of ADH falls.
Which of the following is an example of a negative feedback system?
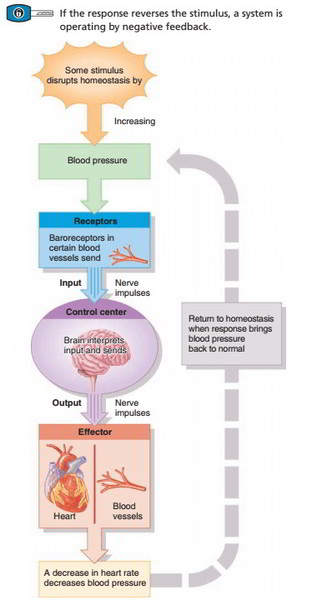
Which of the following is an example of negative feedback? If blood pressure increases, baroreceptors in major arteries detect the change and send signals to the brain. The brain then sends signals to the heart to cause it to beat slower and signals to the blood vessels to cause them to dilate.
What is a negative feedback quizlet?
define negative feedback. a process that brings about a reversal of any change in conditions. it ensures that an optimum steady state can be maintained, as the internal environment is returned to its original set of conditions after any change. it is essential for homeostasis.
What are some examples of negative feedback loops?
Other examples of negative feedback loops include the regulation of blood sugar, blood pressure, blood gases, blood pH, fluid balance, and erythropoiesis.
Why is positive feedback important?
Instead of reversing it, positive feedback encourages and intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition, actually driving it farther out of the normal range. This type of feedback is normal for the body, provided there is a definite endpoint.
What is the process of blood coagulation?
When the body is damaged inside or outside, the damaged tissues release factors that cause platelets to adhere to the tissue (the effector) at the site of the wound. The platelets release granules that activate and attract more platelets and cause them to bind to each other. Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin which creates a meshwork that traps blood cells and platelets, forming a clot and stopping the bleeding. The cascade comes to an end when thrombin binds to the cofactor thrombomodulin, activating protein C which inhibits the coagulation cycle.
How does the body regulate temperature?
Core body temperature in mammals is regulated by thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus in the brain, spinal cord, large veins, and internal organs. When the core temperature gets too high, the animals first reaction is usually behavioral thermoregulation, also called allostasis. The animal may seek shade to get out of the sun or move into the water to cool its skin. This type of thermoregulation is the primary reaction because the effects will occur faster than the physiological mechanisms. It is important to realize that this feedback mechanism is based on controlling heat loss or heat gain in the body. The body does not “cool itself” in the literal sense, meaning it does not turn on an internal air conditioning system or synthesize chemicals that cool the body.
What are the components of a feedback loop?
Feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they monitor conditions inside and outside the body. Some examples are thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. The control center, often in the brain, compares the value the sensor receives to the values in the range.
Why is thermoregulation the primary reaction?
This type of thermoregulation is the primary reaction because the effects will occur faster than the physiological mechanisms. It is important to realize that this feedback mechanism is based on controlling heat loss or heat gain in the body.
What is homeostasis in biology?
Last Updated: April 15, 2018. Homeostasis refers to the steady state of internal conditions maintained by living organisms. Humans have control centers in the brain and other parts of the body that constantly monitor conditions like temperature, pressure, and blood and tissue chemistry. When any condition gets out of balance, ...
What is positive feedback?
A positive feedback mechanism is the exact opposite of a negative feedback mechanism. With negative feedback, the output reduces the original effect of the stimulus. In a positive feedback system, the output enhances the original stimulus. A good example of a positive feedback system is child birth. During labor, a hormone called oxytocin is ...
When is the body in homeostasis?
Generally, the body is in homeostasis when its needs are met and its functioning properly. Every organ in the body contributes to homeostasis. A complex set of chemical, thermal, and neural factors interact in complex ways, both helping and hindering the body while it works to maintain homeostasis.
What is the response to a stimulus?
Response – a response from the effector balances out the original stimulus to maintain homeostasis.
What is the meaning of afferent pathways?
Here’s a few more definitions you may want to know. Afferent pathways – carry nerve impulses into the central nervous system. For instance, if you felt scorching heat on your hand, the message would travel through afferent pathways to your central nervous system.
What is the tendency of an organism or cell to regulate its internal environment and maintain equilibrium, usually by a system of?
Homeostasis. The biological definition of homeostasis is “the tendency of an organism or cell to regulate its internal environment and maintain equilibrium, usually by a system of feedback controls, so as to stabilize health and functioning”. Generally, the body is in homeostasis when its needs are met and its functioning properly.
What is the function of stimulus and receptor?
Receptor – detects the change. The receptor monitors the environment and responds to change (stimuli). Input – information travels along the (afferent) pathway to the control center.
Does positive feedback enhance or inhibit original stimulus?
Just remember that positive feedback mechanisms enhance the original stimulus and negative feedback mechanisms inhibit it.
What is negative feedback loop?
A negative feedback loop, also known as an inhibitory loop, is a type of self-regulating system. In a negative feedback loop, increased output from the system inhibits future production by the system.
Why is homeostasis important?
Homeostasis is very important in the human body. Many systems have to self regulate in order for the body to stay in optimal ranges for health. 3 . When individuals have problems maintaining these systems, it can involve dysregulation of a negative feedback loop.
Why does the pancreas not respond to insulin?
For example, in diabetes, the pancreas does not respond properly to high blood sugar by producing more insulin. 3 In type 1 diabetes, this is because there are fewer cells available to make insulin. A person's immune system has damaged the insulin-producing cells.