What is meant by skewed distribution?
What is skewed distribution? A statistical distribution is called skewed is the data included in it is concentrated on either the left or the right side of the scale, resulting in a non-symmetrical curve. Any distribution with its left side shaped differently than its right side can be called a skewed distribution.
Why do we convert skewed data into a normal distribution?
We see that the target variable SalePrice has a right-skewed distribution. We need to log transform this variable so that it becomes normally distributed. A normally distributed (or close to normal) target variable helps in better modeling the relationship between target and independent variables.
Is binomial probability distribution always negatively skewed?
The binomial probability distribution is always negatively skewed. The shape of the binomial distribution can be positively skewed, negatively skewed, or symmetric. The shape varies based on the probability of success and the number of trials. In a Poisson distribution, the probability of success may vary from trial to trial.
What does it mean to say data is positively skewed?
There are two types of skewed distributions. A distribution is positively skewed if the scores fall toward the lower side of the scale and there are very few higher scores. Positively skewed data is also referred to as skewed to the right because that is the direction of the 'long tail end' of the chart.

What is an example of a negatively skewed distribution?
Negative skew example An example of negatively skewed data could be the exam scores of a group of college students who took a relatively simple exam. If you draw a curve of the group of students' exam scores on a graph, the curve is likely to be skewed to the left.
What does negative skewness tell you about data?
Negative values for the skewness indicate data that are skewed left and positive values for the skewness indicate data that are skewed right. By skewed left, we mean that the left tail is long relative to the right tail. Similarly, skewed right means that the right tail is long relative to the left tail.
What causes a negatively skewed distribution?
Left-Skewed (Negatively Skewed) Left skewed distributions occur when the long tail is on the left side of the distribution. Statisticians also refer to them as negatively skewed. This condition occurs because probabilities taper off more slowly for lower values.
Is a negatively skewed distribution Good or bad?
A negative skew is generally not good, because it highlights the risk of left tail events or what are sometimes referred to as “black swan events.” While a consistent and steady track record with a positive mean would be a great thing, if the track record has a negative skew then you should proceed with caution.
How do you explain a skewed distribution?
A skewed distribution is neither symmetric nor normal because the data values trail off more sharply on one side than on the other. In business, you often find skewness in data sets that represent sizes using positive numbers (eg, sales or assets).
What does skewness tell us about data?
Skewness measures the deviation of a random variable's given distribution from the normal distribution, which is symmetrical on both sides. A given distribution can be either be skewed to the left or the right. Skewness risk occurs when a symmetric distribution is applied to the skewed data.
How do you know if data is positively or negatively skewed?
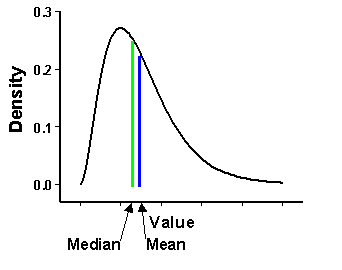
If the median is to the right of the mean, then it is negatively skewed. And if the mean is to the right of median, then it is positively skewed.
When data are negatively skewed the mean will usually be?
-when the data are negatively skewed, the mean will usually be less than the median. - z-score of zero in- dicates that the value of the observation is equal to the mean.
What does skewness tell us about data?
Skewness measures the deviation of a random variable's given distribution from the normal distribution, which is symmetrical on both sides. A given distribution can be either be skewed to the left or the right. Skewness risk occurs when a symmetric distribution is applied to the skewed data.
How do you interpret positive and negative skewness?
Positive Skewness means when the tail on the right side of the distribution is longer or fatter. The mean and median will be greater than the mode. Negative Skewness is when the tail of the left side of the distribution is longer or fatter than the tail on the right side. The mean and median will be less than the mode.
What is negative skewed distribution?
Negatively skewed distribution refers to the distribution type where the more values are plotted on the right side of the graph , where the tail of the distribution is longer on the left side and the mean is lower than the median and mode which it might be zero or negative due to the nature of the data as negatively distributed.
Why is skewed distribution important?
In finance, skewed distribution is used to evaluate the return on the investment. Negatively skewed data is the sign of lower return on investment; hence the investor finds it risky to invest in the countries where the income is negatively skewed due to long term losses and currency fluctuation in the international market.
Why do underdeveloped countries pay high income taxes?
This is due to the unequal distribution of income and wealth.
What is central tendency?
Central tendency refers to the mean, median, and mode of the distribution. In the case of the normally skewed data, the mean, median, and mode are equal, which shows the equal distribution of income and wealth and the positive role of the government efforts and the development of the economy.
What does the 'The Underdevelopment' show?
It shows the underdevelopment of the economy.
Which is higher, median or mode?
Median is the middle value, and mode is the highest value. But due to unequal distribution median will be higher than the mean.
Why does the government need to take measures to provide rights to the laborers?
It reflects the exploitation of labor or the availability of cheap labor. Hence the government needs to take measures to provide rights to the laborers.
What is skewed distribution?
Skewness is a way to describe the symmetry of a distribution. A distribution is negatively skewed if it has a “tail” on the left side of the distribution: Note: Sometimes negatively skewed distributions are also called “left skewed” distributions.
Why is the stock market skewed?
The distribution of daily stock market returns is negatively skewed because the stock market delivers a slightly positive return on most days, but occasionally returns huge negative returns on a few days.
Why is the distribution of scores on easy tests skewed?
The distribution of scores on easy exams or tests tend to be negatively skewed because most students score very high, while a few students score much lower than the average.
Is the GPA distribution skewed?
The distribution of GPA among college students is negatively skewed since most students have a GPA between 2 and 4 with a few having a GPA much lower.
What Does Skewness Tell You?
Investors note skewness when judging a return distribution because it, like kurtosis, considers the extremes of the data set rather than focusing solely on the average. Short- and medium-term investors in particular need to look at extremes because they are less likely to hold a position long enough to be confident that the average will work itself out.
What is negatively skewed distribution?
Negatively-skewed distributions are also known as left-skewed distributions. Skewness is used along with kurtosis to better judge the likelihood of events falling in the tails of a probability distribution.
What is the difference between a negative skew and a positive skew?
Negative skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on the left side of the distribution, while positive skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on the right. The mean of positively skewed data will be greater than the median. In a distribution that is negatively skewed, the exact opposite is the case: the mean of negatively skewed data will be less ...
How does Pearson's second coefficient of skewness work?
Pearson’s second coefficient of skewness, or Pearson median skewness, subtracts the median from the mean, multiplies the difference by three, and divides the product by the standard deviation.
Why is skewness used in kurtosis?
Skewness is used along with kurtosis to better judge the likelihood of events falling in the tails of a probability distribution.
What is skewed data?
Skewness refers to a distortion or asymmetry that deviates from the symmetrical bell curve, or normal distribution, in a set of data. If the curve is shifted to the left or to the right, it is said to be skewed. Skewness can be quantified as a representation of the extent to which a given distribution varies from a normal distribution.
What is negative skew?
In the curve of a distribution, the data on the right side of the curve may taper differently from the data on the left side. These taperings are known as "tails.". Negative skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on ...
What is a skew-normal distribution?
A skew-normal distribution is a normal distribution with an extra parameter that skews its shape to either the left or the right. Given the fact that the only thing that changes is the skew of the normal distribution, it shares many characteristics with the normal distribution, such as:
What does it mean when a chart skews left?
Left-skewed distribution, also called negatively skewed distribution, refers to the situation when the chart has a longer tail in the negative direction of its number line. Judging a chart's distribution is not usually done based on the position of the peak value. The elements that constitute a negatively skewed distribution are:
What is a right skewed graph?
A right-skewed distribution, also called a positive skew distribution, is when the chart's tail is longer on its right side and its peak veers to the left. Although there are exceptions, most right-skewed distributions have the mean to the right of the median. Given the fact that a right-skewed graph has no clear center point, it is usually difficult to assign it a typical value, as opposed to a normal distribution with its mean, median and mode equally distributed around the center of the data set.
What is the average human life span?
The average human life span chart is skewed left. If the chart shows values from 1 to 100, representing years of life, the data would show that most people live to around 75 to 80 years old. This means that the chart's tail is longer on its left side, as the values around 75 and 80 are closer to 100 than to 1. It also means that the chart's peak, meaning the average human life span, is closer to the right of the chart.
What happens if the skew value is zero?
The skew value is different from zero. If the value is zero, the skew-normal distribution becomes a normal distribution
How can skewed distribution help you?
Learning about skewed distribution can help you improve your knowledge of statistics. Regardless of how you use statistics in your line of work, knowing what skewed distribution is and how to interpret it can have a direct impact on your job success. Being familiar with skewed distribution is a valuable skill, but it requires research and practice. In this article, we discuss what skewed distribution is, explain the meaning of the distribution skewing left or right and provide examples of skewed distribution.
Why is the chart skew right?
One of the main reasons for the occurrence of a right-skewed distribution is that the chart's lower limits are considerably lower than the rest of the chart's data, causing the entire chart to skew right.
What is a negatively skewed distribution in trading?
Skewness has a probability distribution that is not normally distributed.
What is a negative skewed strategy?
What are negatively skewed trading strategies? Negatively skewed trading strategies are “accidents waiting to happen”: You have many small winners and rare big losers. Unfortunately, the big losers can put you out of business. This is what a negatively skewed trading strategy is – you need to understand the profit distribution of the strategy. Unfortunately, most traders don’t know that they are trading negatively skewed strategies until they blow up. We provide an example of a negatively skewed distribution (of a trading strategy).
What is distribution in strategy?
Distribution refers to the profit and loss distribution of a strategy . When it’s negatively distributed, or skewed, there are more observations on the right side of the y-axis, but the left side of the y-axis is longer and thus contains many more big losers than comparatively winners on the right side.
What is the problem with negative skewness?
Another problem with negative skewness and distribution is that most of the time we feel good. Most behavioral tests confirm that we continue hopeless strategies as long as we win frequently. We ignore the fat left tails, unfortunately.
Which side of the fat tail is negative?
Opposite, if it’s on the left side the fat tail has negative skewness. Below is an example of a trading strategy that is negatively skewed and thus has a left fat tail:
What is the worst thing that can happen to a new trader?
The worst that can happen to a new trader, is to make much money from the start. The chances are that he’s just being lucky. It will feed his ego and increase his risk. He’ll not learn. I have yet to see a trader that does not experience significant losses from time to time. The more you learn, the better you can handle those losses.
Is it good to trade for a long time?
As you could imagine, it’s not good. You trade happily for a long time until you have a rare, but big loser that wipes out many months, or years, of trading profits.

Explanation
Negatively Skewed Distribution Examples
Real-Life Examples of Negatively Skewed Distribution
Interpretation
Central Tendency of Negatively Skewed Distribution
Negatively Skewed Distribution in Finance
- In finance, skewed distribution is used to evaluate the return on the investment. Negatively skewed data is the sign of lower return on investment; hence the investor finds it risky to invest in the countries where the income is negatively skewed due to long term losses and currency fluctuation in the international market. Those investors who look ...
Recommended Articles