Does neon have a high or low melting point?
The elements on the right, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine and neon all have low melting points and are all non-metals. It requires a lot of energy to disrupt these strong covalent bonds holding the carbon atoms in place in the lattice so the melting point of carbon (either as graphite or diamond) is high. Why is the boiling point of nitrogen?
What is the freezing point of neon?
What Is the Freezing Point of Neon? The freezing point of neon is minus 415.5 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 248.6 degrees Celsius), which is only slightly lower than its boiling point of minus 410.66 F (minus 245.92 C). This very low freezing point is a characteristic of all noble gases.
What is the melting point of neon in degrees Celsius?
The melting point of neon is 24.56 degrees Kelvin or -247.59 degrees Celsius or degrees Celsius. The boiling point of neon is 27.07 degrees Kelvin or -245.08 degrees Celsius or degrees Celsius. Uses of neon. Neon is a very common element in the universe, but it is quite rare on Earth. Neon is not commonly used as it is a very expensive item.
Is a boiling point higher than a melting point?
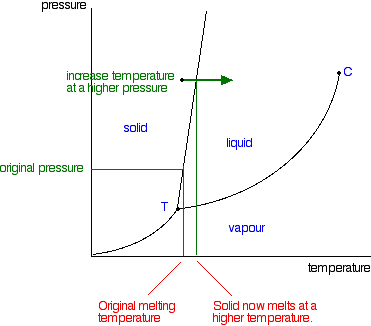
The boiling point doesn’t remain same it changes with the inference of the external pressure, whereas melting point has nothing to do with external pressure. Melting and freezing point of a substance are not the same as in the case of agar, which melts at 85 0 C but gets back in solid form at 31 0 C to 40 0 C.

What is Neons boiling and melting point?
neonatomic number10atomic weight20.183melting point−248.67 °C (−415.5 °F)boiling point−246.048 °C (−411 °F)density (1 atm, 0° C)0.89990 g/litre2 more rows
What is the boiling point of neon?
-410.9°F (-246°C)Neon / Boiling point
What is the melting and boiling point of neon in Kelvin?
Periodic Table of the ElementsNameWeightBoiling PointFluorine18.998485 KelvinNeon20.179727.1 KelvinSodium22.989771156 KelvinMagnesium24.3051380 Kelvin89 more rows
Does neon have a high or low boiling point?
Neon at room temperature is a gas. In fact, the boiling point of neon is 246 C. There is a low level of intermolecular interactions, therefore contributing to its low boiling point.
What is Neons melting point?
-415.5°F (-248.6°C)Neon / Melting point
Is neon a gas or liquid?
Neon is a chemical element with symbol Ne and atomic number 10. Classified as a noble gas, Neon is a gas at room temperature.
What are the melting and boiling points of elements?
This is a modal window....List of melting and boiling points of first 20 elements.ElementMelting Point (K)Boiling Point (K)Nitrogen (N2)6377.35Oxygen (O2)54.3590.15Fluorine53.5585.05Neon24.5527.1516 more rows
Which has highest melting point?
The metal with the highest melting point is tungsten, at 3,414 °C (6,177 °F; 3,687 K); this property makes tungsten excellent for use as electrical filaments in incandescent lamps.
Which element has the highest melting and boiling point?
Carbon (C):Atomic Number is 6.Carbon occurs naturally as anthracite, graphite, and diamond.It is used in the production of steel.Carbon has two stable, naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12 and carbon-13.It has the highest melting and boiling point.
Why does neon have a high boiling point?
Strength of Dispersion Forces Neon is a relatively small atom with only 10 electrons, so its dispersion forces are only weak. Even so, the dispersion forces of neon are sufficient to facilitate a boiling temperature 23 degrees higher than helium, which only has two electrons.
Which has highest boiling point?
Xenon has the highest boiling point.
Why does ne have the lowest boiling point?
Because of the greater temporary dipoles, xenon atoms are "stickier" than neon atoms. Neon atoms will break away from each other at much lower temperatures than xenon atoms - hence neon has the lower boiling point.
Can neon melt?
Melting point of Neon is -248°C.
What are 5 interesting facts about neon?
Top 10 Facts About NeonReal neon lights are only reddish-orange colours. ... Neon is used in television sets and lasers. ... Neon gas is rare. ... The first neon light was revealed in 1910. ... Neon is a Greek word. ... The first neon light sign was sold in 1912. ... A neon sign once sold for $48,300! ... The Paris Opera House was decorated with Neon.More items...•
Is neon gas toxic?
Neon is a rare atmospheric gas and as such is non-toxic and chemically inert. Neon poses no threat to the environment, and can have no impact at all because it's chemically unreactive and forms no compounds.
What is the boiling point of helium?
-452.1°F (-268.9°C)Helium / Boiling point
How many electrons does neon have?
Neon is a chemical element with atomic number 10 which means there are 10 protons and 10 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Neon is Ne.
Which element has the lowest boiling point?
In the periodic table of elements, the element with the lowest boiling point is helium. Both the boiling points of rhenium and tungsten exceed 5000 K at standard pressure. Since it is difficult to measure extreme temperatures precisely without bias, both have been cited in the literature as having the higher boiling point.
How many protons does lithium have?
Lithium is a chemical element with atomic number 3 which means there are 3 protons and 3 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Lithium is Li.
What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
What is the temperature of nitrogen?
Liquid nitrogen (made by distilling liquid air) boils at 77.4 kelvins (−195.8°C) and is used as a coolant.
What is the boiling point of a substance?
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change (boiling or vaporization) occurs. The temperature at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given pressure is also known as the saturation temperature and at this conditions a mixture of vapor and liquid can exist together. The liquid can be said to be saturated with thermal energy. Any addition of thermal energy results in a phase transition. At the boiling point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Below the boiling point, the liquid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the gaseous form is preferred. The pressure at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given temperature is called the saturation pressure. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from vapor to liquid, it is referred to as the condensation point.
Is a sulfate a colorless gas?
It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas, the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is the lowest among all the elements.
How many electrons does neon have?
Neon is a chemical element with atomic number 10 which means there are 10 protons and 10 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Neon is Ne.
What is the melting point of a substance?
In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. Adding a heat will convert the solid into a liquid with no temperature change. At the melting point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Below the melting point, the solid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the liquid form is preferred. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point.
How many protons does nitrogen have?
Nitrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 7 which means there are 7 protons and 7 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Nitrogen is N.
What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
Is lithium a solid or a metal?
It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and is stored in mineral oil.
Is oxygen a nonmetal?
It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. By mass, oxygen is the third-most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.
What is the boiling point of neon?
Because its boiling point is −246 °C (−411 °F), neon remains, along with helium and hydrogen, in the small fraction of air that resists liquefaction upon cooling to −195.8 °C (−320.4 °F, the boiling point of liquid nitrogen).
What temperature does neon liquefy?
This element is more abundant in the cosmos than on Earth. Neon liquefies at −246.048 °C (−411 °F) and freezes at a temperature only 2 1/2 ° lower. When under low pressure, it emits a bright orange-red light if an electrical current is passed through it.
What is neon made of?
Neon was discovered (1898) by the British chemists Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers as a component of the most volatile fraction of liquefied crude argon obtained from air. It was immediately recognized as a new element by its unique glow when electrically stimulated. Its only commercial source is the atmosphere, in which it is 18 parts per million by volume. Because its boiling point is −246 °C (−411 °F), neon remains, along with helium and hydrogen, in the small fraction of air that resists liquefaction upon cooling to −195.8 °C (−320.4 °F, the boiling point of liquid nitrogen). Neon is isolated from this cold, gaseous mixture by bringing it into contact with activated charcoal, which adsorbs the neon and hydrogen; removal of hydrogen is effected by adding enough oxygen to convert it all to water, which, along with any surplus oxygen, condenses upon cooling. Processing 88,000 pounds of liquid air will produce one pound of neon.
How is neon isolated?
Neon is isolated from this cold, gaseous mixture by bringing it into contact with activated charcoal, which adsorbs the neon and hydrogen; removal of hydrogen is effected by adding enough oxygen to convert it all to water, which, along with any surplus oxygen, condenses upon cooling.
How many electrons are in the shell of n = 2?
and m s, until a total of six have been added. This completes the n = 2 shell, containing a total of eight electrons in its two…
Where does neon gas come from?
Colourless, odourless, tasteless, and lighter than air, neon gas occurs in minute quantities in Earth’s atmosphere and trapped within the rocks of Earth’s crust. Though neon is about 3 1/2 times as plentiful as helium in the atmosphere, dry air contains only 0.0018 percent neon by volume.
Which noble gas has a closed shell electron configuration?
At this point it should be noticed that the second noble gas, neon, has a closed-shell electron configuration, as does the first noble gas, helium. Note also that eight electrons are needed to pass from helium…. spectroscopy: Electron configurations.
What color is neon?
Neon is often used in signs and produces an unmistakable bright reddish-orange light. Although tube lights with other colors are often called "neon", they use different noble gases or varied colors of fluorescent lighting.
What is neon element?
talk. edit. | references. Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air.
What is neon used for?
Neon is used in vacuum tubes, high-voltage indicators, lightning arresters, wavemeter tubes, television tubes, and helium–neon lasers. Liquefied neon is commercially used as a cryogenic refrigerant in applications not requiring the lower temperature range attainable with more extreme liquid-helium refrigeration.
What is the second lightest noble gas?
Neon is the second-lightest noble gas, after helium. It glows reddish-orange in a vacuum discharge tube. Also, neon has the narrowest liquid range of any element: from 24.55 to 27.05 K (−248.45 °C to −245.95 °C, or −415.21 °F to −410.71 °F).
How much of the atmosphere is neon?
Neon comprises 1 part in 55,000 in the Earth's atmosphere, or 18.2 ppm by volume (this is about the same as the molecule or mole fraction), or 1 part in 79,000 of air by mass. It comprises a smaller fraction in the crust. It is industrially produced by cryogenic fractional distillation of liquefied air.
How many solar masses does neon have?
This requires temperatures above 500 megakelvins, which occur in the cores of stars of more than 8 solar masses. Neon is abundant on a universal scale; it is the fifth most abundant chemical element in the universe by mass, after hydrogen, helium, oxygen, and carbon (see chemical element ).
How many isotopes does neon have?
Neon has three stable isotopes: 20 Ne (90.48%), 21 Ne (0.27%) and 22 Ne (9.25%). 21 Ne and 22 Ne are partly primordial and partly nucleogenic (i.e. made by nuclear reactions of other nuclides with neutrons or other particles in the environment) and their variations in natural abundance are well understood.
Which element has the lowest boiling point?
In the periodic table of elements, the element with the lowest boiling point is helium. Both the boiling points of rhenium and tungsten exceed 5000 K at standard pressure. Since it is difficult to measure extreme temperatures precisely without bias, both have been cited in the literature as having the higher boiling point.
What is the melting point of a solid?
Sodium chloride melts at 801°C. On the other hand, ice (solid H 2 O) is a molecular compound whose molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds, which is effectively a strong example of an interaction between two permanent dipoles. Though hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces, the strength of hydrogen bonds is much less than that of ionic bonds. The melting point of ice is 0 °C.
What are phonons in crystals?
The quanta of the crystal vibrational field are referred to as ‘‘ phonons .’’ A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, like solids and some liquids. Phonons play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter, like thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. In fact, for crystalline, nonmetallic solids such as diamond, k ph can be quite large, exceeding values of k associated with good conductors, such as aluminum. In particular, diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity (k = 1000 W/m.K) of any bulk material.
How does thermal conduction work?
As was written, in liquids, the thermal conduction is caused by atomic or molecular diffusion, but physical mechanisms for explaining the thermal conductivity of liquids are not well understood. Liquids tend to have better thermal conductivity than gases, and the ability to flow makes a liquid suitable for removing excess heat from mechanical components. The heat can be removed by channeling the liquid through a heat exchanger. The coolants used in nuclear reactors include water or liquid metals, such as sodium or lead.
What is the boiling point of a substance?
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change (boiling or vaporization) occurs. The temperature at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given pressure is also known as the saturation temperature and at this conditions a mixture of vapor and liquid can exist together. The liquid can be said to be saturated with thermal energy. Any addition of thermal energy results in a phase transition. At the boiling point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Below the boiling point, the liquid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the gaseous form is preferred. The pressure at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given temperature is called the saturation pressure. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from vapor to liquid, it is referred to as the condensation point.
Which gases have high thermal conductivity?
The mean free path also depends on the diameter of the molecule, with larger molecules more likely to experience collisions than small molecules, which is the average distance traveled by an energy carrier (a molecule) before experiencing a collision. Light gases , such as hydrogen and helium typically have high thermal conductivity. Dense gases such as xenon and dichlorodifluoromethane have low thermal conductivity.
What is the most important thermal expansion coefficient?
The volumetric the rmal expansion coefficient is the most basic thermal expansion coefficient, and the most relevant for fluids. In general, substances expand or contract when their temperature changes, with expansion or contraction occurring in all directions.
