
Symptoms
There's no proof that natural remedies can treat it, but some might help with movements:
- Ginkgo biloba
- Melatonin
- Vitamin B6 Vitamin E Talk to your doctor before you take any supplements for your symptoms.
Causes
What Is Tardive Dyskinesia?
- Symptoms. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of tardive dyskinesia if you’re taking medications. ...
- Causes. Causes of tardive dyskinesia are long-term use of a class of medications called neuroleptics, also known as antipsychotic drugs.
- Treatments. ...
- Dyskinesia vs. ...
- Next steps. ...
Complications
Tardive dyskinesia affects all ages, genders, races and ethnicities. People who are older, Black or female are more likely to develop this problem. Diabetes. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Substance use disorder. Traumatic brain injury (TBI). What medications cause tardive dyskinesia? Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications.
What natural remedies can be used to treat tardive dyskinesia?
What symptoms can tardive dyskinesia cause?
- Jerky movements. These are irregular movements which are not rhythmic.
- Slow movements. These are slow and flowing movements.
- Muscle spasms. These are movements where your muscles suddenly tighten. They might last for a short time or longer periods.
What are the causes of tardive dyskinesia?
Are You prone to developing tardive dyskinesia?
What are the symptoms of tardive dyskinesia?
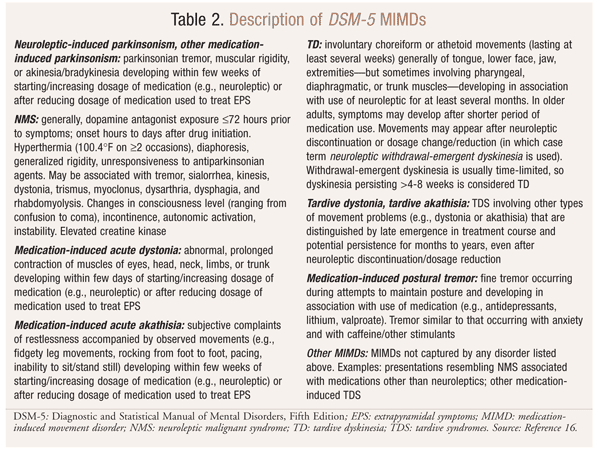
What neuroleptic drugs cause tardive dyskinesia?
Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a disorder that involves involuntary movements....Medicines that most commonly cause this disorder are older antipsychotics, including:Chlorpromazine.Fluphenazine.Haloperidol.Perphenazine.Prochlorperazine.Thioridazine.Trifluoperazine.
What is tardive dyskinesia caused by?
Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is an involuntary neurological movement disorder caused by the use of dopamine receptor blocking drugs that are prescribed to treat certain psychiatric or gastrointestinal conditions.
What Anti Depression Meds cause TD?
Antidepressants. As mentioned previously, SSRIs are associated with TD. Fluoxetine, in particular, can lead to TD or symptoms similar to TD, and these symptoms have been reported for up to 1 year after discontinuation and withdrawal from the medication.
What is a neuroleptic medication?
Neuroleptics, also known as antipsychotic medications, are used to treat and manage symptoms of many psychiatric disorders. They fall into two classes: first-generation or "typical" antipsychotics and second-generation or "atypical" antipsychotics." Neuroleptic drugs block dopamine receptors in the nervous system.
What are examples of TD movements?
TD movements may: Be rapid and jerky, or slow and writhing. Occur in a repetitive, continuous, or random pattern. Present as face twitching, involuntary eye movements, darting tongue, piano fingers, clenched jaw, rocking torso, and gripping feet.
Who is most at risk for tardive dyskinesia?
The risk may be greater if more than one of these applies to you....Some research suggests that you may be more likely to develop TD if you:are over the age of 50.are female.are post-menopause.are Black.have a drug or alcohol addiction.have diabetes.have a learning disability.have a brain injury.
How serious is tardive dyskinesia?
Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a movement disorder that causes a range of repetitive muscle movements in the face, neck, arms and legs. TD symptoms are beyond a person's control. These symptoms can make routine physical functioning difficult, significantly affecting quality of life.
What is the best treatment for tardive dyskinesia?
Other than ceasing or switching antipsychotic medication, the strongest current evidence for TD treatment is the use of the VMAT inhibitors, deutetrabenazine and valbenazine.
Can tardive dyskinesia be fatal?
Tardive dyskinesia is not usually fatal in itself. Some studies have suggested increased mortality rates in patients with tardive dyskinesia, however, there is no evidence to show a specific association with any specific cause of death and tardive dyskinesia.
What are some examples of neuroleptic drugs?
Common low-potency, first-generation neuroleptics include thioridazine, chlorpromazine, and thiothixene. Among second-generation medications, clozapine, olanzapine, paliperidone, and risperidone are the most frequently prescribed.
Which drugs are neuroleptic drugs?
DDS MEDICAL ADVISORY #2000-2TRADEGENERICRepoisebutaperazineRisperdalRisperidoneSerentilmesoridazineSparinepromazine25 more rows
Does your brain go back to normal after antipsychotics?
For neurological, neuropsychological, neurophysiological, and metabolic abnormalities of cerebral function, in fact, there is evidence suggesting that antipsychotic medications decrease the abnormalities and return the brain to more normal function.
How serious is tardive dyskinesia?
Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a movement disorder that causes a range of repetitive muscle movements in the face, neck, arms and legs. TD symptoms are beyond a person's control. These symptoms can make routine physical functioning difficult, significantly affecting quality of life.
Is tardive dyskinesia caused by too much dopamine?
Tardive dyskinesia is thought to be caused by too much dopamine signaling in the brain . Other medications used to treat upset stomach, nausea, and vomiting may also trigger the development of TD.
Can tardive dyskinesia be fatal?
Tardive dyskinesia is not usually fatal in itself. Some studies have suggested increased mortality rates in patients with tardive dyskinesia, however, there is no evidence to show a specific association with any specific cause of death and tardive dyskinesia.
What is the best treatment for tardive dyskinesia?
Other than ceasing or switching antipsychotic medication, the strongest current evidence for TD treatment is the use of the VMAT inhibitors, deutetrabenazine and valbenazine.
What is tardive dyskinesia?
Causes of tardive dyskinesia. TD is most often a side effect of neuroleptic, or antipsychotic, drugs. These medications are prescribed to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other mental health conditions. TD medications are also sometimes prescribed to treat GI disorders.
What is the role of neuroleptic drugs in the brain?
Sometimes neuroleptic drugs are prescribed for gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. These drugs block dopamine receptors in the brain. Dopamine is a chemical that helps control emotions and the pleasure center of your brain. It also plays a role to in your motor functions.
How long does it take for neuroleptics to show symptoms?
The symptoms might take several months or years to appear, but some people may experience the reaction after just one dose.
How many people develop TD?
Some studies suggest that between 30 to 50 percent of people taking these medications will develop TD over the course of their treatment. The condition can be permanent, but treatment after symptoms begin may prevent the progression of, and in many cases, the reversal of symptoms.
How to prevent TD?
The best way to prevent TD is to be aware of your body and any unusual symptoms you experience. Make an appointment to see your doctor if anything unfamiliar occurs. Together, you can decide how to stop the movements and still treat underlying issues. Last medically reviewed on January 2, 2018.
What are some movements that can be seen in a symlink?
These movements may include blinking frequently, smacking or puckering the lips, and sticking the tongue out.
Is TD a movement disorder?
TD is just one type of dyskin esia. Other types can be the result of other conditions or diseases. People with Parkinson’s disease, for example, may experience dyskinesia. People with other movement disorders may experience symptoms of the movement disorder, too.
What is tardive dyskinesia?
Tardive dyskinesia is a neurological syndrome caused by the long-term use of neuroleptic drugs. Neuroleptic drugs are generally prescribed for psychiatric disorders, as well as for some gastrointestinal and neurological disorders.
Can tardive dyskinesia last long?
Symptoms of tardive dyskinesia may remain long after discontinuation of neuroleptic drugs. In many cases, the symptoms stop spontaneously, but in some cases they may persist indefinitely.
Is there any treatment for tardive dyskinesia?
Treatment is highly individualized. The first step is generally to stop or minimize the use of the neuroleptic drug, but this can be done only under close supervision of the physician.
How does tardive dyskinesia occur?
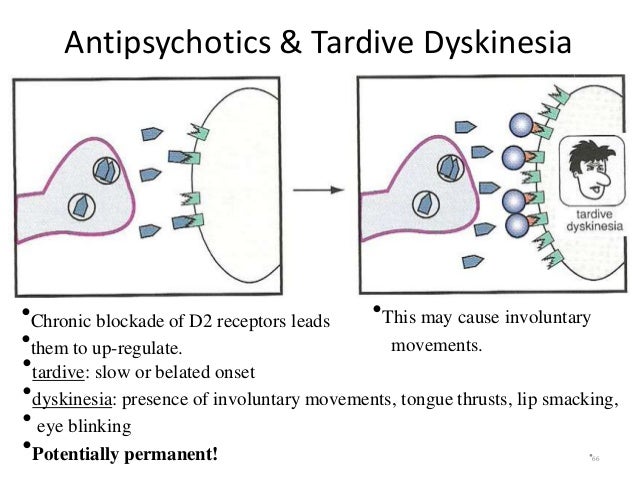
The most compelling line of evidence suggests that tardive dyskinesia may result primarily from neuroleptic-induced dopamine supersensitivity in the nigrostriatal pathway, with the D2 dopamine receptor being most affected. Neuroleptics act primarily on this dopamine system, and older neuroleptics, which have greater affinity for the D2 binding site, are associated with high risk for tardive dyskinesia. The D2 hypersensitivity hypothesis is also supported by evidence of a dose–response relationship, withdrawal effects, studies on D2 agonists and antagonists, animal studies, and genetic polymorphism research.
When did the term "tardive dyskinesia" come into use?
The term "tardive dyskinesia" first came into use in 1964 .
What is tardive myoclonus?
Tardive myoclonus, a rare disorder, presents as brief jerks of muscles in the face, neck, trunk, and extremities. "AIMS Examination": This test is used when psychotropic medications have been prescribed because people sometimes develop tardive dyskinesia due to prolonged use of antipsychotic medications. The Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ...
What is TD in medicine?
Valbenazine, tetrabenazine, botulinum toxin. Prognosis. Variable. Frequency. 20% (atypical antipsychotics) 30% (typical antipsychotics) Tardive dyskinesia ( TD) is a disorder that results in involuntary, repetitive body movements, which may include grimacing, sticking out the tongue, or smacking the lips.
What is the name of the neurotransmitter that causes smacking of the lips?
Tardive dyskinesia is believed to involve the neurotransmitter dopamine. Tardive dyskinesia ( TD) is a disorder that results in involuntary, repetitive body movements, which may include grimacing, sticking out the tongue, or smacking the lips. Additionally, there may be rapid jerking movements or slow writhing movements.
What is the name of the disorder that results in involuntary, repetitive body movements?
Tardive dyskinesia. Not to be confused with dyskinetic cerebral palsy. Tardive dyskinesia is believed to involve the neurotransmitter dopamine. Tardive dyskinesia ( TD) is a disorder that results in involuntary, repetitive body movements, which may include grimacing, sticking out the tongue, or smacking the lips.
Why do people have tardive dyskinesia?
Such individual differences may be due to genetic polymorphisms , which code for D2 receptor binding site affinity, or prior exposure to environmental toxins. Decreased functional reserve or cognitive dysfunction, associated with aging, intellectual disability, alcohol and drug use, or traumatic head injuries, has also been shown to increase risk of developing the disorder among those treated with neuroleptics. Antipsychotic drugs can sometimes camouflage the signs of tardive dyskinesia from occurring in the early stages; this can happen from the individual having an increased dose of an antipsychotic drug. Often the symptoms of tardive dyskinesia are not apparent until the individual comes off of the antipsychotic drugs; however, when tardive dyskinesia worsens, the signs become visible.
What medications cause tardive dyskinesia?
Antipsychotic medications that can cause tardive dyskinesia include antipsychotics like: Haloperidol (Haldol) Fluphenazine. Risperidone (Risperdal) Olanzapine (Zyprexa) Your chances of getting TD go up the longer you take an antipsychotic medicine.
What is the best medicine for tardive dyskinesia?
There are two FDA-approved medicines to treat tardive dyskinesia: Deutetrabenazine ( Austedo) Valbenazine ( Ingrezza) Both of these medicines work in similar ways to regulate the amount of dopamine flow in brain areas that control certain kinds of movements. Both can sometimes cause drowsiness.
What is TD in mental health?
Diagnosis. Treatment and Prevention. Tardive dyskinesia is a side effect of antipsychotic medications. These drugs are used to treat schizophrenia and other mental health disorders. TD causes stiff, jerky movements of your face and body that you can't control. You might blink your eyes, stick out your tongue, ...
How long do you have to be on antipsychotics to get TD?
You can get TD if you take an antipsychotic drug. Usually you have to be on it for 3 months or more. But there have been rare cases of it after a single dose of an antipsychotic medicine. Older versions of these drugs are more likely to cause this problem than newer ones. Some studies find a similar risk from both types, though.
Does TD go up with antipsychotics?
Your chances of getting TD go up the longer you take an antipsychotic medicine.
Can TD cause jerky movements?
TD causes stiff, jerky movements of your face and body that you can't control. You might blink your eyes, stick out your tongue, or wave your arms without meaning to do so. Not everyone who takes an antipsychotic drug will get it. But if it happens, it’s sometimes permanent.
What is respiratory dyskinesia?
Respiratory dyskinesia is an under-recognised and distressing condition that clinicians need to be aware of when treating patients with anti-psychotic medications.
Is respiratory dyskinesia a neuroleptic side effect?
Respiratory dyskinesia--an under-recognized side-effect of neuroleptic medications. Respiratory dyskinesia is an under-recognized side effect of neuroleptic administration. There are only few studies that have addressed the prevalence of respiratory dyskinesia in patients with tardive dyskinesia.
Overview
Causes
Signs and symptoms
Risk factors
Prevention
Treatment
Tardive dyskinesia was first described in the 1950s shortly after the introduction of chlorpromazine and other antipsychotic drugs. However, the exact mechanism of the disorder remains largely uncertain. The most compelling line of evidence suggests that tardive dyskinesia may result primarily from neuroleptic-induced dopamine supersensitivity in the nigrostriatal pathway, with the D2 dopamine receptor being most affected. Neuroleptics act primarily on this dopamine system, …
Epidemiology
Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements. Some examples of these types of involuntary movements include:
• Grimacing
• Tongue movements
• Lip smacking