What is current Nike debt to equity?
Nike has comparatively high equity capital, with a debt-to-equity ratio of 0.66 In order to maintain liquidity during the COVID-19 pandemic, Nike suspended share repurchases and issued $5.9 ...
What is current Nike Total debt?
- NIKE total liabilities for the quarter ending May 31, 2021 were $24.254B, a 41.22% increase year-over-year.
- NIKE total liabilities for 2020 were $23.287B, a 58.66% increase from 2019.
- NIKE total liabilities for 2019 were $14.677B, a 15.35% increase from 2018.
- NIKE total liabilities for 2018 were $12.724B, a 17.25% increase from 2017.
What is Nike's EBITDA Interest Coverage Ratio?
NIKE's ebitda interest coverage ratio for fiscal years ending May 2015 to 2019 averaged 91.2x. NIKE's operated at median ebitda interest coverage ratio of 63.5x from fiscal years ending May 2015 to 2019. Looking back at the last five years, NIKE's ebitda interest coverage ratio peaked in May 2016 at 166.6x.
What is the formula for debt equity ratio?
Therefore, the long formula for calculating debt to equity ratio would be: Debt to equity ratio = (Long term liabilities + short term liabilities + other liabilities) A company’s debt to equity ratio provides investors with an easy way to gauge the company’s financial health and its capital infrastructure.

What is NIKE's debt to equity 2021?
Compare NKE With Other StocksNIKE Debt/Equity Ratio Historical DataDateLong Term DebtShareholder's Equity2021-08-31$23.57B$14.34B2021-05-31$24.97B$12.77B2021-02-28$24.25B$11.93B51 more rows
What is NIKE's leverage ratio?
NIKE's financial leverage last quarter was 2.6x. NIKE's financial leverage for fiscal years ending May 2018 to 2022 averaged 2.9x. NIKE's operated at median financial leverage of 2.6x from fiscal years ending May 2018 to 2022.
Is NIKE highly leveraged?
Understaning Nike Use of Financial Leverage So if creditors own a majority of Nike assets, the company is considered highly leveraged.
What is adidas debt ratio?
Calculated as: Total Debt / Shareholders Equity. Adidas AG (ADDYY) had Debt to Equity Ratio of 0.32 for the most recently reported fiscal year, ending 2021-12-31.
What is a good debt/equity ratio?
What is a good debt-to-equity ratio? Although it varies from industry to industry, a debt-to-equity ratio of around 2 or 2.5 is generally considered good. This ratio tells us that for every dollar invested in the company, about 66 cents come from debt, while the other 33 cents come from the company's equity.
What is NIKE's short term debt?
Liabilities & Shareholders' EquityItem Item31-May-202131-Aug-2021Short Term Debt Short Term Debt469M477MCurrent Portion of Long Term Debt Current Portion of Long Term Debt--Accounts Payable Accounts Payable2.84B2.14BAccounts Payable Growth Accounts Payable Growth--24.72%8 more rows
What is NIKE's most valuable asset?
brandNike's most valuable asset is undoubtedly its brand. According to the latest report from Brand Finance, a leading valuation and strategy consultancy firm, the current value of Nike's brand is estimated to be approximately $32 Billion.
Does NIKE have publicly traded debt?
How Much Debt Does NIKE Carry? As you can see below, at the end of February 2021, NIKE had US$9.42b of debt, up from US$3.48b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, its balance sheet shows it holds US$12.5b in cash, so it actually has US$3.11b net cash.
What type of bond is NIKE?
NIKE Inc. DL-Notes 2020(20/30)BondISINUS654106AK94Coupon2.850%Denomination1000Quotation TypePayment Typeregular interest17 more rows•Aug 12, 2022
What is long term debt to equity ratio?
Long term debt to equity ratio is a leverage ratio comparing the total amount of long-term debt against the shareholders' equity of a company. The goal of this ratio is to determine how much leverage the company is taking. A higher ratio means the company is taking on more debt.
What is adidas gross profit margin?
adidas's latest twelve months gross profit margin is 49.9%. adidas's gross profit margin for fiscal years ending December 2017 to 2021 averaged 51.0%. adidas's operated at median gross profit margin of 50.7% from fiscal years ending December 2017 to 2021.
What is Adidas capital structure?
The capital structure analysis shows that Adidas has more assets than debts; however, the elevated credit ratio puts the company in a risky state that only relies on liabilities for capital. Generally, the profitability of the company in the global market is relatively low.
How is leverage ratio calculated?
What are Leverage Ratios?Debt-to-Assets Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets.Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity.Debt-to-Capital Ratio = Today Debt / (Total Debt + Total Equity)Debt-to-EBITDA Ratio = Total Debt / Earnings Before Interest Taxes Depreciation & Amortization (EBITDA)More items...•
What was NIKE's debt ratio in 2019?
NIKE's total debt decreased in 2019 ($3.853 billion, -0.8%), 2021 ($12.813 billion, -1.6%) and 2022 ($12.627 billion, -1.5%) and increased in 2018 ($3.885 billion, +2.2%) and 2020 ($13.015 billion, +237.8%).
How does interest payment affect cash flow?
Interest-payment obligations can impact the cash-flow of the company. Equity owners can keep excess profit, generated from the debt capital, when companies use the debt capital for its business operations .
What is the difference between current and long term debt?
Let's define some of the terms we used in the paragraph above. Current debt is the portion of a company's debt which is due within 1 year, while long-term debt is the portion due in more than 1 year. Cash equivalents include cash and any liquid securities with maturity periods of 90 days or less.
How much debt does Nike have in 2021?
According to the Nike's most recent financial statement as reported on January 5, 2021, total debt is at $9.45 billion, with $9.41 billion in long-term debt and $41.00 million in current debt. Adjusting for $8.63 billion in cash-equivalents, the company has a net debt of $816.00 million.
What is Nike's debt ratio?
Considering Nike's $34.84 billion in total assets, the debt-ratio is at 0.27. As a rule of thumb, a debt-ratio more than one indicates that a considerable portion of debt is funded by assets.
Why is debt important?
Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth. Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives. Interest-payment obligations can impact the cash-flow of the company.
Why is debt ratio 35% important?
A debt ratio of 35% might be higher for one industry and average for another. Importance Of Debt. Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth. Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives.
How much debt does Nike have?
Nike's Debt. According to the Nike’s most recent financial statement as reported on July 24, 2020, total debt is at $9.66 billion, with $9.41 billion in long-term debt and $251.00 million in current debt.
What is Nike's debt ratio?
Considering Nike’s $31.34 billion in total assets, the debt-ratio is at 0.31. As a rule of thumb, a debt-ratio more than one indicates that a considerable portion of debt is funded by assets.
Can equity owners keep excess profit?
However, due to interest-payment obligations, cash-flow of a company can be impacted. Equity owners can keep excess profit, generated from the debt capital, when companies use the debt capital for its business operations.
What is the long term debt of Nike?
Long term debt can be defined as the sum of all long term debt fields. NIKE long term debt for the quarter ending May 31, 2021 was $9.412B, a 171.79% increase year-over-year. NIKE long term debt for 2020 was $9.406B, a 171.54% increase from 2019. NIKE long term debt for 2019 was $3.464B, a 0.12% decline from 2018.
Where is Nike located?
Nike, Inc., based near Beaverton, Oregon, is the world's leading designer, marketer and distributor of authentic athletic footwear, apparel, equipment and accessories for a wide variety of sports and fitness activities.
What is macroaxis analysis?
Macroaxis puts the power of mathematics on your side. We analyze your portfolios and positions such as Nike Inc using complex mathematical models and algorithms, but make them easy to understand. There is no real person involved in your portfolio analysis. We perform a number of calculations to compute absolute and relative portfolio volatility, correlation between your assets, value at risk, expected return as well as over 100 different fundamental and technical indicators.
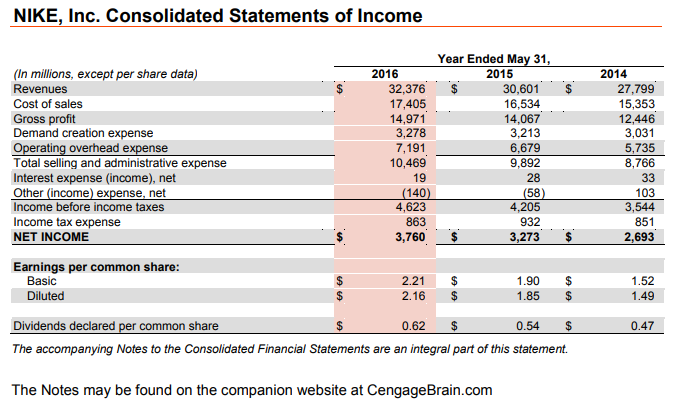
What are the documents that are included in Nike's financial statements?
These documents include Nike income statement, its balance sheet, and the statement of cash flows. Nike investors use historical funamental indicators, such as Nike's Debt to Equity Ratio, to determine how well the company is positioned to perform in the future. Although Nike investors may use each financial statement separately, they are all related. The changes in Nike's assets and liabilities, for example, are also reflected in the revenues and expenses that we see on Nike's income statement, which results in the company's gains or losses. Cash flows can provide more information regarding cash listed on a balance sheet, but not equivalent to net income shown on the income statement. We offer a historical overview of the basic patterns found on Nike Financial Statements. Understanding these patterns can help to make the right decision on long term investment in Nike. Please read more on our technical analysis and fundamental analysis pages.
How does Nike's value differ from its book value?
The market value of Nike Inc is measured differently than its book value, which is the value of Nike that is recorded on the company's balance sheet. Investors also form their own opinion of Nike's value that differs from its market value or its book value, called intrinsic value, which is Nike's true underlying value. Investors use various methods to calculate intrinsic value and buy a stock when its market value falls below its intrinsic value. Because Nike's market value can be influenced by many factors that don't directly affect Nike Inc underlying business (such as pandemic or basic market pessimism), market value can vary widely from intrinsic value.
How to determine Nike value?
Investors typically determine Nike value by looking at such factors as earnings, sales, fundamental and technical indicators, competition as well as analyst projections. However, Nike's price is the amount at which it trades on the open market and represents the number that a seller and buyer find agreeable to each party.
Is Macroaxis bullish on Nike?
Predominant part of Macroaxis users are now bullish on Nike Inc. What is your trading attitude regarding investing in Nike Inc? Are you bullish or bearish?
Is Nike debt to equity ratio increasing?
Nike Debt to Equity Ratio is increasing over the years with slightly volatile fluctuation. Debt to Equity Ratio is expected to dwindle to 1.68. During the period from 2010 to 2021 Nike Debt to Equity Ratio anual values regression line had geometric mean of 1.00 and mean square error of 0.19. Nike Income Tax Expense is projected to increase significantly based on the last few years of reporting. The past year's Income Tax Expense was at 934 Million.
Where is Nike located?
NIKE, Inc. was founded in 1964 and is headquartered in Beaverton, Oregon. Nike operates under Footwear Accessories classification in the United States and is traded on New York Stock Exchange. It employs 75400 people.
Debt to Equity (including Operating Lease Liability)
Nike Inc., debt to equity (including operating lease liability) calculation, comparison to benchmarks
Debt to Capital (including Operating Lease Liability)
Nike Inc., debt to capital (including operating lease liability) calculation, comparison to benchmarks
Debt to Assets (including Operating Lease Liability)
Nike Inc., debt to assets (including operating lease liability) calculation, comparison to benchmarks
Debt to Equity (including Operating Lease Liability)
Nike Inc., debt to equity (including operating lease liability) calculation (quarterly data)
Debt to Assets (including Operating Lease Liability)
Nike Inc., debt to assets (including operating lease liability) calculation (quarterly data)
Why Investors Look At Debt?
Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth . Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives.
What is the difference between current and long term debt?
Let's define some of the terms we used in the paragraph above. Current debt is the portion of a company's debt which is due within 1 year, while long-term debt is the portion due in more than 1 year. Cash equivalents include cash and any liquid securities with maturity periods of 90 days or less.
How much debt does Nike have?
Nike's Debt. According to the Nike’s most recent balance sheet as reported on October 8, 2020, total debt is at $9.55 billion, with $9.41 billion in long-term debt and $138.00 million in current debt. Adjusting for $8.15 billion in cash-equivalents, the company has a net debt of $1.40 billion.
Why is debt important?
Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth. Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives. However, interest-payment obligations can have an adverse impact on the cash-flow of the company.
Does interest payment affect cash flow?
However, interest-payment obligations can have an adverse impact on the cash-flow of the company. Having financial leverage also allows companies to use additional capital for business operations, allowing equity owners to retain excess profit, generated by the debt capital.
Why Investors Look At Debt?
Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth . Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives.
Why is leverage important in business?
Having financial leverage also allows companies to use additional capital for business operations, allowing equity owners to retain excess profit, generated by the debt capital.
How much debt does Nike have in 2021?
Nike's Debt. Based on Nike's balance sheet as of April 2, 2021, long-term debt is at $9.41 billion and current debt is at $4.00 million, amounting to $9.42 billion in total debt. Adjusted for $8.52 billion in cash-equivalents, the company's net debt is at $900.00 million.
What is the difference between current and long term debt?
Let's define some of the terms we used in the paragraph above. Current debt is the portion of a company's debt which is due within 1 year, while long-term debt is the portion due in more than 1 year. Cash equivalents include cash and any liquid securities with maturity periods of 90 days or less.
Why is debt important?
Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth. Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives. However, due to interest-payment obligations, cash-flow of a company can be impacted.
1 NIKE INC Debt-to-Equity Ratio by Year
The first section will help you learn the yearly D/E ratio values of NKE. Every year, the shareholder's confidence and share prices vary. Similarly, depending upon the growth plans or crisis recovery plans, the leverage of a company will vary as well.
2 NKE Debt-to-Equity Ratio by Quarter
Having seen the yearly D/E values, now it is time to see the quarterly ratios for NIKE INC.
3 NIKE INC's 5 Highest Quarterly Debt-to-Equity Ratio Figures
Now let us see the top five D/E quarters for NKE. Since the debt-to-equity ratio is a measure of risk, one can even call these quarters as the top 5 riskiest quarters of NIKE INC. Knowing these quarters, you can research further on the company's actions during those quarters.
4 NKE's 5 Lowest Quarterly Debt-to-Equity Ratio Figures
If the previous section highlighted the riskiest quarters of NIKE INC, this section will help you find the safest D/E quarters. This section lists those quarters with the lowest D/E values. Just like the previous section, you will first see a graph followed by a table.
Want to become a smart investor?
Netcials reports section helps you with deep insights into the performance of various assets over the years. We are constantly upgrading and updating our reports section. Feel free to access them. Do not forget to leave your feedback.