Full Answer
What are neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA)?
The widespread use of neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA) was a significant milestone in the development of anesthesia. Before the introduction of NMBA, anesthesia was induced and maintained with intravenous and inhalational agents.
What are NMBAs and how do they work?
Surgical: NMBAs have been a staple of anesthesiology and surgery since the introduction of succinylcholine in 1952. 3-7 The choice of agent and dosing varies widely depending on the surgical procedure and also on the use of alternative agents, including general anesthetics, local anesthetics, and IV sedation medications.
What is the history of NMBA?
The evolution of NMBA began when Spanish explorers, known as the Conquistadors, returned home bringing tales of ‘flying death”. The South American Indians used arrows and darts coated with curare.
How did NMBA change the practice of anesthesia?
Before the introduction of NMBA, anesthesia was induced and maintained with intravenous and inhalational agents. The introduction of NMBA led to a significant conceptual change in the practice of anesthesia.

What is Nmba in Australia?
The Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) The NMBA operates as an independent authority and its functions include: overseeing practitioner registration. developing professional standards, codes and guidelines. handling notifications and complaints in relation to the profession.
What does the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation do?
About the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation The ANMF is run by nurses and midwives with the purpose of advancing the industrial, political and professional status of its members. The ANMF also actively promotes the need for high quality, affordable and accessible healthcare for every Australian.
What's the difference between a nurse and a nurse practitioner?
Registered nurses need a bachelor's degree in nursing, to pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX), and to obtain a state licensure to get started in the medical field. Nurse practitioners, on the other hand, must have earned a master's degree in nursing (MSN) or higher.
How much do RNS make in Australia?
How much does a Registered nurse make in Australia? The average registered nurse salary in Australia is $79,972 per year or $41.01 per hour. Entry-level positions start at $76,077 per year, while most experienced workers make up to $97,868 per year.
Are nurses unionized in Australia?
The Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation is the union for Registered Nurses, Registered Enrolled Nurses, Registered Midwives, and Registered Assistants in Nursing doing nursing/midwifery work in every state and territory throughout Australia.
What does ANMF stand for?
ANMF Meaning3ANMFAutomated Non-Master File + 1 Business, Tax, Government1ANMFAthelas New Music Festival1ANMFAustralian Nursing and Midwifery Federation + 2 Medical, Government1ANMFAustralian Nursing and & Midwifery Federation Nursing, Australia, Nurse1ANMFAustralian Nursing and Midwifery Federation9 more rows
Is a nurse practitioner as good as a doctor?
Nurse practitioners, or NPs, are registered nurses who have completed additional training, education and nursing experience. It enables them to diagnose and treat illnesses, prescribe medication and do other tasks similar to a doctor that a regular registered nurse cannot.
What is the highest degree in nursing?
doctoral levelThe highest level of nursing education is the doctoral level. Positions that require doctoral nursing degrees include certain types of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), as well as leadership positions such as chief nursing officer or director of nursing.
How many years does it take to become a nurse practitioner?
How Many Years Does it Take to Become a Nurse Practitioner? Generally, it takes around 6 to 8 years of studying and training to become a nurse practitioner.
Are nurses rich in Australia?
The highest paying and most senior position in clinical nursing is a director in nursing with a national average salary of $132,341 per year. Managing teams of nurses in hospitals or medical clinics, directors have a lot of responsibility in providing a high standard of patient care.
What is the highest paid job in Australia?
Neurosurgeons earn the highest annual salary in Australia at over $600,000.
What kind of nurses get paid most?
Highest Paid Nursing Jobs:Family Nurse – $113,000.Urgent Care Nurse – $113,000.Oncology Nurse – $113,000.Orthopedic Nurse – $115,000.Cardiac Nurse – $116,000.Emergency Room Nurse – $116,000.Neonatal Nurse – $127,000.Nurse Anesthetist – $189,000.More items...•
Who developed the NMBA?
Another milestone in the development of NMBA was done by French Physiologist Claude Bernard when he injected curare into frog legs, the muscle in the leg would not contract when the nerve was directly stimulated but would contract when the muscle was directly stimulated.
What was the first NMBA?
This was the first use of NMBA as muscle relaxant in anesthesia. The 1940s, 1950s and 1960s saw the rapid development of several synthetic NMBA. Gallamine was the first synthetic NMBA used clinically. Scientists later developed atracurium, vecurnoium, rocuronium, suxamethonium and pancuronium .
How does neuromuscular blocking affect the neuron?
Physiology at the Neuromuscular Junction. Neuromuscular blocking agents exert its effect by modulating the signal transmission in skeletal muscles. An action potential is, in other words, a depolarisation in neurone membrane due to a change in membrane potential greater than the threshold potential leads to an electrical impulse generation.
Does LAs help with NMBA?
LAs may enhance the effects of depolarisation and nondepolarising NMBAs through pre and post-synaptic interactions at the NMJ. It may result in blood levels high enough to potentiate NMBA-induced neuromuscular block. Epidurally administered levobupivacaine and mepivacaine potentiate amino-steroidal NMBAs and delay recovery from neuromuscular blockade.
Can succinylcholine be administered before or after NMBA?
In some clinical circumstances, succinylcholine may be administered before and after a nondepolarising NMBA or two different nondepolarising NMBAs are administered in sequence. Combining different NMBAs can result in different degrees of neuromuscular block and management should be guided with the use of a neuromuscular function monitor .
What is NMBA compliance?
Compliance (audit of registration standards, conditions) The NMBA works in partnership with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). For information about legislation governing our operations see AHPRA's Legislation and Publications pages.
What are the functions of the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia?
The functions of the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia include: registering nursing and midwifery practitioners and students. developing standards, codes and guidelines for the nursing and midwifery profession. handling notifications, complaints, investigations and disciplinary hearings.
What boards are there in Australia?
The Queensland Board of the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia. The South Australian Board of the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia. The Tasmanian Board of the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia. The Victorian Board of the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia. The Western Australian Board of the Nursing and Midwifery Board ...
How does NMBA work?
NMBAs work in two ways to block this process. Depolarizing NMBAs act as agonists at nicotinic receptors. 1 They hold open the ion-gated channels, leading to muscular fasciculation until the ion potential is depleted, and then to paralysis. 2 Succinylcholine is the only depolarizing NMBA available.
What is a kinetic profile for NMBA?
Rapid onset and short duration are useful for indications such as rapid sequence intubation (RSI), whereas those with a longer duration are of more value in surgery. See TABLE 1 for a brief overview of kinetic profiles, including dosing and common side effects.
Why are neuromuscular blocking agents important?
Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) play an important role in the management of a large number of hospital patients. In addition to their routine use in surgical anesthesia, NMBAs may be valuable in many new and evolving critical care situations. Therefore, it is essential for the hospital pharmacist to become familiar with ...
Is there a trial for neuromuscular blockade?
There are no trials providing specific guidance on the management of unintentional awareness during neuromuscular blockade. Regardless, it is considered standard practice to establish and maintain appropriate levels of analgesia and deep sedation prior to and during neuromuscular blockade. 1.
Can NMBAs cause a long term injury?
In the acute setting, the use of NMBAs can lead to increased ICU stay, prolonged mechanical ventilation, venous thromboembolism, skin tearing and ulcerations, infection, corneal damage, and anaphylaxis. Long-term administration can lead to immobility or increased recovery time because of impaired neuromuscular transmission and muscular weakness. 30 Several recommendations for preventing these effects are outlined in TABLE 2.
Neuromuscular junction
Normal neuromuscular transmission results from the release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic nerve terminal, its movement across the synaptic cleft, and binding to the postsynaptic nicotinic receptor on the sarcolemma of the skeletal muscle.
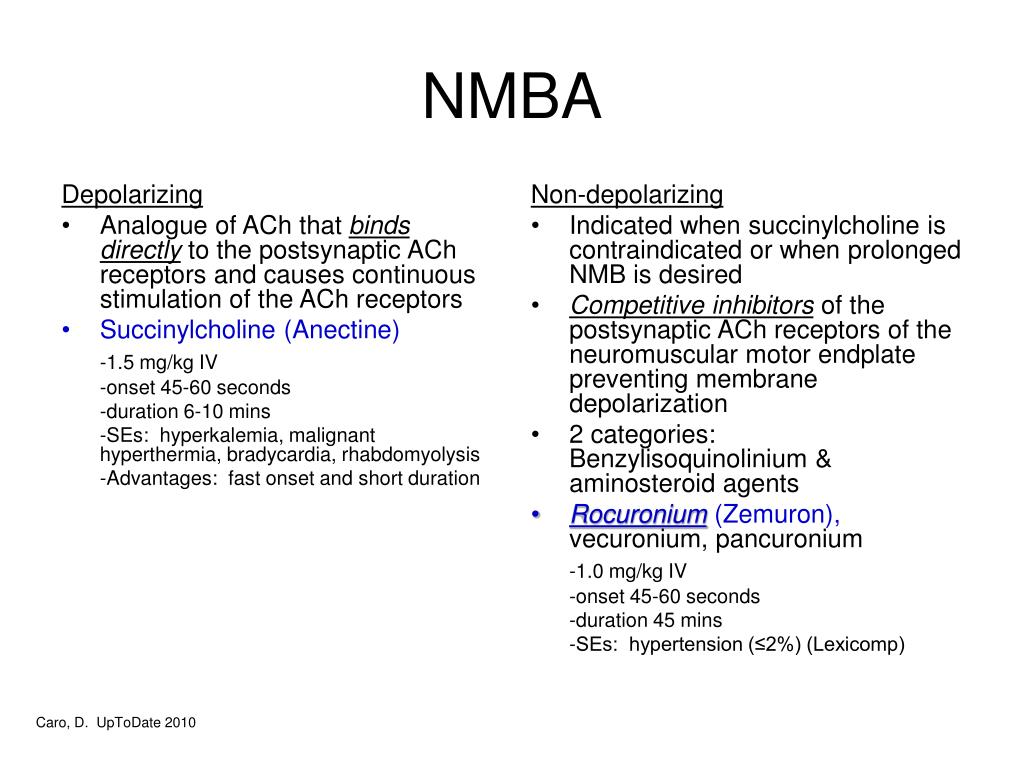
Neuromuscular blocking agents: Depolarizing agents
The two general classes of NMBAs (depolarizing and nondepolarizing agents) differ in their basic mechanism of action. Depolarizing agents such as succinylcholine (suxamethonium in Europe and the United Kingdom) mimic the effects of acetylcholine, binding to the acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction and activating it.
Neuromuscular blocking agents: Nondepolarizing agents
Nondepolarizing NMBAs function as competitive antagonists at the neuromuscular junction, antagonizing the effects of acetylcholine at the acetylcholine receptor. Unlike succinylcholine, these agents do not activate the acetylcholine receptor and therefore do not result in fasciculations and their associated problems (see earlier discussion).
Pancuronium
Pancuronium is an aminosteroid compound, generally available in a solution containing 1 mg/mL or 2 mg/mL of pancuronium depending on the manufacturer. A dose of 0.1 to 0.15 mg/kg provides adequate conditions for endotracheal intubation in 90 to 120 seconds.
Vecuronium
Like pancuronium, vecuronium is an aminosteroid compound. It was released for clinical use in the 1980s. Despite minor differences in its pharmacologic structure from pancuronium, its plasma clearance is 2 to 3 times as rapid.
Rocuronium
Rocuronium is an aminosteroid NMBA that was released for clinical use in the early to mid-1990s. It is commercially available in a solution containing 10 mg/mL in either 5- or 10-mL vials.
Rapacuronium
Although it was withdrawn from the market, a brief review of rapacuronium is helpful to outline the history of NMBAs and provide insight into their potential effects on sites other than the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle.
What is nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker?
Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers are competitive acetylcholine (ACh) antagonists that bind directly to nicotinic receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, thus blocking the binding of ACh so the motor endplate cannot depolarize. [4] This leads to muscle paralysis.
Why do we use neuromuscular blockers?
Neuromuscular blockers are commonly administered during anesthesia to assist with endotracheal intubation and improve surgical conditions. It is important to understand when each class of NMBAs should be used and when they should be avoided. The depth of paralysis should be closely monitored via TOF for the duration of the procedure, ...
Why is neuromuscular blockade used in anesthesia?
Neuromuscular blockade is frequently used in anesthesia to facilitate endotracheal intubation, optimize surgical conditions, and assist with mechanical ventilation in patients who have reduced lung compliance.
Codes of conduct
Please note that from 1 March 2018, professional boundaries expectations are included in the codes of conduct and are no longer separate documents.
Codes of ethics
From 1 March 2018, the International Council of Nurses Code of ethics for nurses is in effect for all nurses in Australia and the International Confederation of Midwives Code of ethics for midwives is in effect for all midwives in Australia.
What is non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA)?
Non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA) is one of four network types in the Open Shortest Path First ( OSPF) communications protocol. In an NBMA network all hosts are connected on a single network, but data is sent from one host directly to the next host and is not broadcast across to all hosts.
Where are NBMA networks used?
Various technologies are used in NBMA networks to provide the switching or virtual circuits. These can be inherent to the network type itself or be applied as virtual tunnel encapsulation.
Other NBMA network attributes
OSPF networks use timers and HELLO packets to determine if a route is still available. The hello interval sets the amount of time between when devices will send out a HELLO packet. If a host does not receive a HELLO packet from its neighbor on the route within the dead interval, it will declare that the route is unavailable.

Overview
Medical Usage
Administration of neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA) during anesthesia can facilitate endotracheal intubation. This can decrease the incidence of postintubation hoarseness and airway injury.
Short-acting neuromuscular blocking agents are chosen for endotracheal intubation for short procedures (< 30minutes), and neuromonitoring is required soon after intubation. Options include
History
In South America in the 16th century, native people extracted curare, a crude extract, from plants primarily Chondrodendron species of the family Menispermaceae and Strychnos species of the family Loganiaceae.
Edward Bancroft, a chemist and physician in the 16th century brought samples of crude curare from South America back to the Old-World. The effect of curare was experimented with by Sir B…
Mechanism
Succinylcholine interacts with nicotinic receptor to open the channel and cause depolarization of the end plate, which later spread to and result in depolarization of adjacent membranes. As a result, there is disorganisation of contraction of muscle motor unit. Later, since succinylcholine is not able to be metabolised and removed effectively at the synapse, the depolarized membranes remain in state of depolarisation and cannot respond to additional impulses. Phase I blok effect …
Side Effects
The usage of succinylcholine, the depolarizing neuromuscular agent, can lead to hyperkalemia, malignant hyperthermia, myalgia, increased intragastric pressure, increased intraocular pressure, increased intracranial pressure, cardiac dysrhythmias (bradycardia is the most common type) and allergic reactions. As a result, it is contraindicated for patients with susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia, denervating conditions, major burns after 48 hours, and severe hyperkalemia.
Interactions
Some drugs enhance or inhibit the response to NMBAs which require the dosage adjustment guided by monitoring.
In some clinical circumstances, succinylcholine may be administered before and after a nondepolarising NMBA or two different nondepolarising NMBAs are administered in sequence. Combining different NMBAs can result in different degrees of neuromuscular block and manage…
Pharmacology
Neuromuscular blocking agents exert its effect by modulating the signal transmission in skeletal muscles. An action potential is, in other words, a depolarisation in neurone membrane due to a change in membrane potential greater than the threshold potential leads to an electrical impulse generation. The electrical impulse travels along the pre-synaptic neurone axon to synapse with the muscle at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) to cause muscle contraction.
Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
- Depending on the situation, it is useful to have a variety of kinetic profiles available when an NMBA is being selected. Rapid onset and short duration are useful for indications such as rapid sequence intubation (RSI), whereas those with a longer duration are of more value in surgery. See TABLE 1for a brief overview of kinetic profiles, including dosing and common side effects.
Clinical Usage
- Surgical: NMBAs have been a staple of anesthesiology and surgery since the introduction of succinylcholine in 1952.3-7 The choice of agent and dosing varies widely depending on the surgical procedure and also on the use of alternative agents, including general anesthetics, local anesthetics, and IV sedation medications. Of primary concern in the surgical use of NMBAs is t…
Critical Care
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS):One of the primary clinical concerns for patients who develop ARDS is to reduce pressure and stress on the lungs, thereby reducing additional inflammation beyond the initial damage or insult. Because of their effects on diaphragmatic tone, NMBAs have been suggested as a method for decreasing ventilator asy...
Reversal Agents
- Although uncommon in the ICU, reversal of NMBAs is an important part of the surgical management of patients receiving paralytics. Historically, this has occurred through the use of neostigmine postoperatively.4 Neostigmine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (ACheI) that reduces the breakdown of acetylcholine in the motor endplate, causing an increase in the conce…
Sedation
- It is extremely important to recognize that although NMBAs prevent muscular movement, they have no effect on the patient’s level of consciousness or ability to perceive pain or discomfort, resulting in a phenomenon described as unintentional awareness.1 Whether for surgical or for medical indications, patients may be at risk for insufficient sedation or analgesia. A case series …
Monitoring
- The monitoring of patients on NMBAs is imperative, but methods are often complicated by clinical course, coadministration of sedatives and analgesics, and additional therapeutic modalities (e.g., therapeutic hypothermia). PNS is commonly regarded as the monitoring method of choice, but it has limitations. Additional monitoring parameters include spontaneous breathing and trends in …
Complications
- Although there are significant benefits to the use of NMBAs in particular situations, there are also short-term and long-term complications. In the acute setting, the use of NMBAs can lead to increased ICU stay, prolonged mechanical ventilation, venous thromboembolism, skin tearing and ulcerations, infection, corneal damage, and anaphylaxis. Long-term administration can lead to i…
Conclusion
- The pharmacist can play a highly important role in the regulation and use of NMBAs across a wide range of clinical-practice sites. By understanding the mechanism of action, therapeutic indications, supporting literature, and clinical side effects of this high-alert class of medications, the pharmacist can have an invaluable effect on patient care and patient safety.