
On the other hand, non-associative learning is another variety of learning in which an association between stimuli does not take place. The main difference is that stimuli are linked in associative learning; in non-associative learning this does not occur. What is the definition of associative memory in psychology?
What is the difference between associative and non associative learning?
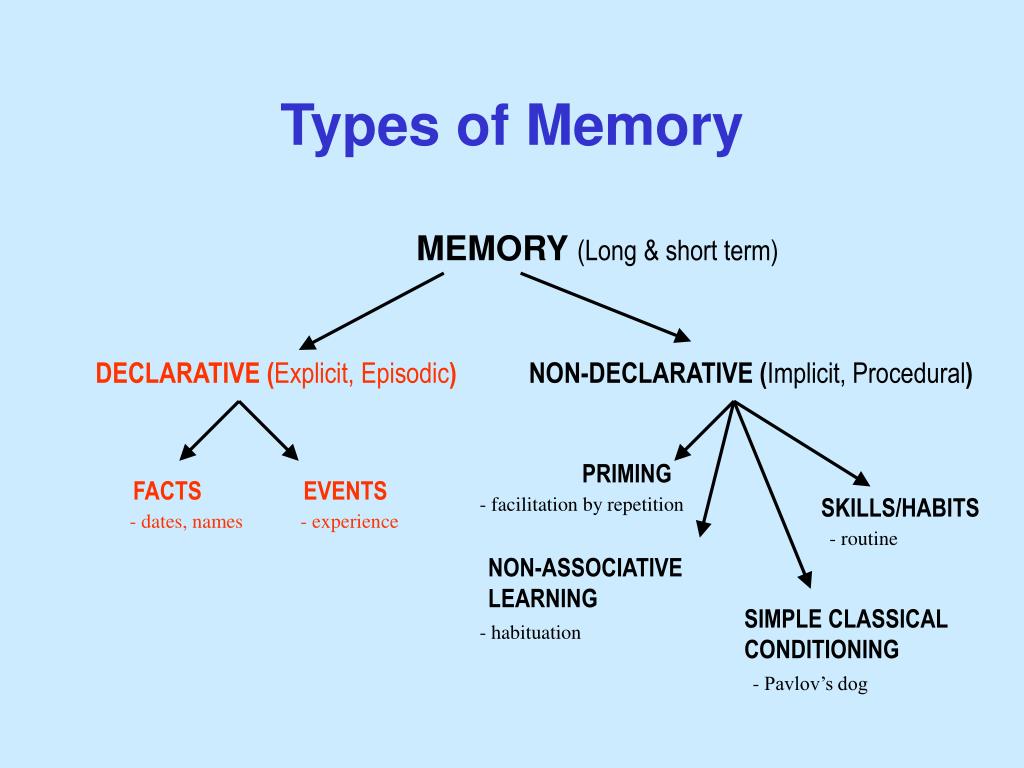
Non-Associative Learning: Linking does not take place. Types: Associative Learning: Classical and Operant conditioning can be considered as types of associative learning. Non-Associative Learning: Habituation and Sensitization can be considered as types of non-associative learning.
What is associative memory?
Associative memory is a declarative memory structure and episodically based. Two important processes for learning associations, and thus forming associative memories, are operant conditioning and classical conditioning.
What is non-associative learning in zebrafish?
Non-associative learning is also important in zebrafish cognitive behavior. Habituation is a simple form of such learning, as the response to repeated stimulation gradually declines unrelated to sensory adaptation or fatigue (Thompson and Spencer, 1966; Rankin et al., 2009 ).
Do associative and non-associative learning abnormalities explain PTSD symptoms?
Though associative and non-associative learning abnormalities are well positioned to account for a subset of PTSD symptoms (re-experiencing, avoidance, hyper-arousal), they do not seem particularly well suited to explain the full clinical picture of PTSD, including symptoms related to guilt, shame, dissociation, and anger.

What is non-associative learning in memory?
Definition. Nonassociative learning is an implicit (non-declarative) or procedural form of learning that systematically attenuates (habituates) or augments (sensitizes) an animal's sensory percept or behavioral response to a sensory stimulus upon repeated or continual presentation of the stimulus.
What are some examples of non-associative learning?
Nonassociative learning refers to a change in a behavioral response to a novel stimulus after repeated or continuous exposure to that stimulus. Sensitization and habituation are examples of nonassociative learning.
What does non-associative learning mean?
When experimental psychologists speak of nonassociative learning, they are referring to those instances in which an animal's behaviour toward a stimulus changes in the absence of any apparent associated stimulus or event (such as a reward or punishment).
Why is it called non-associative learning?
The reason why this is non-associative learning is that it does not contain any reinforcement or punishment.
What is the difference between associative and non-associative learning?
Associative learning occurs through the association of two previously unrelated stimuli, and includes reinforcement, whereas non-associative learning occurs in response to a single stimulus, without reinforcement.
What are the two forms of non-associative learning?
Moreover, habituation and sensitization are the two basic non-associative learning methods. Habituation is a decrease in an innate response to a frequently repeated stimulus.
What is an example of associative learning?
This is a psychological concept. Examples of associative learning include: If someone puts their hand on a hot stove and hurts themselves, they may learn to associate hot stoves with pain, and have therefore been conditioned not to put their hands on them.
What does associative learning mean in psychology?
Associative learning is defined as learning about the relationship between two separate stimuli, where the stimuli might range from concrete objects and events to abstract concepts, such as time, location, context, or categories.
What is sensitization in non-associative learning?
Sensitization is defined as a non-associative learning process occurring when repeated administrations of a stimulus result in a progressive amplification of a response (Shettleworth, 2010).
What is non associative learning in animals?
Simple nonassociative learning When experimental psychologists speak of nonassociative learning, they are referring to those instances in which an animal's behaviour toward a stimulus changes in the absence of any apparent associated stimulus or event (such as a reward or punishment).
What is associate learning?
associative learning, in animal behaviour, any learning process in which a new response becomes associated with a particular stimulus. In its broadest sense, the term has been used to describe virtually all learning except simple habituation (q.v.).
Is operant conditioning associative learning?
Operant conditioning (also called trial-and-error learning) is another type of associative learning in which a voluntary motor behavior is strengthened or weakened, depending on its favorable or unfavorable consequences.
What is Associative Learning
Associative learning is a type of learning that happens when two unrelated elements get connected in our brains through the process of conditioning. Our brains usually do not recall information in isolation; we generally group information together with our associative memory. This is something we do quite naturally.
What is Non-associative Learning
Non-associative learning is a type of learning where there is no association between a stimulus and a behavior. It’s a very simple form of learning.
Difference Between Associative and Non-associative Learning
Associative learning is a type of learning that happens when two unrelated elements get connected in our brains through the process of conditioning.
What is Associative Memory?
Associative memory refers to the ability to remember relationships between concepts, and not just the individual concepts themselves. In humans, this relates to visual and verbal information, such as remembering how two words are related (e.g., man – women), or seeing an object and its alternate names (e.g., a guitar). Associative memory is thought to be mediated by the medial temporal lobe of the brain. 1
How to improve associative memory?
To improve associative memory, one can practice retrieval of associations, which helps strengthen synaptic connections in the brain and enhances their ability to be activated more quickly.
What does "association" mean in a sentence?
2. Associate one person or thing to another in some way, such as using a rhyme, sentence or phrase. The association can be general (e.g., "grass is green") or specific (e.g., "the doctor is in the house").
Why do we need associations?
Establishing associations helps you to remember information more easily, such as names of people and places, phone numbers, birthday s and anniversaries. This may help you to recall other related information about them (e.g., someone's birthday might remind you that he or she has a party planned for that evening).
What are the physiological processes that are affected by implicit memory?
Physiological processes that are affected by implicit memory include the following: performance, arousal level, reaction time, habituation, and thalamic (in the brain) processing speed.
Who is the author of the associative memory theory?
Modern-day understanding of associative memory is guided by the theories of cognitive neuroscience, including those of David C. Rubin and Robert A. Bjork, who compiled their research into the dual-trace theory of explicit memory in 1975 3. Tulving's recency hypothesis is frequently cited in support of implicit associative memory, which states that when given a list to study with a short delay between each word, one is more likely to recall the words at the end of the list than the beginning.
Is associative memory a science?
Associative memory is not always a perfect science. Below are some ways that associative memory might connect in ways that you don't intend when a bad memory is brought back to your mind or a random association is created.
What is Non-Associative Learning?
Non-associative learning is another variety of learning in which an association between stimuli does not take place. To be more descriptive, in non-associative learning the behavior and stimulus are not paired or linked together. This form of learning is quite common in animals. Mainly there are two types of non-associative learning. They are,
What is the difference between associative and non-associative learning?
Associative learning refers to a variety of learning in which ideas and experiences are connected. On the other hand, Non-associative learning is another variety of learning in which an association between stimuli does not take place.
Which type of learning is associative?
Associative Learning: Classical and Operant conditioning can be considered as types of associative learning.
How does associative learning take place?
According to psychologists, associative learning takes place when we learn something with the assistance of a new stimulus. Here the theory of conditioning comes into play. Through conditioning, psychologists emphasize how human behavior can be altered or how new patterns of behavior can be created in the individual. The process of associative learning takes place through two types of conditioning. They are,
What are some examples of non-associative learning?
An example of non-associative learning we would have when being in a bar. It is normal that, when entering the establishment, we hear the voices of the other customers, who are chatting about their things.
What are the two processes that are considered non-associative learning?
Non-associative learning can occur through one of the following two processes: habituation or sensitization. Generally, these processes are complementary and opposite, and are the basis of many of our daily experiences and behavior.
Why is non-associative learning important?
Thus, you risk increasing the damage of the drug in your body.
What is the process of learning that diminishes the individual's innate response to a stimulus?
However, the way they do it each is different. 1. Habituation . We can define habituation as the learning process in which one or more of the components of the individual's innate response to a stimulus diminish by being continuously exposed to the same stimulus or on several occasions.
What is associative memory?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. In psychology, associative memory is defined as the ability to learn and remember the relationship between unrelated items. This would include, for example, remembering the name of someone or the aroma of a particular perfume.
Which part of the brain is involved in associative memory?
Additionally, involvement from the prefrontal cortex, frontal motor areas, and the striatum has been shown in the formation of associative memories. Associative memory is not considered to be localized to a single circuit, with different types of subsets of associative memory utilizing different circuitry.
What are the two processes that are important for learning associations?
Two important processes for learning associations, and thus forming associative memories, are operant conditioning and classical conditioning. Operant conditioning refers to a type of learning where behavior is controlled by environmental factors that influence the behavior of the subject in subsequent instances of the stimuli.
Where are associative memories found?
The neuroanatomical structures that govern associative memory are found in the medial temporal lobe and functionally connected cortical areas . The main locations are the hippocampus and its surrounding structures of the entorhinal, perirhinal, and parahippocampal cortices. More recently, the parietal-hippocampal network has been identified as a key circuit for associative memory Humans with large medial temporal lobe lesions have shown to have impairments in recognition memory for different types of stimuli. The hippocampus has also shown to be the main location for memory consolidation, especially related to episodic memory. The inputs from these unrelated stimuli are collected in this location and the actual synaptic connections are made and strengthened. Additionally, involvement from the prefrontal cortex, frontal motor areas, and the striatum has been shown in the formation of associative memories. Associative memory is not considered to be localized to a single circuit, with different types of subsets of associative memory utilizing different circuitry.
Does direct current stimulation improve associative memory?
Transcranial direct-current stimulation over prefrontal cortex has improved performance on associative memory tasks, but recent studies that stimulated posterior parietal cortex showed more reliable effects. Patients with Alzheimer's disease have been shown to be poorer in multiple forms of associative memory.
Does associative memory improve as you age?
Associative memory becomes poorer in humans as they age. Additionally, it has been shown to be non-correlational with a single item (non-associative) memory function. Non-invasive brain stimulation techniques have emerged as promising tools for the improvement of associative memory. Transcranial direct-current stimulation over prefrontal cortex has improved performance on associative memory tasks, but recent studies that stimulated posterior parietal cortex showed more reliable effects. Patients with Alzheimer's disease have been shown to be poorer in multiple forms of associative memory.
What Is Associative Memory?
History of Associative Memory
- Associative memory has been studied for over a century, with early writings describing the phenomenon as "the law of association" in 1885 by George H. Lewes. William James was the first to name the concept of associative memory, and his studies in 1890 formally investigated the phenomenon. Studies on associative memory continued through the 1940s and '50's, with the fir…
Types of Associative Memory
- There are two main types of associative memory: implicit and explicit. Implicit associative memory is an unconscious process relying on priming, whereas explicit associative memory involves consciousrecollection.
How to Improve Associative Memory
- To improve associative memory, one can practice retrieval of associations, which helps strengthen synaptic connectionsin the brain and enhances their ability to be activated more quickly. Below are some ways to practice the retrieval of associations. 1. Create a network of associations. This means associating yourself with people who are able to recall many things (o…
Impact of Associative Memory
- The value in developing associative memory capabilities has far-reaching implications for your daily life. Establishing associations helps you to remember information more easily, such as names of people and places, phone numbers, birthdays and anniversaries. This may help you to recall other related information about them (e.g., someone's birthday might remind you that he o…
Pitfalls of Associative Memory
- Associative memory is not always a perfect science. Below are some ways that associative memory might connect in ways that you don't intend when a bad memory is brought back to your mind or a random association is created. 1. You associate your kindergarten teacher with a monkey because she had one on her desk. 2. A smell brings back an event, like the apple pie tha…
A Word from Verywell Mind
- In summary, associative memory is important in daily life. Effectively harnessing this ability is a huge asset for the success of an individual. If you struggle with your associative memory, there are many techniques you can use to improve it. Some of these include the use of mnemonic devices, visualization, and association-forming strategies (such as linking things with each other…