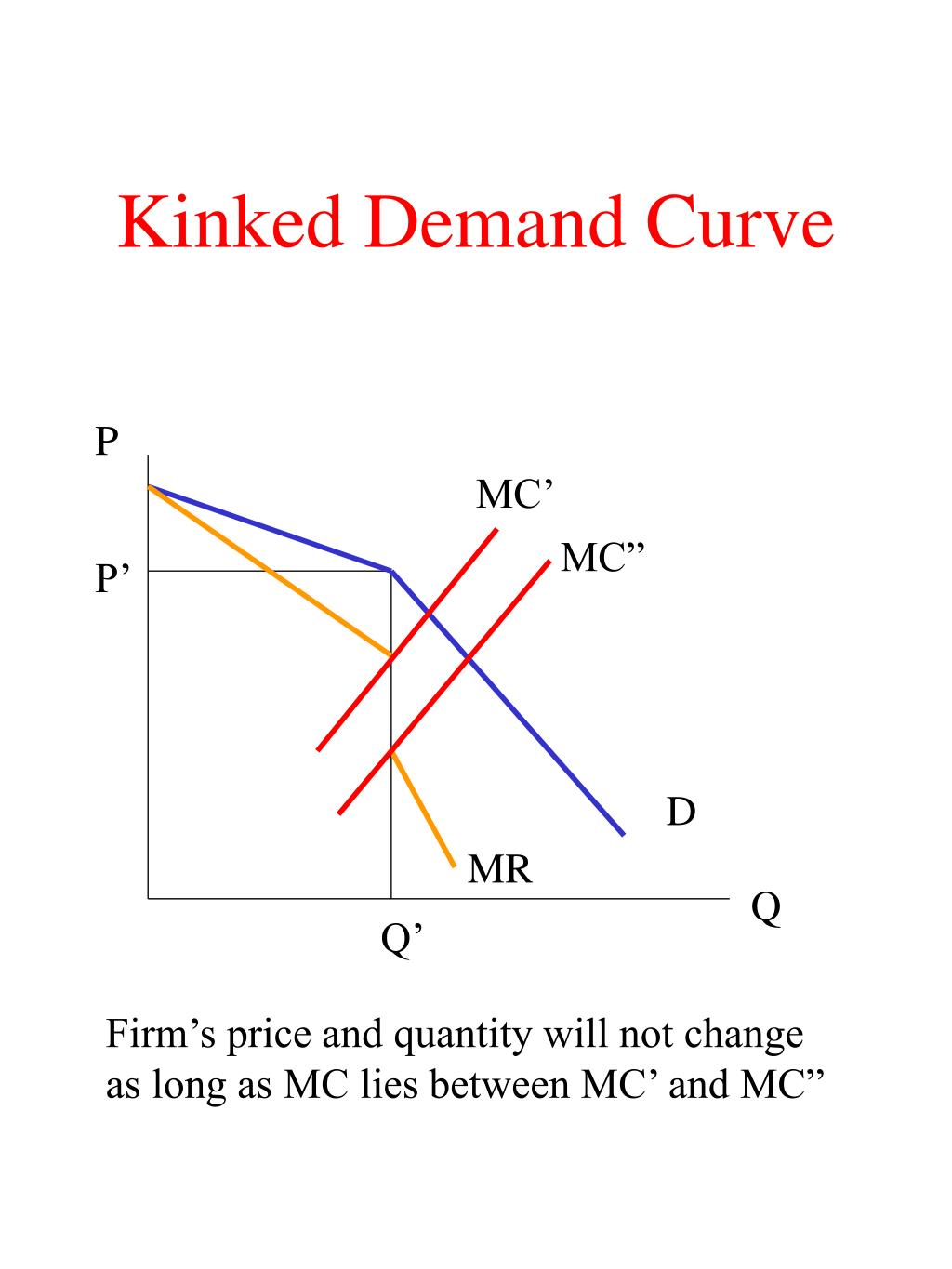
Non-price competition under oligopoly can be explained in terms of sales revenue maximization subject to a minimum profit constraint. The effect of price cut on total revenue, according to Baumol
William Baumol
William Jack Baumol was an American economist. He was a professor of economics at New York University, Academic Director of the Berkley Center for Entrepreneurship and Innovation, and Professor Emeritus at Princeton University.
How can firms engage in non price competition?
What product has the highest profit margin?
- Jewelry. As far as unisex products go, jewelry is at the top.
- TV Accessories.
- Beauty Products.
- DVDs.
- Kids Toys.
- Video Games.
- Women’s Boutique Apparel.
- Designer & Fashion Sunglasses.
What are three examples of non price competition?
General Advantages
- Innovation within the companies and industry: sales tactics, social media posts, virtual/technological advertisements, direct sales
- Quality assurance and improvement
- Brand establishment and reputation
- Economies of scope: offering products and services to various demographics.
Which markets compete in non-price competition?
Monopolistic markets engage in non-price competition because of how the market is designed where the firm dominates the market. In order to sustain in the market, they have to innovate and improve on their product development to appeal to consumers.
What do companies use non price competition?
What do companies use non price competition? Non-price competition is a marketing strategy that typically includes promotional expenditures such as sales staff, sales promotions, special orders, free gifts, coupons, and advertising. Put simply, it means marketing a firm’s brand and quality of products, rather than lowering prices.

What do you mean by non-price competition?
Definition: Non-price competition involves ways that firms seek to increase sales and attract custom through methods other than price. Non-price competition can include quality of the product, unique selling point, superior location and after-sales service.
What are the 4 types of non-price competition?
Marketing involves a range of approaches (based round the 4Ps), including product differentiation, advertising, promotion and distribution.
What is non-price competition in monopoly?
Non-price competition refers to the efforts on the part of a monopolistic competitive firm to increase its sales and profits through product variation and selling expenses instead of a cut in the price of its product.
Why are non-price strategies important in oligopoly?
When competing, oligopolists prefer non-price competition in order to avoid price wars. A price reduction may achieve strategic benefits, such as gaining market share, or deterring entry, but the danger is that rivals will simply reduce their prices in response.
What are the benefits of non-price competition?
Non price competition allows firms to compete without reducing their prices. This involves encouraging consumers to buy a good by making it appear different or better to the other products.
What is an oligopoly competition?
a competitive situation in which there are only a few sellers (of products that can be differentiated but not to any great extent); each seller has a high percentage of the market and cannot afford to ignore the actions of the others.
How do price and non-price competition differ?
Points of Difference between Price and Non-price Competition In case of price competition the firm tries to distinguish its product or service from competing product on the basis of low price. Non Price competition involves promotional expenditures, marketing research, new product development and brand management cost.
What is the difference between price and non-price?
The difference between price and non-price competition is when the price competition is present, the firm accepts the given demand curve while in the non-price competition, the firm attempts to change the shape and location of the demand curve.
What is non price competition?
Non-price competition through such devices as selling efforts, model changes and product differentiation is a characteristic of oligopolistic rivalry in the absence of significant price competition. An oligopolistic firm has, no doubt, strong reasons to support and maintain its existing relations within its industry, primarily for avoiding reaction of rivals to unstable situations. Yet it has strong reason to build a defensive position for itself as a protection against possible changes.
How do oligopolists achieve quality advantages?
Oligopolists generally achieve quality advantages first by innovations in product (and service) design and subsequently by product and process improvements. ADVERTISEMENTS: Market share and profitability are strongly related. A business unit’s return on investment is directly related to its share of the market.
Why is product differentiation important in an oligopoly?
The reason is that price cuts can be quickly and completely matched by competitors and this often leads to destructive price war. But a successful advertising campaign or the introduction of an innovator product is less easily imitated.
Why is product differentiation better than price war?
But product differentiation is a better strategy because it gives a firm a long -term and, at times, a special advantage over its rivals.
Why is price cutting dangerous?
They view price-cutting as a dangerous tactic because it can initiate a price war that may have disastrous consequences in the long run. In contrast, alternative strategic weapons such as advertising and product differentiation are looked at as less risky ways of attracting customers and diverting them away from competitors.
What is the most important factor influencing an oligopolist's profitability?
Product Differentiation: The most important single factor influencing an oligopolist’s profitability is the quality of its products and services relative to those of its rivals. In the short run, better quality enhances profits because the firm is able to charge premium prices.
How does a firm protect itself from competition?
A firm seeks to protect itself from actual and potential competition through product differentiation. Product differentiation is achieved by using brand names and by incurring large selling costs. It is a form of non-price competition in which essentially similar products are offered for sale with relatively small quality differences.
What is non price competition?
Definition: Non-price competition involves ways that firms seek to increase sales and attract custom through methods other than price. Non-price competition can include quality of the product, unique selling point, superior location and after-sales service.
Why do retailers go out of business?
Foreseeing trends in markets. Many successful retailers have gone out of business because they were stuck with old business models. Successful firms need tremendous adaptability and innovation to move into new markets and trends. For example, retailers who successfully moved into an online presence have been more adaptable to trends in consumer behaviour.
Why do firms have a degree of market power?
In monopolistic competition, there is freedom of entry, but firms have a degree of market power (inelastic demand curve) because of product differentiation. Therefore, firms in monopolistic competition have a motive to try and improve their product differentiation and brand image.
What is the purpose of offering bundles of products?
Offering bundles of products. Supermarkets may group ingredients which make an Indian meal together. The hope is that it will encourage people to try new ingredients. The profit margin can often be higher on bundles of products. For a company like Apple, they push new technology – which requires you to buy very expensive adapters from them. Recently I got a new MacBook Pro. To connect my Apple Monitor to the new USB-C port, I had to buy an adapter from Apple costing £45. (This is using market power to push related goods/services0
Do consumers want to buy the cheapest potatoes?
And for a homogenous product like potatoes, consumers will generally want to buy the cheapest potatoes. However, many markets do not fit this model of perfect competition. In many markets, the price is only one of many factors which influence which good/service you buy.
Is Tesco investing in online delivery?
Supermarkets like Tesco and Sainsbury’s are also investing in online delivery of groceries. Again the cost to supermarkets of delivery is higher than the price customers are paying, but now it is established supermarkets don’t want to risk losing market share by making delivery more expensive. Ethical/charity concerns.
Why is non price competition so common?
Non-price competition is particularly common when there is an oligopoly, perhaps because it can give an impression of fierce rivalry while the firms are actually colluding to keep prices high.”.
Why is non price competition more common in markets where there is imperfect competition?
Non-price competition is more common in markets where there is imperfect competition, such as those with very few competitors – oligopolies – maybe because it can give an impression of a very competitive market, when in fact the rivals are colluding to keep their prices high.
What are the branches of non price competition?
This video explains what non-price competition is. The speaker says it consists of two branches: 1. Advertising, and 2. Product development.
What happens when a company reduces the packaging around a product?
For example, if a company reduces the packaging around a product, it will save on materials, weight and shelf-space. It may draw attention to a message on the packaging that says: “New packaging, same fantastic product!”
Does McDonald's have fair trade?
It claims to buy coffee beans that are ‘fair trade’ and have the ‘Rainforest Alliance Group’ seal of approval.
Does a brand name owner use pricing strategies?
However, in virtually every case, the brand-name owner avoids reacting with pricing strategies, and instead uses a non-price competition marketing approach.
Is Unilever an oligopoly?
(P&G) and London/Rotterdam-based Unilever plc (Unilever NV), are the major players in the global household consumer goods market – which is currently an oligopoly. Their matching products are always virtually identically priced. The two companies focus on advertising, promotions, competitions, special offers, and different packaging and presentations to make their goods and brands stand out in the marketplace.
Non-Price Competition in Oligopoly/Imperfect Competition
How Firms Compete
- This shows a mixture of factors both price and non-price competition, that can become important in markets
Examples of Non-Price Competition
- Loyalty card– Some big business have invested considerably in loyalty cards which give ‘rewards’ or money back to customers who build up points/spending. Airlines use Airmiles to try and encourage repeat custom. Supermarkets use loyalty cards like Tesco points/Nectar(Sainsburies) Direct mailing– a key method of retaining customers is through gaining access to their email ad…
Non-Price Competition – Oligopolies
Non-Price Competition – Two Phases
- There are typically two phases to a non-price competition strategy. The first implements new aspects of production or services, while the second lets consumers know about them. The Economist describes non-price competition as follows: “Trying to win business from rivals other than by charging a lower price. Methods include advertising, slightly differentiating your product…
Non-Price Competition – Pros & Cons
- There are several advantagesassociated with this type of marketing campaign: 1. Better sales tactics, including social media posts, efficient forms of online advertising, and direct sales through the manufacturer. 2. Improved product quality. 3. Different presentation of products for varied demographics. For example, sales may increase if the same product is presented differen…
Non-Price Competition – Pharma Companies
- The pharmaceutical industry is full of brand name products and generics, which become available when the active ingredient’s patent has expired. Companies face strong pricing competition from businesses that manufacture generic equivalents of their brand-name medications. However, in virtually every case, the brand-name owner avoids reacting with pricing strategies, and instead u…
Non-Price Competition – McDonald’s
- McDonald’s, the American hamburger and fast food restaurant giant, uses a wide range of both non-price and price competition. It claims to buy coffee beans that are ‘fair trade’ and have the ‘Rainforest Alliance Group’seal of approval. This is an effective way for McDonald’s to boost sales because it does not have to alter the price of the cups of coffee it sells. In nearly every McDonal…
Video – Non-Price Competition – Definition and Meaning
- This video explains what non-price competition is. The speaker says it consists of two branches: 1. Advertising, and 2. Product development.