
Examples of nondisjunction:
- Down syndrome.
- Triple-X syndrome.
- Klinefelter’s Syndrome.
- Turner’s Syndrome.
What does nondisjunction lead to?
Nondisjunction is the most common mechanism resulting in aneuploidy. Nondisjunction is an error in which there is unequal distribution of the members of a single chromosome pair in cell division. After fertilization, this results in daughter cells with either one or three copies of the involved chromosome rather than the usual two copies.
What does nondisjunction mean?
Nondisjunction means that a pair of homologous chromosomes has failed to separate or segregate at anaphase so that both chromosomes of the pair pass to the same daughter cell. This probably occurs most commonly in meiosis, but it may occur in mitosis to produce a mosaic individual.
What is an example of nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction causes abnormal number chromosomes in all the cells called aneuploidy or in some cells called mosaicism. Some of the important examples are: Down’s syndrome – Trisomy of autosomes, i.e. chromosome 21. It contains one extra chromosome 21.
What diseases are caused by nondisjunction?
Some of the important examples are:
- Down’s syndrome – Trisomy of autosomes, i.e. chromosome 21. ...
- Edwards syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 18 th.
- Patau syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 13 th.
- Klinefelter syndrome – Trisomy of sex chromosomes. Here cells have one extra X chromosome (XXY)
- Turner syndrome – Monosomy. ...
- Nondisjunction is also seen to cause malignancy. ...
What are some examples of nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction ExamplesDown's syndrome – Trisomy of autosomes, i.e. chromosome 21. ... Edwards syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 18th.Patau syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 13th.Klinefelter syndrome – Trisomy of sex chromosomes. ... Turner syndrome – Monosomy. ... Nondisjunction is also seen to cause malignancy.
What are examples of nondisjunction in humans?
Conditions that arise from non-disjunction events include:Patau's Syndrome (trisomy 13)Edwards Syndrome (trisomy 18)Down Syndrome (trisomy 21)Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY)Turner's Syndrome (monosomy X)
What is an example of nondisjunction during meiosis?
Nondisjunction in meiosis I occurs during anaphase I when one pair of homologous chromosomes fails to separate. In this example, one cell with 5 chromosomes and one cell with 3 chromosomes are produced. Each cell undergoes meiosis II, resulting in two cells with n + 1, or 5, and two cells with n - 1, or 3.
What is nondisjunction short answer?
A Conjunction is a word that joins parts of a sentence, phrases or other words together. Conjunctions are used as single words or in pairs. Example: and, but, or are used by themselves, whereas, neither/nor, either/or are conjunction pairs.
What is disease caused by nondisjunction?
Final answer. A disease caused by an autosomal primary nondisjunction is Down's syndrome.
When can nondisjunction occur?
Non-disjunction of chromosomes during mitosis occurs during anaphase. If a somatic cell undergoes mitosis and experiences non-disjunction, the two daughter cells formed will be aneuploid. In meiosis, nondisjunction can take place either during anaphase I or during anaphase II.
What is non disjunction in genetics?
Nondisjunction is the failure of the chromosomes to separate, which produces daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes.
What is non disjunction name the different types?
There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis. Nondisjunction results in daughter cells with abnormal chromosome numbers (aneuploidy).
When can nondisjunction occur choose the best answer?
When can nondisjunction occur? Choose the best answer. Nondisjunction errors can occur in meiosis I, when homologous chromosomes fail to separate, or in either mitosis or meiosis II, when sister chromatids fail to separate.
Is Down syndrome nondisjunction?
Down syndrome is caused by a random error in cell division that results in the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. The type of error is called nondisjunction (pronounced non-dis-JUHNGK-shuhn).
Why is nondisjunction more common in females?
As a woman ages, her meiotic machinery is exposed to an accumulation of age-related insults, becoming less efficient/more error-prone. The susceptible telomeric exchange pattern still increases susceptibility to nondisjunction, but now even homologous chromosomes with optimally placed exchanges are at risk.
Is Klinefelter a nondisjunction?
Klinefelter Syndrome and Its Variants The classic form of Klinefelter syndrome is associated with a 47,XXY karyotype and is caused by meiotic nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes during gametogenesis (Fig.
What is a common cause for Down syndrome in humans?
About 95 percent of the time, Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21 — the person has three copies of chromosome 21, instead of the usual two copies, in all cells. This is caused by abnormal cell division during the development of the sperm cell or the egg cell.
What causes nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction is caused due to inactivation of topoisomerase II, separase or condensin. During anaphase, the cohesin which binds the sister chromatids together is broken by separase. Catenation is removed by condensin and topoisomerase II.
What is the term for loss of one or more chromosomes?
Meiotic nondisjunction leads to chromosomal disorders known as aneuploidy, where there is loss or gain of one or more chromosomes. Meiosis I nondisjunction is a more common cause of aneuploidy than meiosis II nondisjunction. Aneuploidy can be monosomy (2n-1), trisomy (2n+1), nullisomy (2n-2), disomy (n+1).
What happens to homologous chromosomes during meiosis I?
In the first type, due to nondisjunction during meiosis I, homologous chromosomes fail to segregate at anaphase I and lead to all the haploid cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes. The second type of nondisjunction occurs during meiosis II when sister chromatids fail to segregate. It leads to half of the haploid cells with abnormal ...
What is nondisjunction in biology?
Nondisjunction is defined as the failure of chromosomes or chromatids to segregate during cell division. It leads to daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes, which is known as aneuploidy. The irregular distribution of chromosomes during cell division leads to one cell with an extra chromosome and the other with a less chromosome.
What is the result of Mitotic Nondisjunction?
It leads to half of the haploid cells with abnormal chromosomes. Mitotic nondisjunction leads to somatic mosaicism as only the daughter cells lineage originating from the defective cell contains an abnormal set of chromosomes. It can lead to various forms of cancer such as retinoblastoma.
How to diagnose nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction can be diagnosed by karyotyping. Amniocentesis is carried out to take out amniotic fluid, which is analysed and any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus can be diagnosed.
When does nondisjunction occur in oocytes?
Nondisjunction is more common in oocytes as the oocyte meiotic division gets arrested first at diplotene of prophase I and then later at metaphase II, which resumes only after fertilization. Most of the aneuploidy in children is derived from the mother.
What is nondisjunction in biology?
Definition. Nondisjunction occurs when chromosomes do not separate properly during cell division. This produces cells with imbalanced chromosome numbers. Chromosomes contain the cell ’s DNA, which is crucial for its functions and reproduction. Normally, when a cell divides, the chromosomes line up in an orderly fashion at the centre of the cell.
What happens if a sister chromatid fails to separate properly during anaphase of meios?
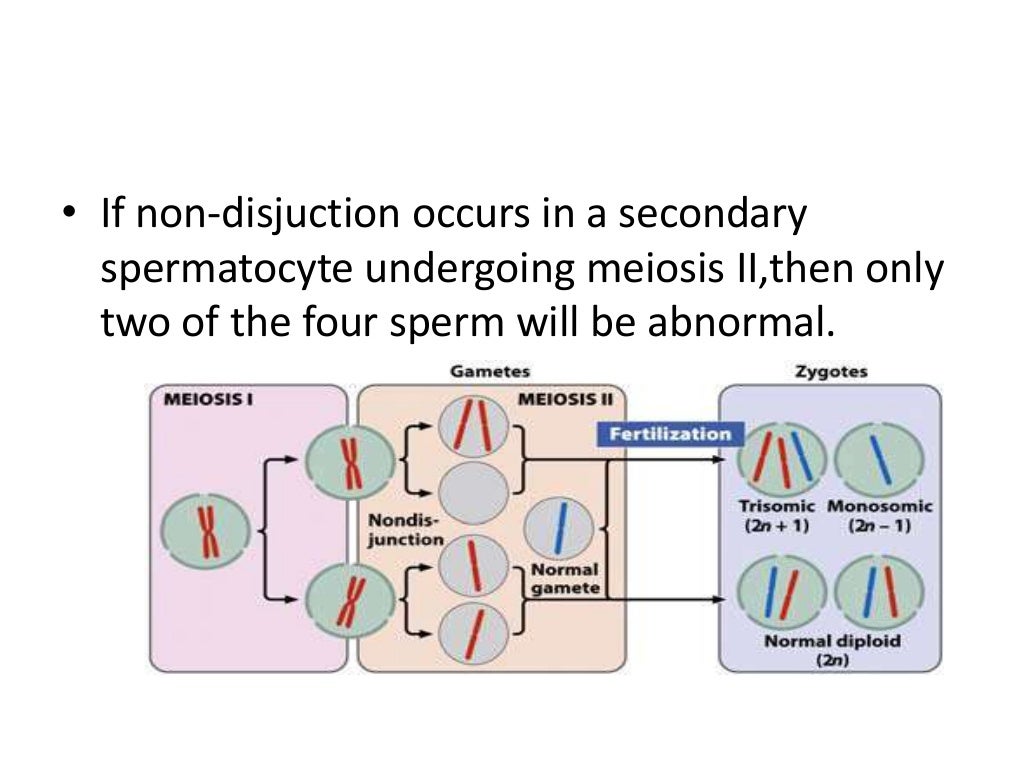
If a pair of sister chromatids fail to separate properly during anaphase of meiosis II, one daughter cell will have an extra chromosome and one daughter cell will be missing a chromosome. If the other daughter cell created in meiosis I splits properly, the other two of the four total daughter cells created during meiosis II will have ...
What happens when homologous chromosomes do not separate?
Nondisjunction happens during anaphase, when a pair of homologous chromosomes do not separate before being distributed into two daughter cells. In the resulting cells, one cell has two copies of a chromosome, while the other cell has no copies. When each of these cells goes on to divide into two cells during meiosis II, the four total cells produced will all have chromosomal abnormalities.
What happens when one cell has both chromatids and the other cell has neither?
The result is that one cell receives both chromatids, while the other cell receives neither. Each daughter cell then has an abnormal number of chromosomes when mitosis is complete; one cell has an extra chromosome, while the other is missing one. Nondisjunction during mitosis.
Why is nondisjunction important in cancer?
However, if nondisjunction goes undetected, it can contribute to the development of cancer. This is because imbalances in the expression of the genes in the chromosomes can lead ...
Why do older people have a higher chance of having a child with Down syndrome?
The extra chromosome in the cells of those with Down syndrome is responsible for a host of characteristics, including delays in physical growth, certain facial features, and mild intellectual disability. Rates of nondisjunction in the gametes increase with age, which is why older mothers have a higher chance of giving birth to a child with Down syndrome. According to the Mayo Clinic, this chance drastically increases between the ages of 35 and 45, going from 1 in 350 at 35 years to 1 in 30 at 45 years.
How many copies of chromosome 21 are in an embryo?
It produces an egg cell with an extra copy of chromosome 21. That means, that the resulting embryo has three copies of chromosome 21, two from the mother, and one from the father. This is called a trisomy. People with Down syndrome have three copies of chromosome 21 in all of their somatic cells.
How many chromosomes are in a Down syndrome egg?
The people infected with Down syndrome, have three copie s of chromosomes 21 in all their somatic cells, two copies from mother and one copy from father.
How many daughter cells are formed in meiosis?
During the process of meiosis I, the gametes are created. One cell divided into four daughter cells by the combined process of both meioses I and meiosis II. The nondisjunction occurs in anaphase of meiosis I when pair of homologous chromosomes not separated. In the result of this problem, one cell copies a chromosome, ...
Why does nondisjunction occur?
Nondisjunction occurs When the chromosomes cannot separate properly. The result of this is that the daughter cells have an incorrect number of chromosomes, as one can have too many, and others may have too few. This problem causes cell function due to a cell cannot function properly without the right numbers of chromosomes.
What happens to somatic cells during mitosis?
During Mitosis: During mitosis, the division of somatic cells takes place. Two identical or similar daughter cells produce from each original parent cell. When the nondisjunction occurs, the chromatids do not separate, and the result comes that one cell gains both chromatids, and gain no one.
What is sex chromosome aneuploidy?
Sex chromosome aneuploidy is the form of abnormal numbers in sex chromosomes. Typically, females consist of two X chromosomes and males consist of one X and one Y chromosome. Nondisjunction is the cause of the individuals to be born female with one X, female with three X chromosomes, males with XXY, or male with XYY.
What happens if the sister chromatids cannot separate?
If the pair of sister chromatids cannot separate accurately during the anaphase of meiosis II, the result will be that one daughter cell has an extra chromosome, and one daughter cel l missed the chromosome.
Why does trisomy 16 occur in the first trimester?
Many other forms of trisomy occur in the result of miscarriage during the first trimester of pregnancy because the fetus cannot survive chromosomal abnormality . The trisomy 16 happens in over 1% of pregnancies and it is the most common trisomy, but many individuals having this trisomy do not survive.
How many chromosomes are produced during Meiosis I?
If nondisjunction occurs during Meiosis I in humans, two gametes with extra chromosomes will be produced (24 chromosomes each, or n+1) and two gametes lacking a chromosome will be produced (22 chromosomes each, n-1 ).
How many chromosomes are in a diploid cell?
In humans, diploid cells contain 46 chromosomes ( 2n = 46 ). Diploid cells, also called somatic cells, include all the non-reproductive cells of the body, including nerve cells, skin cells, muscle cells, bone cells, fat cells, etc. Humans only have two type of haploid cells — sperm and eggs, each of which contain only 23 chromosomes ( n = 23 ). During fertilization, the haploid number of chromosomes in the sperm (23) combine with the haploid number in the egg (23) to produce a diploid zygote (46; n + n = 2n ). This zygote cell will divide thousands of times through mitosis to produce all the diploid cells that make up the body of the new infant (and eventually the adult human).
What is the process of reducing the number of chromosomes in a cell?
Meiosis is the process responsible for reducing the chromosome number; i.e. for turning a diploid cell into four haploid cells.
What is nondisjunction in biology?
-disjunction is a lack of junction, or a separation or breaking apart. Disjunction is a normal process for both mitosis and meiosis — the chromosomes are supposed to split apart during anaphase so each daughter cells can receive a full and complete copy of the original cell's genome. Finally, nondisjunction, the full term, means there is a lack of separation. The chromosomes stay joined together so that too many migrate to one daughter cell while the other has a deficit.
How many rounds of cell division does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in two rounds of cell division — Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The overall process is described in the steps below and outlined in the figure
How are karyotypes obtained?
Karyotyping — A karyotype is an organized picture of an individual's chromosomes, obtained by pausing cell division during metaphase, when the chromosomes are most condensed, staining with various DNA-specific stains, and photographing the chromosomes as they appear under a microscope. A computer is then used to sort the chromosomes by size and banding pattern, identifying homologous chromosomes and looking for abnormalities and any extra (or missing) chromosomes. Two karyotypes are shown below, one from an individual with Down's Syndrome and another from an individual with Klinefelter's syndrome. Karyotyping can be used to diagnose infants, children, and adults by obtaining a skin cell sample. Fetal karyotyping can be done before birth using two common methods.
When are sister chromatids joined?
Sister chromatids are joined together at their centromere, and will remain joined until Anaphase II during the second division in meiosis.
What happens to the second daughter cell produced by meiosis I?
Now let's consider what happens to the second daughter cell produced by meiosis I. It received no copies of chromosome 21 during the meiosis I division. That means that the gametes produced by this cell in meiosis II will have no copies of chromosome 21.
What happens if the homologs in the chromosome 21 tetrad fail to separate during?
If the homologs in the chromosome 21 tetrad fail to separate during meiosis I , one daughter cell would receive both chromosome 21 homologs and the other one would receive none. If those cells proceed to meiosis II, both homologous chromosomes would line up at the metaphase plate in cell number 1, and segregate into the daughter cells. The result would be gametes with two, rather than one copy of chromosome 21.
What is the term for a cell that is monosomic for chromosome 21?
A cell that is monosomic for chromosome 21 isn't viable and would initiate a miscarriage. In summary, nondisjunction is the failure of linked homologs or chromatids to separate during anaphase of mitosis or meiosis. Aneuploidy is a state in which a cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Why is a monosomic cell called monosomic?
This cell would also be considered aneuploid. In this case, the cell would be called monosomic because it only has one copy of chromosome 21. Human Chromosomal Disorders. The importance of faithfully segregating chromosomes during meiosis becomes more apparent when the consequences of aneuploidy are considered.
What is the most common form of aneuploidy?
In a diploid organism, the most common forms of aneuploidy are monosomy and trisomy. Monosomy is a situation in which an otherwise diploid cell has only one copy of a particular chromosome. Trisomy is a situation in which an otherwise diploid cell has three copies of a particular chromosome. Lesson Objectives.
Why is nondisjunction important?
Nondisjunction and aneuploidy within the study of chromosomes are important concepts needed in order to build knowledge and understanding adequately about biology. Learn more about their definitions and read examples. Updated: 11/02/2021
What is aneuploidy in humans?
The first example of aneuploidy we identified was trisomy of chromosome 21. Trisomy of chromosome 21 causes the human chromosomal disorder known as Down Syndrome. Roughly 1 in 700 babies born in the United States has Down Syndrome. A few of the many conditions they can be afflicted with are skeletal abnormalities and heart defects. However, considerable phenotypic variation is observed among individuals with Down Syndrome, with many individuals able to lead relatively long, productive lives.
