What are non-ionic contrast agents?
Nonionic contrast agents are a group of contrast media that do not dissociate into charged particles. Regular non-ionic contrast media inculdes Iodinol, ioverol, iohexol, iodixanol, iopamidol, iopromide, iotroram, gadopentetate dimeglumine, etc.
What is the difference between ionic and non-ionic iodinated contrast media?
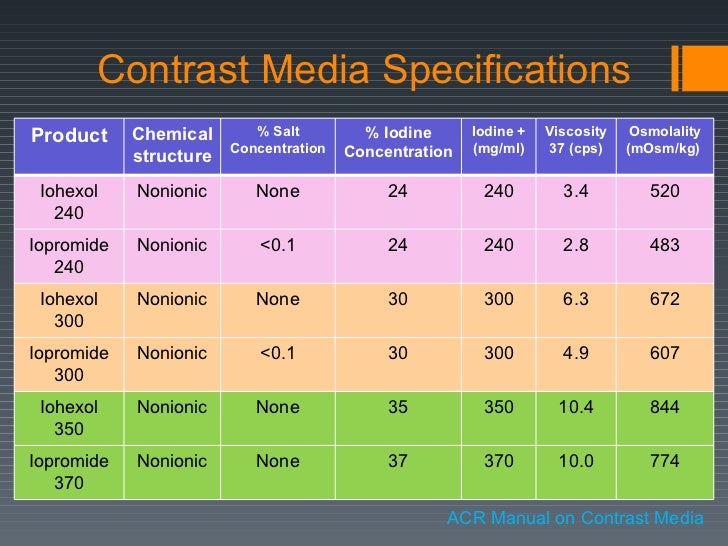
Each group varies in their uses, properties and toxic effects. In non-ionic iodinated contrast media the iodine is bound to an organic (non-ionic) compound and has a low osmolality.
What are the risks of nonionic contrast media exposure?
Mild reactions to nonionic contrast media, such as tachycardia, nausea, or vomiting, occur in approximately 3%. Severe reactions, such as bronchospasm and hypotension, occur in about 0.04%, and fatal reactions in 2–6 per million cases.
What is the osmolality of non ionic contrast media?
In non-ionic iodinated contrast media the iodine is bound to an organic (non-ionic) compound and has a low osmolality. Click to see full answer.
What is the difference between ionic and non-ionic contrast media?
Ionic contrast media are less expensive but are associated with a higher incidence of adverse reactions than nonionic contrast agents; approximately 4 to 12 percent of patients receiving ionic media experience some hypersensitivity reaction within minutes or after several hours compared with 1 to 3 percent of patients ...
What is CT scan non-ionic contrast?
Non-ionic agents are thought to be up to 10 times safer than ionic contrast media. Uses of contrast include intravenous urography, contrast-enhanced CT scans, venography and angiography.
What are the two types of contrast?
Contrast agents can be classified into two broad groups, depending on their interaction with x-radiation—positive contrast agents (radiopaque) and negative contrast agents (radiolucent).
What is non iodinated contrast media?
What are Non-iodinated contrast media? Contrast media is used in radiography to increase the clarity of the image. A non-iodinated contrast media is one that does not contain iodine and may instead contain barium or other non-iodinated media as the radio opaque substance.
Can I refuse contrast dye for CT scan?
Contrast dye: Doctors won't always choose to use dye for a CT scan, but it's always a possibility. If they do opt to use it for your scan, it may be administered via injection or taken orally. This dye helps the images show up with greater clarity and contrast.
Is gadolinium non-ionic?
Abstract. Extracellular gadolinium contrast agents (Gd-CA) are either linear or macrocyclic chelates available as ionic or non-ionic preparations.
Which of the following is a nonionic contrast material?
List of Non-ionic iodinated contrast media:Drug NameReviewsOmnipaque 350 Generic name: iohexol4 reviewsOmnipaque 300 Generic name: iohexol3 reviewsUltravist (Pro) Generic name: iopromide1 reviewOptiray 320 Generic name: ioversol1 review20 more rows
What is ionic contrast?
What are Ionic iodinated contrast media? Iodinated contrast media is a contrast media containing iodine that is used in radiography to increase the clarity of the image. Iodinated contrast media can be divided into the two groups, ionic and non-ionic, which vary in their uses, properties and toxic effects.
What are the 4 types of contrast media?
There are three broad kinds of contrast available: IV, PO, and PR (rectal). IV contrast is either gadolinium for MRI or iodinated contrast for CT. PO contrast for all ER and inpatient CT scans is dilute iodinated contrast (same agent used for IV contrast in CT).
Which of the following is an example of a non-ionic contrast agent?
Non-ionic contrast agents are now available; iopamidol, iohexol, ioversol, iopromide, iodixanol and iotrolan. Like Hexabrix, the first four are RATIO 3 AGENTS but they do not dissociate in solution.
Can you have CT contrast if allergic to iodine?
The contrast material used in MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) called gadolinium is less likely to produce an allergic reaction than the iodine-based materials used for x-rays and CT scanning.
Is non-ionic contrast water-soluble?
Low osmolality contrast media Modern LOCM are generally, but not always, nonionic monomers composed of tri-iodinated benzene rings with various side chains that contain polar alcohol (-OH) groups that make them water-soluble 3.
What is iodinated water soluble contrast?
They are mainly used intravascularly, but can also be injected into body cavities, particularly the low-osmolar contrast agents. Some are also used for oral or rectal administration, and the high-osmolar water-soluble contrast agent diatrizoate is suitable only for these purposes. Low-osmolar and iso-osmolar iodinated contrast media have almost completely replaced high-osmolar agents for intravascular use and administration into body cavities.
What is a niti stent?
Niti-S stents (Taewoong Medical, Seoul, South Korea) are single- or double-layered polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-covered Nitinol stents. The double-layered type consists of an inner PTFE-covered stent and an outer uncovered stent attached to the middle part of the inner covered stent.
Can low osmolar contrast media cause allergic reactions?
Acute and delayed allergic reactions after the intravenous administration of iodinated low-osmolar contrast media are well documented but rare. They range in intensity from mild, involving urticaria, rash, and pruritus, to severe, including cardiopulmonary arrest and death.
What is Ionic Contrast Media?
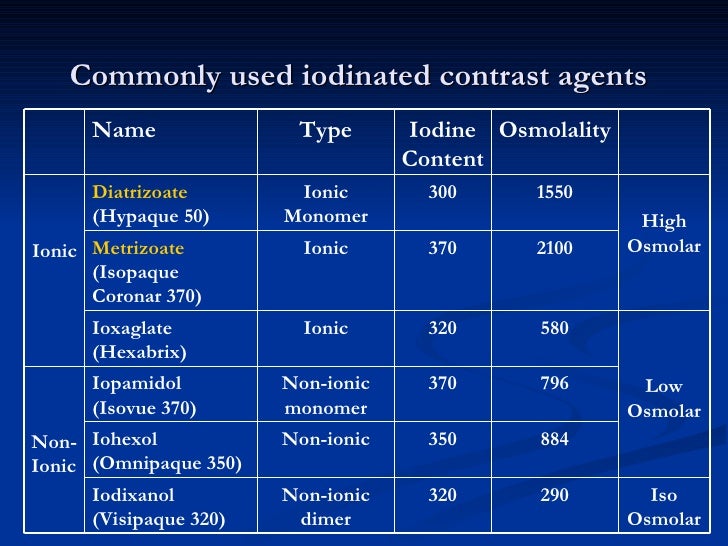
Ionic contrast media are iodinated contrast agents that can dissociate into cations and anions when they enter a solution. In other words, ionic contrast media can dissolve into charged particles when entering a solution. In this type of media, every two cations are associated with three anionic components.
What is Nonionic Contrast Media?
Nonionic contrast media are iodinated contrast agents that do not dissociate into cations and anions when entering a solution. In other words, nonionic contrast media cannot dissolve into charged particles when it enters a solution. This type of media contains one neutral component per every three iodine molecules.
What is the Difference Between Ionic and Nonionic Contrast Media?
Iodinated contrast media is available in two types as ionic and nonionic contrast media. The key difference between ionic and nonionic contrast media is that ionic contrast media can dissolve into charged particles when it is entering a solution, whereas nonionic contrast media cannot dissolve into charged particles when it enters a solution.
Summary – Ionic vs Nonionic Contrast Media
Both ionic and nonionic contrast media are useful in radiology because they are relatively harmless agents that are highly soluble.
What is contrast media?
Contrast media, also known as medical contrast mediums or contrast agents, are chemical compounds used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body during the medical testing processes. Iodine-based contrast media are usually classified as ionic or non-ionic.
Which contrast agent has the highest adverse reaction rate?
The hypertonic contrast agent is with higher adverse reactions rate than non-ionic contrast media. Non-ionic contrast media is with better viscosity due to its good water solubility. It disperses quickly in the blood and is not easy to aggregate, so it rarely causes capillary obstruction.
Is contrast media safe?
Contrast medias currently used are quite safe under normal circumstances. Studies have shown that serious adverse effect is very rare for both ionic or non-ionic contrast agents.However, some patients still have mild or moderate adverse reactions, and there may be rare serious adverse reactions.
What are the two types of iodinated contrast agents?
Currently, there are two major categories of iodinated contrast agents—high and low osmolar. With high-osmolar (“ionic”) contrast there is a small, but well-recognized, risk of adverse reactions, some of which are life threatening. However, the vast majority of patients receiving highosmolar contrast do not experience any significant side effects. Lowosmolar (“non-ionic”) contrast has a substantially lower rate of serious reactions (though not fatalities), but is considerably more expensive even in view of a significant decrease in price over the past few years. 1
Is lowosmolar ionic or non ionic?
Lowosmolar (“non-ionic”) contrast has a substantially lower rate of serious reactions (though not fatalities), but is considerably more expensive even in view of a significant decrease in price over the past few years. 1.
