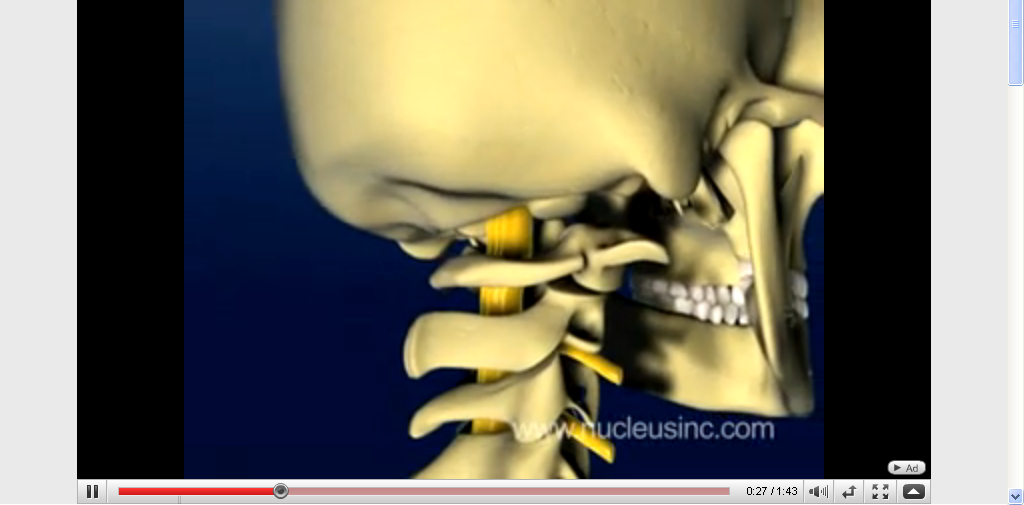
What is a cervical rotation?
Cervical rotation: turning the head to the left or the right. Cervical side-bending: tipping the head to the side or touching an ear to the shoulder of the same side.
How is cervical rotation measured?
Tape Measure The acromion process on each side is identified as the fixed point or reference point. Then, ask the patient to turn his/her head to one side. Measure the distance between the reference point to the chin during maximal cervical rotation. Repeat the same for the contralateral side (5).
What cervical level does most cervical rotation occur?
Approximately 50% of cervical flexion-extension and rotation occurs in the upper cervical spine (occiput-C2), with the remainder distributed among the subaxial segments. Ligamentous structures provide the main support to the cervical spine as there is little inherent bony stability.
What is a normal cervical curve?
The normal spine has an S-shaped curve when viewed from the side. This shape allows for an even distribution of weight and flexibility of movement. The spine curves in the following ways: The cervical spine curves slightly inward, sometimes described as a backward C-shape or lordotic curve.
What happens when your C1 is out of place?
Common C1 and C2 vertebrae misalignment symptoms include pain in the upper back, the neck, and the top of the head. It can also cause pain behind the eyes, at the temples, and behind the ears. Dizziness, fatigue, nausea, and a numbness of one side of the tongue can occur.
How can I improve my neck rotation?
Neck Rotation: Rotate head gently and slowly from side to side. Do not turn head completely to either side, keep motion small. Keep chin level with ground without letting chin drop to chest. Repeat 10 times.
What does C5 C6 and C7 control?
C5, as mentioned earlier, along with C3 and C4, contributes to the phrenic nerve that innervates the diaphragm. Roots C5, C6, and C7 produce the long thoracic nerve, responsible for controlling the serratus anterior.
What is C3 C4 C5 C6/C7 of the spine?
The C3,C4, and C5 vertebrae are part of the cervical spinal column. There are seven vertebral levels in total in this region, known as C1-C7. These vertebrae protect the spinal cord running through the cervical region of the spine, as well as provide support for the neck and head.
What's the normal measurement for cervical lordosis?
Conclusion: We found a statistically significant association between cervical pain and lordosis < 20 degrees and a "clinically normal" range for cervical lordosis of 31 degrees to 40 degrees. Maintenance of a lordosis in the range of 31 degrees to 40 degrees could be a clinical goal for chiropractic treatment.
Can cervical curve be restored?
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option to restore the natural curve in the neck. Treatments options include neutral spinal alignment, range of motion, strengthening exercises, trigger point injections, and muscle manipulation and activation.
What happens if your neck is straight instead of curved?
Cervical kyphosis, or military neck, occurs when your cervical spine is straight or curves toward your front instead of its natural curve to your back. When severe, it can cause pain, neurological symptoms and disability.
What causes you to lose the curve in your neck?
As you age, your intervertebral discs begin to degenerate. This causes the discs in your spine to grow thin and collapse. This change to the spine can alter your neck's natural curvature and cause an imbalance due to the weight of your head. Degenerative disc disease usually increases in severity as you get older.
How do you check cervical spine ROM?
0:394:21Cervical Spine - Active Range of Motion testing / C1/C2 (AA Joint)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then what i want you to do is rotate to this side please as far as you comfortably can and thenMoreAnd then what i want you to do is rotate to this side please as far as you comfortably can and then look to see how much range of motion he has and the distance between the finger.
How is cervical lateral flexion measured?
0:051:3541 Cervical Lateral Flexion Goniometer and Tape MeasureYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipRecord the end feel it is typically firmed for this motion. With a cervical spine positioned at theMoreRecord the end feel it is typically firmed for this motion. With a cervical spine positioned at the end of passive.
What is a goniometer used for?
A goniometer is a device that measures an angle or permits the rotation of an object to a definite position. In orthopedics, the former description applies more. The art and science of measuring the joint ranges in each plane of the joint are called goniometry.
How do you perform a Spurling test?
First, your doctor will pull your neck out and move your head downward. Then your doctor will rotate your head from side to side, while your head is still extended and facing downward. You'll do these movements until you feel pain. If you complete the test and feel no pain, you'll get a negative test result.
What is normal neck rotation?
The cervical spine has a range of motion of 80 to 90 degrees of flexion, 70 degrees of extension, 20 degrees to 45 degrees of lateral flexion, and...
How much rotation does a lumbar spine have?
The average total spinal rotation was 282 degrees. The average regional rotation in the cervical spine was 190 degrees, 67 degrees in the thoracic...
How many degrees can a human neck rotate?
A goniometer is used to assess the typical range of motion in neck flexion, which is 40 to 80 degrees. This demonstrates how far your neck can be m...
What is the movement of the neck?
Bringing the head forward to the chest Cervical extension is the backward bending of the head with the face facing the sky. Cervical rotation is th...
Do Scalenes rotate the neck?
All three scalene muscles cause the cervical spine to rotate to the same side. Scalene stretching should involve a rotation to the opposing side. T...
What is the normal range of motion in end range flexion?
Normal range of rotation motion in end range flexion has been shown to be 44° to each side. In contrast, subjects suffering from headache with C1-C2 dysfunction have an average of 17° less rotation.
What is manual cervical exam?
Manual examination has high sensitivity and specificity to detect the presence or absence of cervical joint dysfunction in neck pain and headache patients. However, these tests involve a high degree of skill on the part of the examiner, and their reliability has been questioned.
What nerves are involved in CGH?
CGH is generated by structures innervated by the C1 to C3 nerve roots, including the upper cervical joints and muscles. When the specific causes of the headache are identified, CGH can respond well to physiotherapy management.
Does cervical movement impairment cause headaches?
Recently, it has been shown that cervical movement impairment, in association with palpable upper cervical joint dysfunction and impairment in cranio-cervical muscle control, has 100% sensitivity an 94% specificity to identify Cervicogenic Headache from Migraine. This is clinically important since, for example, physiotherapy has been found to be effective for Cervicogenic Headache (CGH) but not for migraine.
Does age affect mobility during CFRT?
Smith et al. concluded that age did not significantly influence mobility during the CFRT. One explanation for this is could be that the upper cervical spine undergoes minimal age-related degenerative changes, in comparison to joints lower in the cervical spine. Also lifestyle factors including sleep position, time spent sitting, and side dominant lifestyle did not appear to influence variability in cervical mobility.
Is a C1 rotation test positive?
If a firm resistance is encountered, pain provoked, and range is limited before the expected end range, then the test is considered positive, with a presumptive diagnosis of limited rotation of C1 on C2
Does CGH affect range of motion?
Range was most restricted in subjects with CGH (25°), significantly more important impairment than either group’s Migraine (42°) or Multiple Headache forms (MHF) (35°). It would appear that presence of an aura has minimal effect on range of motion during the CFRT.
What is the cervical spine?
The cervical spine is made up of the seven bones in the neck. At the lower portion of the neck, the spine curves backwards (kyphosis) and becomes the thoracic spine. The thoracic spine consists of the 12 thoracic vertebra and the ribs located on each side. When checking cervical range of motion, the examiner tests the movement of the head, or skull, and neck in flexion, extension, lateral bending and rotation. Normal ranges of motion for the cervical spine include 50 degrees of flexion, 60 degrees of extension, 45 degrees of lateral, or side bending, and 80 degrees of rotation. The ranges of motion for the thoracic spine include 30 degrees of rotation and 50 degrees of kyphosis.
What are the ranges of motion of the shoulder?
Common upper extremity ranges of motions for the shoulder include 170 to 180 degrees of flexion, 50 to 60 degrees of extension, 170 to 180 degrees of abduction for moving the arm away from the body, 80 to 90 degrees of internal rotation, and 90 to 100 degrees of external rotation. Ranges of motion in the elbow and forearm include 90 degrees ...
How many vertebrae are in the lumbar spine?
The lumbar spine has five vertebrae and connects the spine to the pelvis. Normal lumbar ranges of motion include 60 degrees of flexion, 25 degrees of extension, and 25 degrees of lateral, or side, bending.
Where is range of motion measured?
Areas Commonly Tested for Range of Motion. Range of motion is commonly tested in the cervical spine, thoracic spine and lumbar spine. In many sports medicine clinics, range of motion in the upper and lower extremities are also tested. The measured degrees are compared with the expected norm and also from a healthy joint with an injured joint.
What are the ranges of motion of the lower extremities?
Lower extremity ranges of motion for the hip include 120 to 130 degrees of flexion, 10 to 20 degrees of extension, 45 degrees of abduction away from the body, 30 degrees of adduction toward body, 45 degrees of internal rotation, and 50 degrees of external rotation. Knee range of motion consists of the flexion and extension arc of motion which totals 135 to 145 degrees. Ankle range of motion includes 50 degrees of plantar-flexion, or toes pointing toward the ground, and 20 degrees of dorsi-flexion with the toes pointing toward head. It also includes 20 degrees of inversion and 5 degrees of eversion.
Why do joints have reduced range of motion?
The human body requires all joints move through a full range of motion to function correctly. Reduced range of motion can occur if damage occurs to the soft tissues of the spine or extremities, the lumbar discs, or if weak or tight muscles affect the posture of the individual.
What is range of motion?
This movement occurs in the various areas of the body including the spine and extremities. Range of motion refers to the amount of movement that a particular joint or body part can move measured in degrees.
What is neck rotation?
Rotation. Neck rotation is turning your head to the right and to the left. You should be able to turn far enough that your chin is almost in line with your shoulder. The accepted range of motion for rotation is 60 to 80 degrees. Advertisement.
What is the range of motion of the head?
In normal flexion, you can touch your chin to your chest. Beginning in a neutral position, an acceptable range of motion for flexion is 40 to 60 degrees.
What is the function of the neck?
Neck. Having normal range of motion in your neck is important for carrying out the activities of daily living. Neck movements include flexion, extension, bending and rotation. Soft tissue injuries and bony immobility can restrict your range of motion.
Can neck pain cause limited range of motion?
Effects. Limited range of motion in your neck can be painful and can hamper many normal activities, such as driving a car. It is difficult to drive your car safely if you cannot turn far enough to check your blind spot. Many factors can cause a limited range of motion.
What is cervical extension?
The normal anterior curve of the spine in the cervical region forms a slightly extended position. Cervical spine extension is movement in the direction of increasing the normal forward curve. It may occur by tilting the head back, bringing the occiput toward the seventh cervical vertebra. It also may occur in sitting or standing by slumping into a round-upper-back, forward-head position, bringing the seventh cervical vertebra toward the occiput.
What instruments are used to measure cervical spine range of motion?
Various methods have been employed to measure the range of motion of the cervical spine: radiographs, goniometers, electrogoniometers, inclinometers, tape measures, Cervical ROM devices, ultrasound and digital optoelectronic instrumentation, as well as simple estimations of observable motion (6). The broad assortment of instruments, and the lack of uniform procedures that have been in both reliability and descriptive studies, have contributed to the wide range of published norms for active and passive neck range of motion. However, the table below provides examples of three sources that do support each other.
How to help kyphosis tight neck?
If the posture of the upper back is habitually faulty but the person is able to assume a normal alignment, efforts should be directed toward maintaining good alignment. Temporary use of a support to help correct faulty posture of the shoulder and upper back may be beneficial.
Why is it important to maintain good neck range of motion?
It is important to maintain good neck range of motion. We are constantly challenged by the need to turn the head to look sideways or tilt it to look downward to avoid colliding with or tripping over something. Hence, it is advisable to establish and justify a means by which measurements can be taken to determine the range of motion of the neck in relation to established standards.
What is the best position for a subject to take range of motion measurements?
It is essential that the subject be placed as close to the ideal postural alignment of the upper back and neck as possible before taking range of motion measurements. Starting with a forward head position will limit movement in every plane.
