| Motion | Females | Males |
|---|---|---|
| Ankle dorsiflexion | 24.8 (22.5 – 27.1) | 22.8 (21.3 – 24.3) |
| Ankle plantar flexion | 67.1 (64.8 – 69.4) | 55.8 (54.4 – 57.2) |
| Shoulder flexion | 178.6 (176.9 – 180.3) | 177.8 (176.7 – 178.9) |
| Elbow flexion | 152.9 (151.5 – 154.3) | 151.4 (150.8 – 152.0) |
What is normal ankle PF ROM?
- A number of things troubled me with this concept of 10 degrees:
- Where did it come from? ...
- What if you walk faster, do you need more? ...
- The textbook definition is to dorsiflex the foot to resistance and measure that angle. ...
What is the normal range of motion for the ankle?
What is normal range of motion for ankle dorsiflexion? The normal range for ankle joint dorsiflexion was established as 0 degrees to 16.5 degrees nonweightbearing and 7.1 degrees to 34.7 degrees weightbearing. A statistically significant (p < 0.01) difference exists between the two measuring systems. What type of joint is the ankle? synovial joint
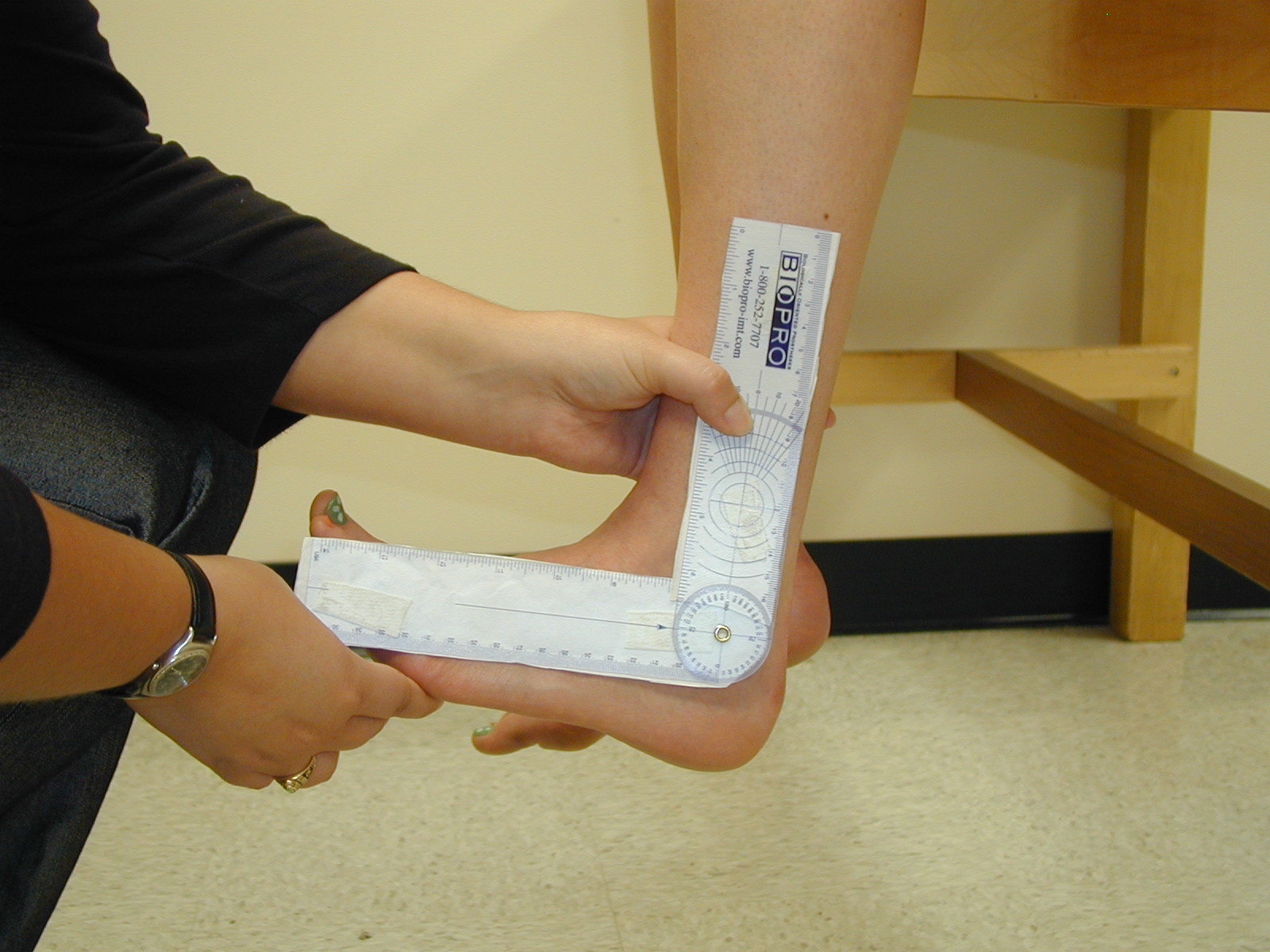
How to measure ankle ROM with goniometer?
- Axis – lateral malleolus
- Stationary arm – aligned with fibular head
- Moving arm – aligned with fifth metatarsal
What is normal ankle measurement?
Ankle Measurement - for Ankle Restraints Measure around your ankle, just above your ankle bone. SIZES INCHES CENTIMETERS XS 8 - 8.5 20.25 - 21.5 S 8.5 - 9 21.5 - 22.75 M 9 - 9.5 22.75 - 24 L 9.5 - 10 24 - 25.25 XL 10 - 10.5 25.25 - 26.5 XXL 10.5 - 11 26.5 - 27.75

What is the normal range of motion for dorsiflexion of the ankle?
The normal range for ankle joint dorsiflexion was established as 0 degrees to 16.5 degrees nonweightbearing and 7.1 degrees to 34.7 degrees weightbearing.
What is the normal active range of motion ROM for ankle plantar flexion?
6 A normal ankle moves from approximately 20° dorsiflexion to 50° plantar flexion in the sagittal plane and total range of motion in the frontal plane is approximately 35° (23° inversion; 12° eversion).
What is normal ROM?
Normal Motion Range of motion is typically measured using a tool called a goniometer. Normal ROM at the knee is considered to be 0 degrees of extension (completely straight knee joint) to 135 degrees of flexion (fully bent knee joint).
What are the 5 ranges of motion of the ankle?
In total, the ankle allows the foot to move in six different ways: dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, inversion, eversion, and medial and lateral rotation. Flexion and extension at the ankle are referred to as dorsiflexion and plantarflexion, respectively (Figure 2).
How do you measure ankle ROM?
0:102:45ROM Measurement Procedures: Ankle Dorsiflexion and Plantar FlexionYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPlace the center of the goniometer. Over the lateral aspect of the lateral malleolus place theMorePlace the center of the goniometer. Over the lateral aspect of the lateral malleolus place the stationary arm along the lateral midline of the lower leg the moving arm is aligned with the fifth.
What does ankle ROM mean?
0:422:36Active Range of Motion (Ankle & Foot) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd inversion is the combined movement of plantar flexion supination. And a deduction for activeMoreAnd inversion is the combined movement of plantar flexion supination. And a deduction for active range of motion assessments.
What is full ROM?
1. Full Range of Motion. What it is: The act of moving as far as anatomically possible during a given exercise. For example, when squatting, you lower down until your butt is just a few inches from the floor — or until your heels pop up — whichever comes first.
What are the 3 types of range of motion?
There are three basic types of range of motion: passive, active-assistive and active, defined by the whether, and to what degree, the patient can move the joint voluntarily.
How do you measure a ROM?
0:062:09ROM Measurement Procedures: Knee Flexion and Extension - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPlace the center of the goniometer. Over the lateral epicondyle of the knee the stationary arm goesMorePlace the center of the goniometer. Over the lateral epicondyle of the knee the stationary arm goes along the lateral mid thigh toward the greater trochanter.
What are the 4 motions of the ankle?
The movements that occur at the ankle joint are plantarflexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, and eversion. The muscles of the leg divide into anterior, posterior, and lateral compartments.
How do you increase ankle mobility?
4:0711:00Top 3 Ankle Mobility Exercises - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd hold it on top sometimes can help some people feel a little bit more stable. But something likeMoreAnd hold it on top sometimes can help some people feel a little bit more stable. But something like this what I'm doing is maybe 20 reps holding for about three seconds.
What is normal plantar flexion?
The normal range of plantar flexion is from a 20-degree angle to a 50-degree angle. Professional ballet dancers can achieve a much greater range of motion. Exercises for plantar flexion may not allow you to dance on your toes, but they will let you maintain a normal range of motion.
What is active range of motion?
Active Range of Motion (AROM). This is the space in which you move a part of your body by using your muscles. You make the effort without outside help. For example, lifting your arms above your head to stretch the muscles happens within your active range of motion.
What are the 3 types of range of motion?
There are three basic types of range of motion: passive, active-assistive and active, defined by the whether, and to what degree, the patient can move the joint voluntarily.
Why is ankle ROM important?
Ankle joint ROM is also important, because balance is most frequently controlled in the ankle joint, and the movement of the joint is large [8–10].
What is ROM rehabilitation?
Regaining range of motion in a joint is one of the first phases of injury rehabilitation. Physical therapists often prescribe specific ROM exercises for each joint. Each joint has a normal ROM, while each person has a different amount of ability to achieve it.
How to improve range of motion in joints?
Joints maintain a balanced range of motion by regular use and stretching of the surrounding soft tissues (muscles, tendons, and ligaments). Just 10 minutes of stretching three times a week can help improve range of motion. A study found that small gains in ROM might be made by applying heat while stretching.
What is limited range of motion?
Limited range of motion is a term used when a joint has a reduction in its ability to move. This can be due to injuries to the soft tissues surrounding a joint. It may also be caused by diseases such as osteoarthritis , rheumatoid arthritis, or other types of arthritis .
What is the instrument used to measure the amount of movement through a normal range of motion?
The amount of movement through a normal range of motion is commonly measured in degrees using an instrument called a goniometer.
What are the different types of range of motion exercises?
There are three types of range-of-motion exercises: 3 . Active range-of-motion: You perform these exercises without assistance. Active assistive range-of-motion: The therapist helps the patient do these exercises. This is may be done if the muscles are weak or when the movement causes discomfort.
What is the range of motion of the ankle?
Range of Motion of the Ankle. Range of motion of the ankle, or any joint, is the measurable amount of movement in the joint. Ankle injuries and other types of injury of the lower leg can diminish range of motion.
How to get your ankle to move?
Continue with pumping your ankle. Sitting in a chair, raise your foot off the floor and flex and point it continually for one minute. If this is too fatiguing, try 15 flexes and 15 points, then resting and switching feet. To increase range of motion, therapists recommend a few simple exercises. Sitting in a chair, raise your foot off ...
What causes a sprained ankle?
Sprained ankle, Achilles tendinitis and arthritis are all conditions that can cause loss of range of motion in your ankle. Achilles tendinitis typically manifests as an inability to fully flex your foot, something for which your doctor will check during an exam.
What causes a loss of range of motion in the ankle?
Causes of Loss of Range. Sprained ankle, Achilles tendinitis and arthritis are all conditions that can cause loss of range of motion in your ankle. Achilles tendinitis typically manifests as an inability to fully flex your foot, something for which your doctor will check during an exam.
How do physical therapists measure ankle flexion?
Measurement. Physical therapists use a device similar to a protractor to measure how far you can move your ankle in specific directions. The device, called a double-armed goniometer, measures the dorsal and plantar flexion of your ankle . To use the goniometer, the therapist places the stationary arm against your calf and measures ...
How to increase range of motion?
They should be approached gently, as you need to build strength over time and pushing too hard may hamper your recovery. Start with sitting in a chair and drawing the alphabet with one foot, then the other, keeping your leg straight the entire time. If you find this too fatiguing, start with the first part of the alphabet, rest and continue. Continue with pumping your ankle. Sitting in a chair, raise your foot off the floor and flex and point it continually for one minute. If this is too fatiguing, try 15 flexes and 15 points, then resting and switching feet.
What is the range of motion for dorsiflexion?
The standard range of motion for dorsi-flexion is between 15 and 30 degrees. For plantar flexion, the typical range of motion is between 20 and 50 degrees. These ranges vary according to age, gender and type of injury.
About the Study
To have a baseline with which to compare people with bleeding disorders, the joints of more than 600 people in the general population without bleeding disorders were measured as part of the study.
Reference Values for Normal Joint Range of Motion
The following table provides the reference values along with 95% confidence intervals for normal range of motion for 11 measurements taken on 5 joints. Values are provided separately by sex and age.
Public Use Data and Resources
The normal range of motion dataset is available for download as a public use dataset in either Microsoft Excel or Statistical Analysis Software (SAS) format. Please read the Data Use Restrictions Policy located on this webpage for important information about the conditions for use of these data files.
What is the dorsiflexion component of ankle pronation?
During the dorsiflexion component of ankle pronation, the talus rolls anteriorly and slides posteriorly; the reverse movements occur during the plantarflexion component. Supination and pronation at the subtalar joint occur as a result of sliding of the calcaneus on the talus (open-chain motion) around an oblique axis. During pronation and supination at the transverse tarsal joint, spin occurs between the concave distal joint surface formed by the navicular and spring ligament and the convex talar head. 32
Why is the end feel of ankle plantarflexion firm?
The normal end-feel for ankle plantarflexion is firm as the result of limitation first by muscular, then by ligamentous, structures. A firm end-feel also occurs at the limits of ankle dorsiflexion because of a muscular limitation to motion (when the knee is extended) or to ligamentous and capsular limitations (when the knee is flexed). ...
Which joint is supported by the long and short ligaments?
More laterally, the plantar surface of the calcaneocuboid joint is supported by the long and short plantar ligaments, both of which originate from the plantar surface of the calcaneus and insert onto the metatarsal and cuboid bones.
Does foot inversion include eversion?
Although measurement of foot inversion and eversion does not include measurement of isolated motion at a single joint, such measurements are commonly used and easily performed, and they are useful as screening techniques.
How many degrees do you dorsiflex your ankle?
Normal ankle dorsiflexion is 10-15 degrees ( fig. 1 ). Normal ankle plantarflexion can range from 40-70°. Step 1: Have the patient lay in a supine position. Step 2: Have the patient dorsiflexed their ankle to first resistant. Use a goniometer to measure the angle.
How to measure angle of a patient's foot?
Step 1: Have the patient lay in a prone position. Step 2: Have the patient evert their foot to first resistant. Use a goniometer to measure the angle. Step 3: Have the patient invert the foot to first resistant. Use a goniometer to measure the angle.
What is the first metatarsal range of motion?
The first metatarsal range of motion. Active and passive range of motion (ROM) of a joint are often accessed to determine if there are any pain, crepitus, or limitations at the joint. The ankle joint primarily movement is dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. Normal ankle dorsiflexion is 10-15 degrees ( fig. 1 ).
How to do a metatarsal splint?
Step 1: Have the patient sit in a tall chair so that the foot does not touch the ground. Step 2: Use the thumb of one hand and place it on the metatarsal heads of digits 2-4 to keep them maximally dorsiflexed. Use the index finger of the same hand and place it dorsally of the head of the second metatarsal.
What is the range of motion of the first metatarsophalangeal joint?
The first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) primarily movement is dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. The first MTPJ normal range of motion is 5 millimeters dorsally and 5 millimeters plantarly with 40-60 degrees of maximum dorsiflexion ( fig 3 ). Step 1: Have the patient sit in a tall chair so that the foot does not touch the ground.
Which ligaments are the weakest in the ankle?
[1] The anterior talofibular ligament connect the talus to the fibula, the weakest of the three lateral ligaments and thus the most frequently injured.
Which surface of the ankle allows for dorsiflexion and plantarflexion?
The talus articulates inferiorly with the calcaneusand anteriorly with the navicular. The upper surface, called the trochlear surface, is somewhat cylindrical and allows for dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the ankle. The talus is wider anteriorly and more narrow posteriorly.
What is the articular capsule?
The articular capsule surrounds the joints, and is attached, above, to the borders of the articular surfaces of the tibia and malleoli; and below, to the talus around its upper articular surface. The joint capsule anteriorly is a broad, thin, fibrous layer.
Which muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle joint?
The tibialis anteriormuscle, found in the anterior compartment of the leg, is the primary muscle that facilitates dorsiflexion of the ankle joint. The peroneus longusand Peroneus Brevismuscles, found in the lateral compartment of the leg, function to facilitate eversion of the ankle joint. [1]
What is the posterior compartment of the leg?
The leg's posterior compartment of the leg divides into the superficial posterior compartment and the deep posterior compartment. The superficial posterior compartment consists of the gastrocnemiusand the soleusmuscles, which are the primary muscles involved in ankle plantarflexion.
Which ligaments are responsible for stabilizing the ankle joint?
The main stabilizing ligaments . Medially the deltoid ligament, consists of four ligaments that form a triangle connecting the tibia to the navicular, the calcaneus, and the talus. It stabilise’s the ankle joint during eversion of the foot and prevents subluxation of the ankle joint.
Which ligament connects the tibia to the talus?
The anterior and posterior tibiotalar ligaments connect the tibia to the talus. The last two ligaments of the triangle are the tibionavicular ligament which attaches to the navicular anteriorly and the tibiocalcaneal ligament which attaches to the calcaneus inferiorly. 2.

Joints and Movements
Normal Ranges of Motion by Joint
Factors Influencing Rom
- Two big factors that can affect your ROM are your age and sex. Researchers studied the range of motion of eight joints in 40 men and women. They had the participants do different exercises and measured how far they were able to move each joint. They also recorded how long it took them to do each exercise. The researchers also reported that the women participants had nearly 30% mo…
Limited Range of Motion
- Limited ROM is when you can't move a joint as fully and easily as it should move. This can be due to a problem within the joint or injuries to the joint's soft tissues. Arthritisis the most common cause of stiff joints and limited ROM. Exercising, stretching, and other forms of regular daily movement help you maintain the ROM you have. If you have limited ROM, static stretching has b…
Types of Exercises For Increased Rom
- Physical therapists often prescribe specific ROM exercises tailored for each joint and condition. These exercises take into account the swelling, pain, and stiffness you have. There are three types of ROM exercises:9 1. Active range of motion:You perform these exercises without assistance to improve your ROM or to prevent other problems from occurr...
Summary
- Range of motion, or ROM, is how much you can move or stretch a particular joint. Knowing what your ROM is can help protect you from an injury. Many factors can affect ROM, such as your age, sex, injuries, and arthritis. This article provides generally accepted ROM ranges for joints that you can use for comparison. If you think you need help, see a doctor and ask about physical therapy…
Measurement
- Physical therapists use a device similar to a protractor to measure how far you can move your ankle in specific directions. The device, called a double-armed goniometer, measures the dorsal and plantar flexion of your ankle. To use the goniometer, the therapist places the stationary arm against your calf and measures the resting position of your foot. This defines neutral. She then …
Standard Range of Motion
- The standard range of motion for dorsi-flexion is between 15 and 30 degrees. For plantar flexion, the typical range of motion is between 20 and 50 degrees. These ranges vary according to age, gender and type of injury.
Causes of Loss of Range
- Sprained ankle, Achilles tendinitis and arthritis are all conditions that can cause loss of range of motion in your ankle. Achilles tendinitis typically manifests as an inability to fully flex your foot, something for which your doctor will check during an exam. A sprained ankle, whether mild or severe, can also lead to loss of range of motion. If the sprain is severe and requires bracing, mu…
Exercises to Increase Range
- To increase range of motion, therapists recommend a few simple exercises. They should be approached gently, as you need to build strength over time and pushing too hard may hamper your recovery. Start with sitting in a chair and drawing the alphabet with one foot, then the other, keeping your leg straight the entire time. If you find this too fatiguing, start with the first part of t…