What is the treatment for NPDR?
Treatment: The main treatment for NPDR is laser photocoagulation for macular edema. Many patients with significant macular edema are asymptomatic with good vision. It is therefore essential to diagnose and treat these patients during the early stage to prevent future visual loss.
What is severe NPDR in eye?
In this more common form — called nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) — new blood vessels aren't growing (proliferating). When you have NPDR , the walls of the blood vessels in your retina weaken. Tiny bulges protrude from the walls of the smaller vessels, sometimes leaking fluid and blood into the retina.
Can NPDR be reversed?
Can DR be treated/reversed? Fortunately, diabetic retinopathy is preventable and also treatable. Maintaining blood sugar at an optimal level can help to prevent this serious condition. As controlled diabetes can also lead to diabetic retinopathy, it is advised to have your eyes examined regularly.
What are the 4 stages of diabetic retinopathy?
The four diabetic retinopathy stages are classified as mild, moderate, and severe nonproliferative and proliferative.
Do glasses help diabetic retinopathy?
If there is macular disease, such as diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration, even properly measured glasses won't work. The vision is decreased due to the macular disease. It simply isn't capable of “seeing” 20/20. The disease is preventing the retina from working to its full potential.
Can vision be restored after diabetic retinopathy?
Treating diabetic retinopathy can repair damage to the eye and even prevent blindness in most people. Treatment can start before your sight is affected, which helps prevent vision loss. Options include: Laser therapy (also called laser photocoagulation).
Is diabetic blindness permanent?
Diabetic eye screening the condition can cause permanent blindness if not diagnosed and treated promptly. screening can detect problems in your eyes before they start to affect your vision. if problems are caught early, treatment can help prevent or reduce vision loss.
What vitamins are good for diabetic retinopathy?
Optimal combinations of vitamins B1, B2, B6, L-methylfolate, methylcobalamin (B12), C, D, natural vitamin E complex, lutein, zeaxanthin, alpha-lipoic acid, and n-acetylcysteine are identified for protecting the retina and choroid. Certain medical foods have been successfully used as therapy for retinopathy.
Does laser surgery cure diabetic retinopathy?
Laser surgery is often helpful in treating diabetic retinopathy. A beam of laser light is focused on the damaged retina. Small bursts of the laser's beam seal leaking retinal vessels to reduce macular edema. This is called photocoagulation.
Does diabetic retinopathy require surgery?
(This is called panretinal photocoagulation.) The small laser scars caused by this process reduce the abnormal blood-vessel growth. Both of these procedures may be performed on an outpatient basis and require no surgical incision.
Can diabetic retinopathy correct itself?
Can diabetic retinopathy be reversed? No, but it doesn't have to lead to blindness, either. If you catch it early enough, you can prevent it from taking your vision. That's why it's vital to have regular visits with an Ophthalmologist or Optometrist who's familiar with diabetes and retina treatment.
What is the first stage of diabetic retinopathy?
The first stage is also called background retinopathy. It means that there are tiny bulges in the tiny blood vessels in your retinas. The bulges are called microaneurysms. They may cause the vessels to leak small amounts of blood into your retinas.
What is stage 3 diabetic retinopathy?
Stage 3: Severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy A larger section of blood vessels in the retina become blocked, causing a significant decrease in blood flow to this area. At this point, the body receives signals to start growing new blood vessels in the retina.
What is the most advanced or severe stage of diabetic retinopathy?
The most advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy is called proliferative diabetic retinopathy. New blood vessels grow on the retina's surface and in the vitreous at this stage. The vitreous is the jelly-like substance that fills the inside of your eye. These new vessels are fragile and can easily leak fluid or bleed.
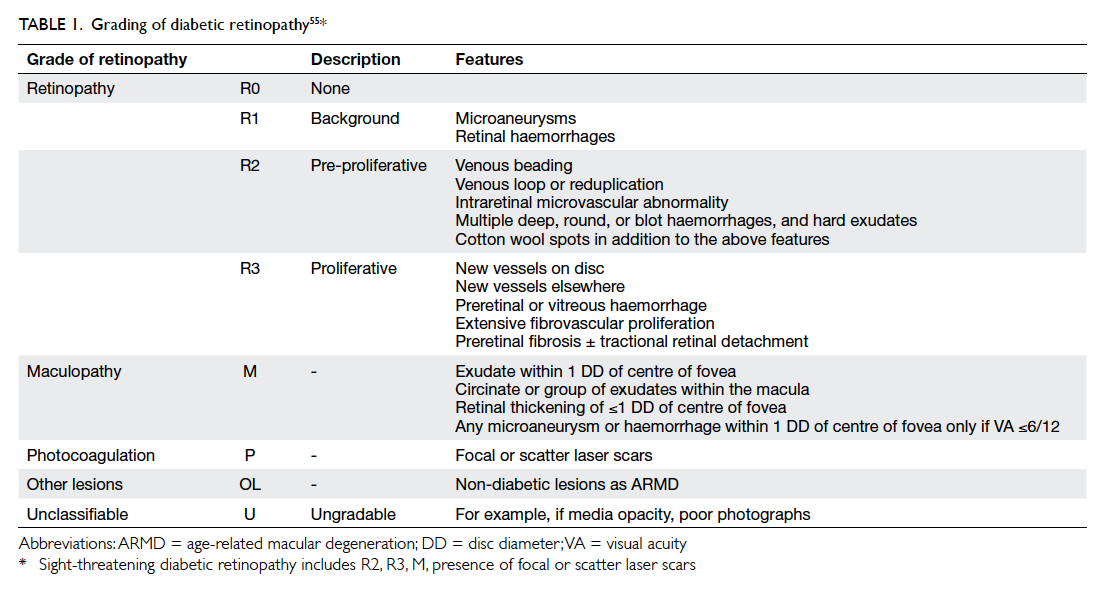
What are the grades of diabetic retinopathy?
Table 1.GradeFeaturesR2Moderate background DR >4 blot haemorrhages in one hemifieldR3Severe non-proliferative or pre-proliferative DR: >4 blot haemorrhages in both hemifields, intra-retinal microvascular anomalies (IRMA), venous beadingR4Proliferative retinopathy NVD, NVE, vitreous haemorrhage, retinal detachment7 more rows
Can non proliferative diabetic retinopathy be cured?
There is no cure for diabetic retinopathy. But treatment works very well to prevent, delay, or reduce vision loss. The sooner the condition is found, the easier it is to treat.
Classification Of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
The modified Airlie House classification has been used to classify nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) since the Diabetic Retinopathy Study (DRS) and Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS).
Helpful Tips
Look at images. Lots of them. While the BCSC and the AAO PPP provide very helpful charts and definitions for grading the severity of diabetic retinopathy, there weren't a lot of images provided for helping know exactly how to grade NPDR.
Classification and Management (1-7)
The following table is adapted from multiple sources. I was able to find some images available for linking under the Creative Commons license, which will hopefully help illustrate each stage of NPDR. Obviously, the management of these stages will differ if there is the presence of any macular edema or clinically significant macular edema.
What causes a retina to be blurred?
Blood and fluid seep from the leaks in the damaged retinal blood vessels, and fatty material (called exudate) can deposit in the retina. This causes swelling of the retina. When leakage occurs and causes swelling in the central part of the retina (the macula), it is called macular edema, and vision will be reduced or blurred.
What happens if blood leaks in the retina?
Normal retinal blood vessels are watertight and do not leak. In diabetes, the retinal blood vessels can become damaged and develop tiny leaks. This is called nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR). Blood and fluid seep from the leaks in the damaged retinal blood vessels, and fatty material (called exudate) can deposit in the retina. This causes swelling of the retina. When leakage occurs and causes swelling in the central part of the retina (the macula), it is called macular edema, and vision will be reduced or blurred. Leakage elsewhere in the retina will usually have no effect on vision.
Can diabetic retinopathy affect both eyes?
If one eye is affected, the other eye is frequently affected also, though the problem may not be equally severe in both eyes. If the diabetic retinopathy has affected each macula severely, central vision may be lost from each eye.
Can a retinal leak cause vision loss?
Leakage elsewhere in the retina will usually have no effect on vision. A patient with macular edema, or with exudate in the macula, will usually experience some loss of vision, including blurring, distortion, and darkening. If one eye is affected, the other eye is frequently affected also, though the problem may not be equally severe in both eyes.
Can NDPR patients see well?
So patient who have severe NDPR will usually be able to see well enough to take care of themselves and continue those activities that do not require detail vision. The AREDS 2 formulation is recommended in elderly populations at risk of AMD to supplement their normal diets. - 21 hours ago.
What Happens When You Have Diabetic Retinopathy?
You can have diabetic retinopathy and not know it. This is because it often has no symptoms in its early stages. As diabetic retinopathy gets worse, you will notice symptoms such as:
Can Diabetic Retinopathy Go Away?
Your treatment is based on what your ophthalmologist sees in your eyes. Treatment options may include:
What is PDR in diabetics?
PDR (proliferative diabetic retinopathy) PDR is the more advanced stage of diabetic eye disease. It happens when the retina starts growing new blood vessels. This is called neovascularization. These fragile new vessels often bleed into the vitreous. If they only bleed a little, you might see a few dark floaters.
What is the purpose of fluorescein angiography?
Fluorescein angiography or OCT angiography helps your doctor see what is happening with the blood vessels in your retina. Fluorescein angiography uses a yellow dye called fluorescein, which is injected into a vein (usually in your arm). The dye travels through your blood vessels. A special camera takes photos of the retina as the dye travels throughout its blood vessels. This shows if any blood vessels are blocked or leaking fluid. It also shows if any abnormal blood vessels are growing. OCT angiography is a newer technique and does not need dye to look at the blood vessels.
What is the cause of vision loss?
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye disease caused by diabetes. Damaged blood vessels and abnormal new ones can cause vision loss. People with diabetes can have an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. This is when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina. These blood vessels can swell and leak.
What is the procedure to remove a PDR?
If you have advanced PDR, your ophthalmologist may recommend surgery called vitrectomy. Your ophthalmologist removes vitreous gel and blood from leaking vessels in the back of your eye. This allows light rays to focus properly on the retina again. Scar tissue also might be removed from the retina.
What happens if you have NPDR?
When that happens, blood cannot reach the macula. Sometimes tiny particles called exudates can form in the retina. These can affect your vision too. If you have NPDR, your vision will be blurry.
What is the treatment for DME?
Historically, patients with DME and CSME were treated with either focal laser photocoagulation of the macula or intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents. 1 Most retina specialists no longer perform laser treatment in these patients because it causes more scarring and overall permanent loss of vision compared with anti-VEGF treatment (Figure 1). Intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents have become the first line of treatment for these patients and generally resolves the CSME (Figure 2). 4
What is a DME?
Patients with diabetic macular edema (DME) exhibit retinal thickening within 2 disc diameters (DDs) of the center of the macula . 1-4 It is considered clinically significant macular edema (CSME) if one of the conditions below is met.
What is the treatment for peripheral neovascularization?
Peripheral neovascularization is usually treated with laser panretinal photocoagulation (PRP, Figure 4). 7 They also often receive anti-VEGF intravitreal injections that may be performed in conjunction with PRP. 7
What type of diabetes was treated with laser PRP in the periphery for PDR in both eyes?
Figure 4. This patient with type 2 diabetes was treated with laser PRP in the periphery for PDR in both eyes.
What is the 4:2:1 rule?
These patients have intraretinal hemorrhages (> 20 in each quadrant), venous beading in two or more quadrants, or an IRMA in one or more quadrants (Figure 3). 2,5-7 This is known as the 4:2:1 rule. These findings must be in the absence of neovascularization, which would indicate PDR.
How thick is the retina?
Thickening of the retina is 500 µm or less (1/3 DD) from the center of the macula. Hard exudates are 500 µm or less (1/3 DD) from the center of the macula with thickening of adjacent retinal tissue.
Why is it important for optometrists to collaborate with PCPs?
As the number of US patients with diabetes grows , it is important for optometrists to collaborate with PCPs, endocrinologists, and retina specialists on managing these patients’ disease. This teamwork, combined with effective communication among caregivers and with patients, will enhance the care that they receive.